atmospheric pressure
also called barometric pressure
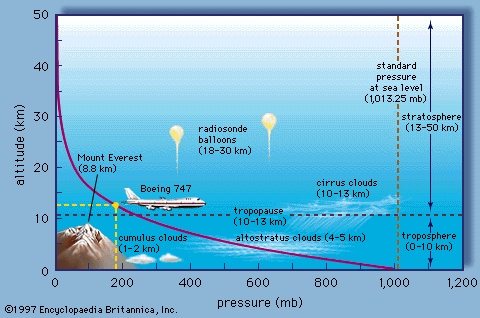 force per unit area exerted by an atmospheric column (that is, the entire body of air above the specified area). Atmospheric pressure can be measured with a mercury barometer (hence the commonly used synonym barometric pressure), which indicates the height of a column of mercury that exactly balances the weight of the column of atmosphere over the barometer. Atmospheric pressure is also measured using an aneroid barometer, in which the sensing element is one or more hollow, partially evacuated, corrugated metal disks supported against collapse by an inside or outside spring; the change in the shape of the disk with changing pressure can be recorded using a pen arm and a clock-driven revolving drum.
force per unit area exerted by an atmospheric column (that is, the entire body of air above the specified area). Atmospheric pressure can be measured with a mercury barometer (hence the commonly used synonym barometric pressure), which indicates the height of a column of mercury that exactly balances the weight of the column of atmosphere over the barometer. Atmospheric pressure is also measured using an aneroid barometer, in which the sensing element is one or more hollow, partially evacuated, corrugated metal disks supported against collapse by an inside or outside spring; the change in the shape of the disk with changing pressure can be recorded using a pen arm and a clock-driven revolving drum.Atmospheric pressure is expressed in several different systems of units: millimetres (or inches) of mercury, pounds per square inch (psi), dynes per square centimetre, millibars (millibar) (mb), standard atmospheres (standard atmosphere), or kilopascals. Standard sea-level pressure, by definition, equals 760 mm (29.92 inches) of mercury, 14.70 pounds per square inch, 1,013.25 × 103 dynes per square centimetre, 1,013.25 millibars, one standard atmosphere, or 101.35 kilopascals. Variations about these values are quite small; for example, the highest and lowest sea-level pressures ever recorded are 32.01 inches (in the middle of Siberia) and 25.90 inches (in a typhoon in the South Pacific). The small variations in pressure that do exist largely determine the wind and storm patterns of the Earth.
Near the Earth's surface the pressure decreases with height at a rate of about 3.5 millibars for every 30 metres (100 feet). However, over cold air the decrease in pressure can be much steeper because its density is greater than warmer air. The pressure at 270,000 metres (10−6 mb) is comparable to that in the best man-made vacuum ever attained. At heights above 1,500 to 3,000 metres (5,000 to 10,000 feet), the pressure is low enough to produce mountain sickness and severe physiological problems unless careful acclimatization is undertaken.
- Ribeyro, Julio Ramón
- riboflavin
- ribose
- ribosome
- Ribot, Alexandre
- Ribot, Théodule-Armand
- Ricardo, Cassiano
- Ricardo, David
- Ricardo Güiraldes
- Ricardo Lagos
- Ricardo Palma
- Ricardo Piglia
- Ricca, Paul
- Riccardo Bacchelli
- Riccardo Giacconi
- Riccardo Muti
- Riccia
- Ricci-Curbastro, Gregorio
- Ricci, Matteo
- Riccio, Andrea
- Riccio, David
- Ricci, Ruggiero
- rice
- Rice, Alice Hegan
- ricebird