beat
music
in music, the basic rhythmic unit of a measure, or bar, not to be confused with rhythm as such; nor is the beat necessarily identical with the underlying pulse of a given piece of music, which may extend over more than a single beat. The number and relative positions of accented and unaccented beats furnish the basis of proper metric articulation, with the strongest accent usually falling on the first beat after the bar line. In Western musical notation the number of beats to the measure is indicated by the upper figure of the time signature at the beginning of a musical composition, while the time value of each separate beat (e.g., a quarter or eighth note) is indicated by the lower figure. See also metre; rhythm.
waves
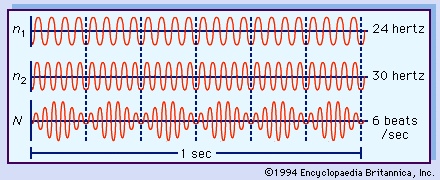 in physics, the pulsation caused by the combination of two waves of slightly different frequencies. The principle of beats for sound waves can be demonstrated on a piano by striking a white key and an adjacent black key at the bass end of the keyboard. The resulting sound is alternately soft and loud—that is, having characteristic pulsations, or throbs, called beats. Toward the treble end of the keyboard, the beat frequency is greater because the difference in frequency of adjacent keys is more than at the lower end. The Figure-->
in physics, the pulsation caused by the combination of two waves of slightly different frequencies. The principle of beats for sound waves can be demonstrated on a piano by striking a white key and an adjacent black key at the bass end of the keyboard. The resulting sound is alternately soft and loud—that is, having characteristic pulsations, or throbs, called beats. Toward the treble end of the keyboard, the beat frequency is greater because the difference in frequency of adjacent keys is more than at the lower end. The Figure--> depicts two waves n1 and n2 with respective frequencies of 24 and 30 vibrations per second (hertz); the beat frequency N is their difference, 6 beats per second.
depicts two waves n1 and n2 with respective frequencies of 24 and 30 vibrations per second (hertz); the beat frequency N is their difference, 6 beats per second.The phenomenon of beats is employed in various ways. For example, in the tuning (tuning and temperament) of instruments, if a tuning fork and piano key of the same note are struck simultaneously and no beat is heard, then they are of identical pitch. Ultrasonic vibrations (having a frequency higher than is audible), such as the vocal sounds made by bats and dolphins, may be detected by superimposing a sound of different frequency to produce audible beats. The principle is also used in the superheterodyne reception of radio waves, in which a low-frequency signal from an oscillator is beat against an incoming high-frequency radio signal to produce an intermediate (beat) frequency that can be amplified to produce audible signals.
- Emanuel, Baron Shinwell of Easington Shinwell
- Emanuel de Witte
- Emanuele d' Astorga
- Emanuel Geibel
- Emanuel Gottlieb Leutze
- Emanuel Lasker
- Emanuel, Rahm
- Emanuel Schikaneder
- Emanuel Shinwell, Baron Shinwell of Easington
- Emanuel Swedenborg
- E Martin Browne
- embalming
- embargo
- Embargo Act
- Embden, Gustav Georg
- embedded processor
- Ember Days and Ember Weeks
- Emberizidae
- embezzlement
- emblema
- emblem book
- Emboabas, War of the
- embolism
- embossing
- Embriaci Family