Bright disease
also called glomerulonephritis or nephritis
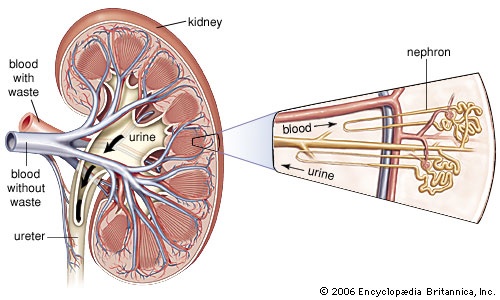
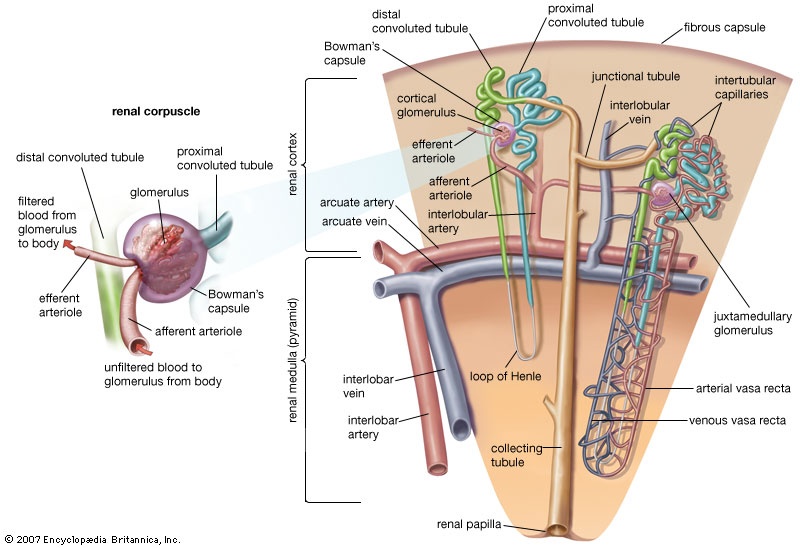 inflammation of the structures in the kidney that produce urine: the glomeruli and the nephrons (nephron). The glomeruli are small round clusters of capillaries (capillary) (microscopic blood vessels (blood vessel)) that are surrounded by a double-walled capsule, called Bowman's capsule. Bowman's capsule in turn connects with a long tubule. The capsule and attached tubule are known as a nephron. In cases of glomerulonephritis, the glomeruli, the nephrons, and the tissues between nephrons are all afflicted. Glomerulonephritis may be caused by disease states that disrupt the normal function of the immune system (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus), compromise the structure or function of the systemic vasculature (e.g., inflammation of the arteries (artery)), or damage the glomeruli (e.g., high blood pressure 【 hypertension】 or diabetic nephropathy). Glomerulonephritis can also arise from streptococcal infections such as strep throat. In some cases, however, a cause cannot be identified. Glomerulonephritis may occur only once or may recur. The successive stages of the disease are known as acute, subacute, and chronic.
inflammation of the structures in the kidney that produce urine: the glomeruli and the nephrons (nephron). The glomeruli are small round clusters of capillaries (capillary) (microscopic blood vessels (blood vessel)) that are surrounded by a double-walled capsule, called Bowman's capsule. Bowman's capsule in turn connects with a long tubule. The capsule and attached tubule are known as a nephron. In cases of glomerulonephritis, the glomeruli, the nephrons, and the tissues between nephrons are all afflicted. Glomerulonephritis may be caused by disease states that disrupt the normal function of the immune system (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus), compromise the structure or function of the systemic vasculature (e.g., inflammation of the arteries (artery)), or damage the glomeruli (e.g., high blood pressure 【 hypertension】 or diabetic nephropathy). Glomerulonephritis can also arise from streptococcal infections such as strep throat. In some cases, however, a cause cannot be identified. Glomerulonephritis may occur only once or may recur. The successive stages of the disease are known as acute, subacute, and chronic.Acute glomerulonephritis is characterized by severe inflammation, renal (kidney) insufficiency, swelling, increased blood pressure, and severe back pain. Recovery is usually fairly complete after an episode of acute glomerulonephritis, but minor infections may do further damage to the kidneys and bring on the subacute and chronic stages. In the acute form of the disease, the kidneys are swollen, the capsule covering each kidney is taut and stretched, the surface is smooth and gray, and usually there are many small hemorrhages from the capillaries. The whole complex of glomeruli and nephrons swells.
Subacute glomerulonephritis does not necessarily follow acute attacks; if it does develop, however, it has usually been preceded by an acute episode several months or years earlier. The kidney becomes considerably enlarged, the surface is smooth and pale, and the internal tissue is darker than normal. The paleness is due to the restriction of blood flow to the surface portion of the kidney and the high accumulation of fat ( lipid) droplets. Bowman's capsules become filled with excess surface (epithelial) cells (cell), red blood cells (erythrocyte), and mineral crystals. The nephron tubules begin to degenerate. Because of the breakdown of kidney tissue, a greater amount of blood protein is lost into urine than should normally be released. Red blood cells forced through the constricted glomeruli become crushed, distorted, and fragmented; their loss leads to anemia.
Chronic glomerulonephritis usually follows the other two stages, if the affected person survives long enough, but it has been found in a few individuals who apparently have not had previous kidney disease. In this stage the kidney is reduced mostly to scar tissue. It is small and shrivelled, and the surface is granular. Because the blood cannot be filtered of waste products, abnormal quantities of nitrogenous substances in the blood cause the condition known as uremia. Treatment of all forms of glomerulonephritis is primarily directed toward controlling high blood pressure with antihypertensive agents and diuretics (diuretic) and through changes in diet, which include fluid restriction and decreased salt intake. Some patients respond to treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs. dialysis may be necessary to manage uremia.
- Antonio Vivaldi
- Antonio Vivarini
- Antoni Słonimski
- Antoni Tàpies
- Anton Ivanovich Denikin
- Antoni Zygmund
- Anton J. Cermak
- Anton Kolowrat, graf von
- Anton Korošec
- Anton Mauve
- antonomasia
- Anton Raaff
- Anton Raphael Mengs
- Anton Rintelen
- Anton, Ritter (knight) von Schmerling
- Anton Rubinstein
- Anton Sailer
- Anton Schmerling, Ritter (knight) von
- Anton Semyonovich Makarenko
- Anton Webern
- Anton Wildgans
- Antony and Cleopatra
- Antony Hewish
- Antony Khrapovitsky
- Antony, Mark