Select nutrient-deficiency diseases
Table
Select nutrient-deficiency diseases
disease (and key nutrient involved) symptoms foods rich in key nutrient
xerophthalmia
(vitamin A) blindness from chronic eye infections, poor growth, dryness and keratinization of epithelial tissues liver, fortified milk, sweet potatoes, spinach, greens, carrots, cantaloupe, apricots
rickets
(vitamin D) weakened bones, bowed legs, other bone deformities fortified milk, fish oils, sun exposure
beriberi
(thiamin) nerve degeneration, altered muscle
coordination, cardiovascular problems pork, whole and enriched grains, dried beans, sunflower seeds
pellagra
(niacin) diarrhea, skin inflammation, dementia mushrooms, bran, tuna, chicken, beef, peanuts, whole and enriched grains
scurvy
(vitamin C) delayed wound healing, internal bleeding, abnormal formation of bones and teeth citrus fruits, strawberries, broccoli
iron-deficiency anemia (iron deficiency anemia)
(iron) decreased work output, reduced growth,
increased health risk in pregnancy meat, spinach, seafood, broccoli, peas, bran, whole-grain and enriched breads
goitre
(iodine) enlarged thyroid gland, poor growth in infancy and childhood, possible mental retardation, cretinism iodized salt, saltwater fish
Source: Gordon M. Wardlaw, Perspectives in Nutrition (1999).
See as table: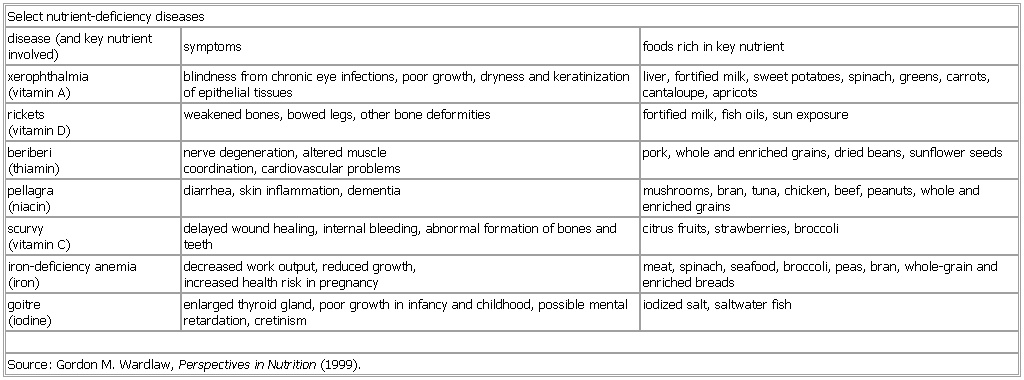

- flag of Ohio
- flag of Oklahoma
- flag of Oman
- flag of Ontario
- flag of Oregon
- flag of Pakistan
- flag of Palau
- flag of Palestine Liberation Organization
- flag of Panama
- flag of Papua New Guinea
- flag of Paraguay
- flag of Pennsylvania
- flag of Peru
- flag of Poland
- flag of Portugal
- flag of Prince Edward Island
- flag of Puerto Rico
- flag of Qatar
- flag of Quebec
- flag of Queensland
- flag of Rhode Island
- flag of Romania
- flag of Russia
- flag of Rwanda
- flag of Saint Kitts and Nevis