Characteristics of oxide glasses
Table
Characteristics of oxide glasses
fused silica soda-lime-silica borosilicate aluminosilicate lead
Approximate composition1
● silica 99.9%
● water 0.1%
● silica 73%
● alumina 1%
● sodium oxide 17%
● magnesia 4%
● lime 5%
● silica 81%
● alumina 2%
● boric oxide 13%
● sodium
oxide 4%
● silica 62%
● alumina 17%
● boric oxide 5%
● sodium oxide 1%
● magnesia 7%
● lime 8%
● silica 56%
● alumina 2%
● sodium oxide 4%
● potash 9%
● lead oxide 29%
coefficient of thermal expansion (linear expansion per degree Celsius 【107】) 5.5 93 33 42 89
strain point2 (degrees Celsius; viscosity about 1014.5 poise) 990 470 515 670 395
annealing point3 (degrees Celsius; viscosity about 1013 poise) 1,050 510 565 715 435
softening point4, 5 (degrees Celsius; viscosity about 107.65 poise) 1,580 695 820 915 630
Young's modulus (pounds per square inch 【106】) 10.5 10 9.1 12.7 8.6
refractive index (for sodium D line) 1.459 1.512 1.474 1.530 1.560
dielectric constant (at 106 cycles per second and 20 degrees Celsius) 3.8 7.2 4.6 7.2 6.7
density (grams per cubic centimetre) 2.20 2.47 2.23 2.52 3.05
1These compositions are typical of the various glass types.
2Temperature at which internal stresses are reduced significantly over a few hours.
3Temperature at which internal stresses are reduced significantly over a few minutes.
4Temperature at which glass will rapidly deform under its own weight.
5The strain point and annealing point roughly define the annealing range.
See as table: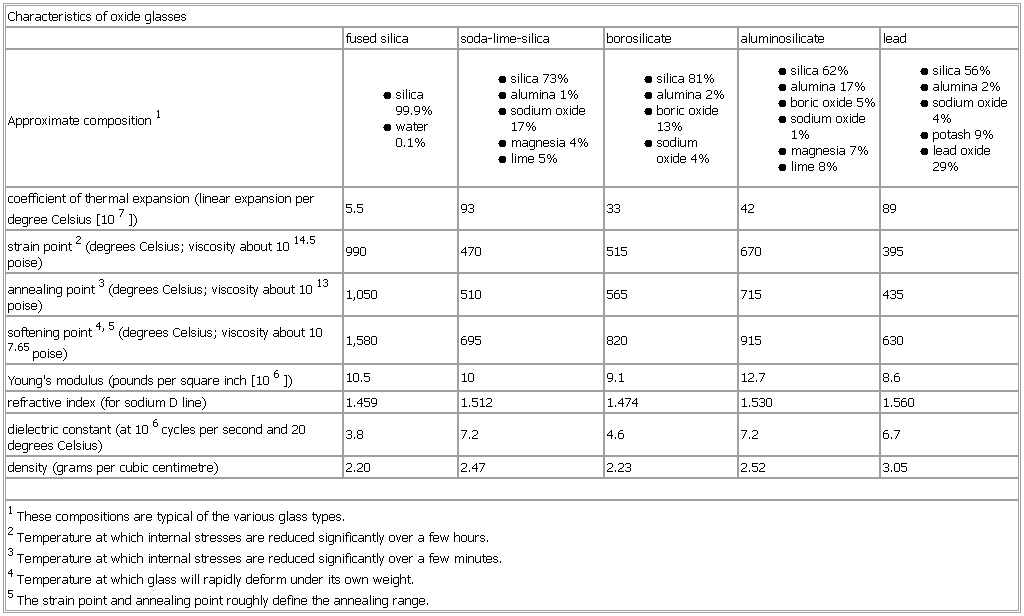

- Brown, Ray
- brown recluse
- Brown, Robert
- Brown, Robert Hanbury
- Brown, Ron
- Brown, Ruth
- Brown, Sir Arthur Whitten
- Brown, Sir John
- brown snake
- Brownson, Orestes Augustus
- Brown, Sterling
- Brownsville
- Brownsville Affair
- Brown Swiss
- Brown-Séquard, Charles-Édouard
- Brown, Thomas
- Brown, Tom
- Brown, Trisha
- brown trout
- Brown University
- Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka
- Brown, William Hill
- Brown, William Wells
- Brown, Willie
- browridge