Chihuahua
Mexico
 city, capital of Chihuahua estado (state), northern Mexico. The city lies at an elevation of about 4,800 feet (1,460 metres) in a valley of the Sierra Madre Occidental at the edge of the Chihuahuan Desert.
city, capital of Chihuahua estado (state), northern Mexico. The city lies at an elevation of about 4,800 feet (1,460 metres) in a valley of the Sierra Madre Occidental at the edge of the Chihuahuan Desert.Originally settled in the 16th century and officially founded in 1709, Chihuahua was a prosperous colonial mining centre and a base of Spanish royal authority in the region. Mexican independence leader Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla (Hidalgo y Costilla, Miguel) and his companions were executed in the plaza in 1811. During the 19th and early 20th centuries Chihuahua continued to play a major role in regional and national politics. The city was captured by U.S. forces during the Mexican (Mexican-American War)-American War (1846–48), and Benito Juárez (Juárez, Benito) based his army there in 1865 to oppose the French occupation of Mexico. Chihuahua was the birthplace of the writer Martín Luis Guzmán (Guzmán, Martín Luis) (1887–1976), whose works examined many aspects of the Mexican Revolution, and also of the prolific muralist and leftist political activist David Alfaro Siqueiros (Siqueiros, David Alfaro) (1896–1974). The city retains many historic buildings, including its 18th-century cathedral, which houses an ecclesiastical art museum. Quinta Luz, a manor where Pancho Villa (Villa, Pancho) once lived, is now a history museum administered by the Mexican army; its most popular exhibit is the bullet-riddled car in which Villa was assassinated (at his ranch near Parral) in 1923.
The city's economy is both industrial and service-oriented. Manufactures include automobile parts and accessories, textiles, electronics, plastics, and medical products. The local, state, and federal governments provide significant employment. Chihuahua is also a market and processing centre for cattle, apples, onions, alfalfa, peanuts, and chili peppers from its hinterland. The Autonomous University of Chihuahua (1954) is located in the city. Chihuahua is a regional transportation hub. Pop. (2000) 657,876.
breed of dog
 smallest recognized dog breed, named for the Mexican state of Chihuahua, where it was first noted in the mid-19th century. The Chihuahua is thought to have been derived from the Techichi, a small, mute dog kept by the Toltec people of Mexico as long ago as the 9th century AD. Typically a saucy-looking, alert dog that is sturdier than its small build would suggest, the Chihuahua stands about 5 inches (13 cm) and weighs 1 to 6 pounds (0.5 to 3 kg). It has a rounded head, large, erect ears, prominent eyes, and a compact body. The coat is variable in colour and may be either smooth and glossy or long and soft. It is valued as a spirited companion especially suited to apartment living.
smallest recognized dog breed, named for the Mexican state of Chihuahua, where it was first noted in the mid-19th century. The Chihuahua is thought to have been derived from the Techichi, a small, mute dog kept by the Toltec people of Mexico as long ago as the 9th century AD. Typically a saucy-looking, alert dog that is sturdier than its small build would suggest, the Chihuahua stands about 5 inches (13 cm) and weighs 1 to 6 pounds (0.5 to 3 kg). It has a rounded head, large, erect ears, prominent eyes, and a compact body. The coat is variable in colour and may be either smooth and glossy or long and soft. It is valued as a spirited companion especially suited to apartment living.state, Mexico

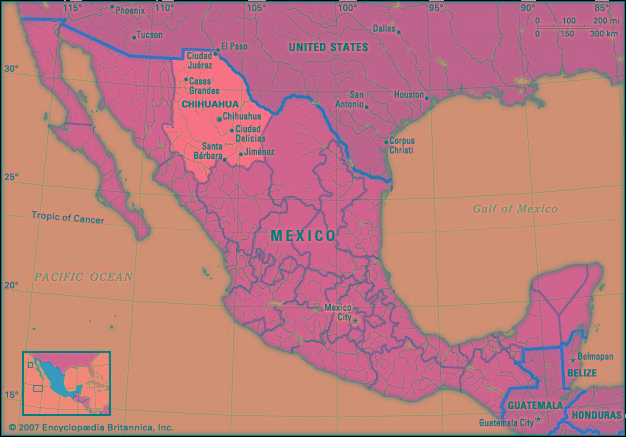 estado (state), northern Mexico. It is bounded to the north and northeast by the United States ( New Mexico and Texas), to the east by the state of Coahuila, to the south by the state of Durango, and to the west by the states of Sinaloa and Sonora. Its capital is the city of Chihuahua.
estado (state), northern Mexico. It is bounded to the north and northeast by the United States ( New Mexico and Texas), to the east by the state of Coahuila, to the south by the state of Durango, and to the west by the states of Sinaloa and Sonora. Its capital is the city of Chihuahua.In precolonial times, Chihuahua was inhabited by nomadic and seminomadic indigenous peoples. With the advent of Spanish explorers in the mid-16th century, these Indian groups began a long string of rebellions against the colonists that lasted several centuries. The Spanish established silver mines in the region, and Chihuahua became a centre for trading. Under Spanish rule, Chihuahua along with Durango formed part of Nueva Vizcaya province. It was not separated from Durango until after Mexico's independence was achieved (1823). Chihuahua city was captured and occupied by U.S. troops in 1847 during the Mexican-American War. The people of the state were active in most of the revolutionary outbreaks in Mexico during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Native influence in the state is now slight, most of those populations having been assimilated or displaced, but isolated communities of Raramuri ( Tarahumara) and Tepehua (Tepehuan) survive in the sierra.
 Chihuahua is Mexico's largest state. For the most part, its relief consists of an elevated plain that slopes gently downward toward the Rio Grande (Río Bravo del Norte) in the northeast. The vast Chihuahuan Desert dominates the northeastern half of the state. Western Chihuahua, however, is broken by the Sierra Madre Occidental and its spurs, which form high, fertile valleys and deep canyons. The elevated plateaus and valleys experience heavy rainfall, but most of the state receives less than 20 inches (500 mm) annually. An impermeable clay subsoil prevents much of the rain's absorption, so what little rain does fall is carried along the bare land surface in torrents. Copper Canyon (Barranca del Cobre), in the western part of the state, reaches depths of 4,600 feet (1,400 metres) in places; it is larger and more spectacular than the Grand Canyon but is virtually inaccessible, though a railway traverses part of it. Among the other scenic areas are Majalca Peaks National Park, some 30 miles (50 km) northwest of Chihuahua city, and the Basaseachic waterfall, in the Sierra Madre. The only river of consequence is the Conchos (Conchos River), which flows north and northeast into the Rio Grande.
Chihuahua is Mexico's largest state. For the most part, its relief consists of an elevated plain that slopes gently downward toward the Rio Grande (Río Bravo del Norte) in the northeast. The vast Chihuahuan Desert dominates the northeastern half of the state. Western Chihuahua, however, is broken by the Sierra Madre Occidental and its spurs, which form high, fertile valleys and deep canyons. The elevated plateaus and valleys experience heavy rainfall, but most of the state receives less than 20 inches (500 mm) annually. An impermeable clay subsoil prevents much of the rain's absorption, so what little rain does fall is carried along the bare land surface in torrents. Copper Canyon (Barranca del Cobre), in the western part of the state, reaches depths of 4,600 feet (1,400 metres) in places; it is larger and more spectacular than the Grand Canyon but is virtually inaccessible, though a railway traverses part of it. Among the other scenic areas are Majalca Peaks National Park, some 30 miles (50 km) northwest of Chihuahua city, and the Basaseachic waterfall, in the Sierra Madre. The only river of consequence is the Conchos (Conchos River), which flows north and northeast into the Rio Grande.Chihuahua is one of Mexico's leading producers of iron, lead, zinc, gold, silver, copper, and other minerals. Scarcity of water has been a serious obstacle to agricultural development in the state except in districts where irrigation is practicable; cotton and beans are the main crops, and apples and nuts are also significant products. Forestry and livestock raising are economically important in the mountainous districts of the west, where there is sufficient precipitation and pasturage for much of the year.
The city of Chihuahua is a transportation hub with air, highway, and railway links to central Mexico and the United States. Other important cities in the state are Hidalgo del Parral and Juárez (or Ciudad Juárez), which lies across the Rio Grande from El Paso, Tex. The population of Juárez has boomed along with the growth of maquiladoras (export-oriented assembly plants) and cross-border migration; however, drug trafficking and violent crime have become major concerns along the border.
The state's government is headed by a governor, who is elected to a single six-year term. Members of the unicameral House of Deputies serve for terms of three years. The legislature can levy taxes, but in reality Chihuahua depends on the federal government for most of its revenue. The state is divided into local governmental units called municipios (municipalities), each of which may include a city or town and its hinterland or a group of villages. Area 94,571 square miles (244,938 square km). Pop. (2000) 3,052,907; (2005) 3,241,444.
- Humbert of Silva Candida
- Humboldt
- Humboldt, Alexander von
- Humboldt Glacier
- Humboldt River
- Humboldt University of Berlin
- Humboldt, Wilhelm, Baron von
- Hume, Alexander
- Hume, Allan Octavian
- Hume Cronyn
- Hume, David
- Hume, Hamilton
- Hume, John
- Hume, Joseph
- Hume Reservoir
- Hume-Rothery, William
- humerus
- Hume, Sir Patrick, 2nd Baronet
- Humfrey, Pelham
- Humfry Payne
- humic acid
- humidity
- humite
- Hummel, Johann Nepomuk
- hummingbird