chondrite
meteorite
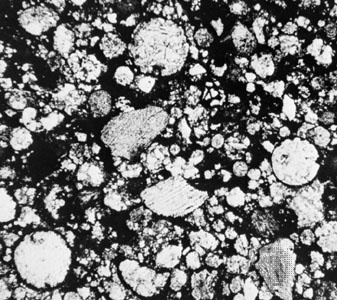 in general, any stony meteorite characterized by the presence of chondrules. The only meteorites classified as chondrites that do not contain chondrules are the CI group. These meteorites are so heavily altered by water that it is unclear whether they once contained chondrules. All other aspects of these objects, however, indicate that they belong with the chondrites.Chondrules are roughly spherical inclusions, typically hundreds of micrometres to a few millimetres in size. They are made up of silicates, metal, and sulfide, and they appear to have formed as molten droplets at high temperatures in the early solar nebula. The chondrules are set in a fine-grained matrix that binds them together. Chondrites are divided into three main classes based on their bulk chemical compositions, oxygen isotopic compositions, and petrology. These are carbonaceous chondrites, ordinary chondrites, and enstatite chondrites.
in general, any stony meteorite characterized by the presence of chondrules. The only meteorites classified as chondrites that do not contain chondrules are the CI group. These meteorites are so heavily altered by water that it is unclear whether they once contained chondrules. All other aspects of these objects, however, indicate that they belong with the chondrites.Chondrules are roughly spherical inclusions, typically hundreds of micrometres to a few millimetres in size. They are made up of silicates, metal, and sulfide, and they appear to have formed as molten droplets at high temperatures in the early solar nebula. The chondrules are set in a fine-grained matrix that binds them together. Chondrites are divided into three main classes based on their bulk chemical compositions, oxygen isotopic compositions, and petrology. These are carbonaceous chondrites, ordinary chondrites, and enstatite chondrites.Chondrites are the most abundant meteorite class, constituting more than 85 percent of meteorite falls. Like most meteorites, chondrites originated in the asteroid belt where collisions and gravitational perturbations put them into Earth-crossing orbits. Chondrites formed about 4.56 billion years ago as part of the formation of their parent asteroids. They are chemically quite similar to one another and, apart from the most volatile elements (e.g., hydrogen and helium), to the Sun. Since most of the mass of the solar system is in the Sun, the initial composition of the solar system would have been similar to the Sun's composition. The great age of the chondrites, their primitive chemistry, and the relatively unmodified state of their constituents all suggest that these meteorites retain a record of processes that happened in the solar nebula before and during the phase of planet formation. Nevertheless, the meaning of this record remains to be fully deciphered. The chondrites also contain material, including organic matter and tiny grains that formed around dying stars, that predates the formation of the solar system.
Most chondrites contain the anhydrous silicate minerals olivine, orthopyroxene and clinopyroxene, and plagioclase, as well as the nickel-iron minerals kamacite and taenite, and the iron sulfide troilite. Some contain claylike hydrous silicates.
- Waltham Forest
- Waltharius
- Waltheof
- Walther Bothe
- Walther, Carl Ferdinand Wilhelm
- Walther Eichrodt
- Walther Flemming
- Walther Funk
- Walther Gerlach
- Walther Hermann Nernst
- Walther, Johann Gottfried
- Walther Model
- Walther Penck
- Walther Rathenau
- Walther von Brauchitsch
- Walther Von Der Vogelweide
- Walther von Reichenau
- Walthère Frère-Orban
- Walt Kelly
- Walt Kuhn
- Walton, Ernest Thomas Sinton
- Walton, Izaak
- Walton-le-Dale
- Walton, Sam
- Walton, Sir William