Some common diseases of domestic cats
Table
Some common diseases of domestic cats
name(s) of disease causative agent nature of disease
feline distemper (panleukopenia, infectious enteritis) virus the most important viral disease of cats; wildcats and raccoons also susceptible; number of white blood cells decreases; fluid losses cause dehydration; treatment includes replacing fluid and preventing bacterial infections; vaccination advisable in kittens
feline rhinotracheitis (pneumonitis, coryza, and influenza) viruses (e.g., Miyagawanella) any upper-respiratory viral infection with eye and nose involvement; common among cats; seldom causes death; similar to severe head cold in humans; treatment includes antibiotic drugs
feline picornavirus pneumonia virus symptoms include watery eyes, nasal inflammation; pneumonia; in severe cases, death is preceded by laboured breathing
lymphocytic leukemia virus cancerous lymphocytic cells enter blood from a malignant tumour (lymphosarcoma); lymph nodes may become enlarged; a progressive anemia, an increase in the level of circulating immature lymphocytes, symptoms may precede death; no curative treatment known thus far
urinary-bladder infection with stones and obstruction (cystitis) unknown urethra is obstructed with crystals of magnesium ammonium phosphate and mucus associated with infection of the urinary bladder (cystitis); death occurs if obstruction not relieved; exact cause of syndrome (set of symptoms) unknown but may be related to diet or to a virus
ringworm (dermatomycosis) fungus (Microsporum canis; Trichophyton species) kittens most often affected; disease (a scaly, spreading skin condition) may be transmitted to children; some cats may carry the disease and show no clinical signs
toxoplasmosis protozoan (Toxoplasma gondii) toxoplasmosis probably occurs frequently in cats; chronic forms affect abdominal organs; organisms may invade nearly any body tissue
ear mites, ear inflammation (otitis externa) mite (Otodectes cynotis) acquired through contact of kitten with an infected mother; constant scratching of ears eventually causes raw sores and scabs; treatment includes killing the mites and controlling secondary bacterial infections
osteodystrophy fibrosa (osteogenesis imperfecta) nutritional deficiencies once considered congenital in kittens but probably is nutritional, resulting from a calcium deficiency; lameness, first noted at 10 to 15 weeks, may lead to paralysis of rear legs, slow growth, bone fractures, and severe pain; treatment includes a diet with adequate calcium
"fur ball" disease physical agent hair balls accumulate in stomach as a result of constant grooming; surgical removal sometimes necessary
See as table: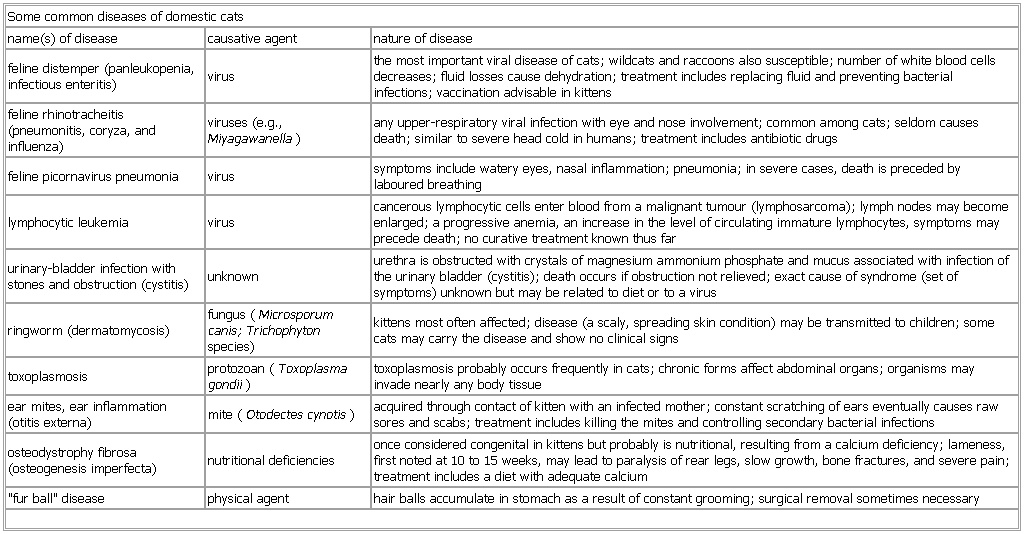

- Troilus and Cressida
- Trois Frères
- Trois-Rivières
- Troitsk
- trojan
- Trojan horse
- Trojan planets
- Trojan War
- troll
- Trolle, Gustav
- trolleybus
- Trollhätte Canal
- trolling
- Trollope, Anthony
- Trombetas River
- trombone
- Tromp, Cornelis
- trompe l'oeil
- Tromp, Maarten
- Tromsø
- trona
- Trondheim
- Trondheims Fjord
- Troodos Mountains
- troparion