cranial nerve
anatomy
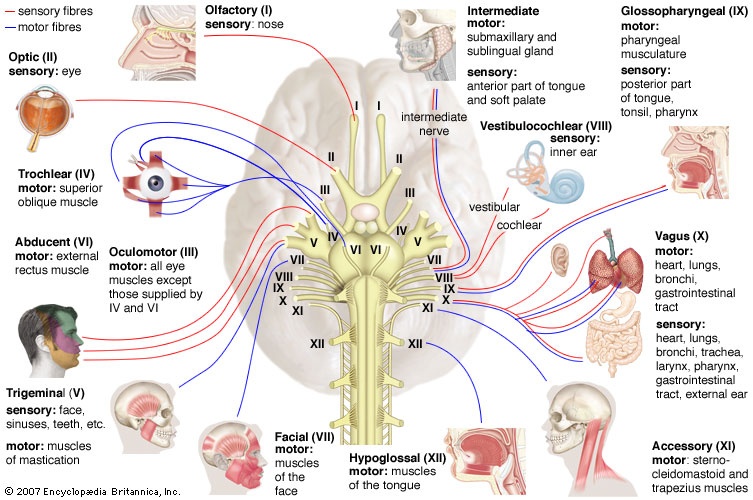 in vertebrates, any of the paired nerves of the peripheral nervous system that connect the muscles and sense organs of the head and thoracic region directly to the brain. In higher vertebrates (reptiles, birds, mammals) there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (I), optic (II), oculomotor (III), trochlear (IV), trigeminal (V), abducent (VI), facial (facial nerve) (VII), vestibulocochlear (VIII), glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (vagus nerve) (X), accessory (XI), and hypoglossal (XII). Lower vertebrates (fishes, amphibians) have 10 pairs.
in vertebrates, any of the paired nerves of the peripheral nervous system that connect the muscles and sense organs of the head and thoracic region directly to the brain. In higher vertebrates (reptiles, birds, mammals) there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (I), optic (II), oculomotor (III), trochlear (IV), trigeminal (V), abducent (VI), facial (facial nerve) (VII), vestibulocochlear (VIII), glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (vagus nerve) (X), accessory (XI), and hypoglossal (XII). Lower vertebrates (fishes, amphibians) have 10 pairs.Cranial nerves are made up of motor neurons (neuron), sensory neurons, or both. The vagus (vagus nerve) nerve is one of the most important; it extends to many of the organs in the chest and upper abdomen.
- George Seferis
- George Segal
- Georges Enesco
- George Seton, 5th Lord Seton
- George Seton Seton, 5th Lord
- Georges-Eugène, Baron Haussmann
- Georges-Eugène Haussmann, Baron
- George Sewall Boutwell
- Georges Feydeau
- Georges Franju
- Georges Friedel
- George Shiras, Jr.
- George Sisler
- Georges Jacob
- Georges J.F. Köhler
- George S. Kaufman
- Georges Leclanché
- Georges Lefebvre
- Georges Lemaître
- Georges-Louis Leclerc Buffon, count de
- Georges-Louis Leclerc, count de Buffon
- Georges Mandel
- Georges Marchais
- Georges-Marie Guynemer
- George S McGovern