Cynognathus
paleontology
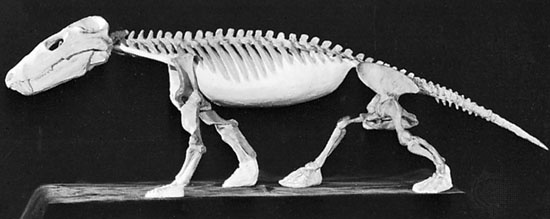 genus of extinct advanced therapsids (mammals and their relatives) found as fossils in Lower Triassic deposits (about 240 million to 250 million years ago) in South Africa and South America. Cynognathus is representative of the Theriodontia, a group of cynodont therapsids that gave rise to the earliest mammals.
genus of extinct advanced therapsids (mammals and their relatives) found as fossils in Lower Triassic deposits (about 240 million to 250 million years ago) in South Africa and South America. Cynognathus is representative of the Theriodontia, a group of cynodont therapsids that gave rise to the earliest mammals.Cynognathus was approximately as large as a modern wolf and, like the wolf, was an active predator. The body of Cynognathus was not massively constructed. The tail was short, and the limbs were tucked well under and close to the body, providing the potential for rapid and efficient locomotion. The skull was long and had openings for the attachment of strong muscles used in opening and closing the jaws. The lower jaw was dominated by the dentary bone; the other lower-jaw elements, characteristic of reptiles, were relatively reduced, as in mammals and their near relatives. The teeth were regionally specialized on the jaw into different forms, as in mammals. Incisors adapted to nipping were followed by strongly developed canines, important features in predatory animals. Separated from the canines by a gap, or diastema, was a series of cheek teeth that sliced the animal's food into smaller, more easily swallowed particles. A well-developed secondary palate separated food passages from breathing passages. The vertebral column was well differentiated.
- Dollfuss, Engelbert
- Dollmann, Friedrich
- Dollmann, Georg von
- Dollond, George
- Dollond, John
- Dollond, Peter
- Dollo's law
- Dolly
- Dolly Lunt Burge: Her Diary
- Dolly Varden trout
- dolma
- dolmen
- Dolmetsch, Arnold
- Dolnośląskie
- Dolomieu, Dieudonné
- dolomite
- Dolomites
- dolomitization
- Dolores Huerta
- Dolores Ibárruri
- Dolores River
- dolphin
- Dolphy, Eric
- Domagk, Gerhard
- domain