erbium
chemical element
 (Er), chemical element, rare-earth metal of the lanthanoid series of the periodic table. Erbium is a grayish silver element that also occurs as a series of pink compounds. It had limited commercial uses until the age of fibre-optic telecommunications, when it became an important constituent of the signal repeaters in long-distance telephone cables.
(Er), chemical element, rare-earth metal of the lanthanoid series of the periodic table. Erbium is a grayish silver element that also occurs as a series of pink compounds. It had limited commercial uses until the age of fibre-optic telecommunications, when it became an important constituent of the signal repeaters in long-distance telephone cables.The element was discovered (1843) as an oxide by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Mosander, Carl Gustaf), who originally called it terbia. In the confusion arising from the similarity in the properties of the rare-earth elements, the names of two, terbium and erbium, became interchanged (c. 1860). The element occurs in many rare-earth minerals, among the more important being xenotime and euxenite. Erbium occurs also in the products of nuclear fission. Commercial purification is accomplished by ion-exchange methods. The metal itself has been prepared by thermoreduction of the anhydrous fluoride with calcium. It is slowly oxidized by oxygen and water. At low temperatures the element is antiferromagnetic, and at very low temperatures, ferromagnetic and superconductive. Natural erbium is a mixture of six stable isotopes: erbium-162 (0.136 percent), erbium-164 (1.56 percent), erbium-166 (33.41 percent), erbium-167 (22.94 percent), erbium-168 (27.07 percent), and erbium-170 (14.88 percent).
Erbium behaves as a typical rare-earth element, forming compounds in which its oxidation state is +3, such as the pink oxide Er2O3. The Er3+ ion is pink in solution and is strongly paramagnetic because of the presence of unpaired electrons. In addition, when raised to a high energy state by absorption of infrared light, the Er3+ ion emits photons at wavelengths of 1.55 micrometres—one of the wavelengths commonly employed in fibre-optic signal transmission. For this reason, erbium-doped fibre amplifiers are used to boost the power of light signals transmitted through long-distance optical cables.
atomic number
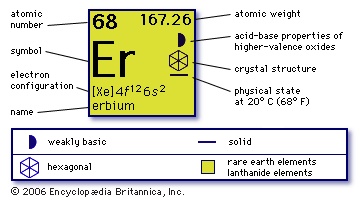
68
atomic weight
167.26
melting point
1,529° C
boiling point
2,862° C
specific gravity
9.066 (25° C)
oxidation state
+3
electronic config.
【Xe】4f 125d06s2
- Otto Friedrich von Gierke
- Otto Gessler
- Otto Graham
- Otto Hahn
- Otto Heckmann
- Otto Heinrich Schindewolf
- Otto Henne am Rhyn
- Otto Hermann Kahn
- Otto I
- Otto II
- Otto III
- Otto IV
- Otto Jespersen
- Ottokar, Count Czernin
- Ottokar Czernin, Count
- Otto Klemperer
- Otto, Kristin
- Otto Lilienthal
- Otto Liman von Sanders
- Otto Loewi
- Otto Ludwig
- Otto Luening
- ottoman
- Ottoman court carpet
- Ottoman Empire