U.S. Soil Taxonomy
Table
U.S. Soil Taxonomy
soil order defining characteristics name derivation percent of Earth's land area*
Alfisol moderate leaching; B horizon enriched in clay; humid forest vegetation Pedalfer (C.F. Marbut) 9.77
Andisol volcanic-ash parent material an do (Japanese: "dark soil") 0.73
Aridisol hot, dry climate; weak B horizon aridus (Latin: "dry") 18.53
Entisol little or no horizonation or swelling clay recent 10.61
Gelisol permafrost within 2 metres (approximately
6 feet) of the land surface gelid (Greek: "very cold") —
Histosol organic parent material histos (Greek: "tissue") 1.84
Inceptisol little or no B horizon development inceptum (Latin: "beginning") 21.80
Mollisol thick, soft, black A horizon mollis (Latin: "soft") 5.99
Oxisol hot, humid climate; B horizon enriched in iron and aluminum oxides and kaolinite oxide (French) 7.00
Spodosol cool, humid climate; B horizon enriched in iron and aluminum oxides and organic matter; sandy parent material spodos (Greek: "wood ashes") 3.45
Ultisol warm, humid climate; B horizon enriched in clay; extensive leaching ultimus (Latin: "last") 8.12
Vertisol little or no horizonation; high content of swelling clay vertere (Latin: "to turn") 2.23
*Rock, sand, and bodies of water account for 5.25% of the continental land area in the world between 75° N and 75° S latitude. Gelisols cover about 18 million square km (7 million square miles) largely outside these latitudes, mostly in Russia and Canada.
See as table: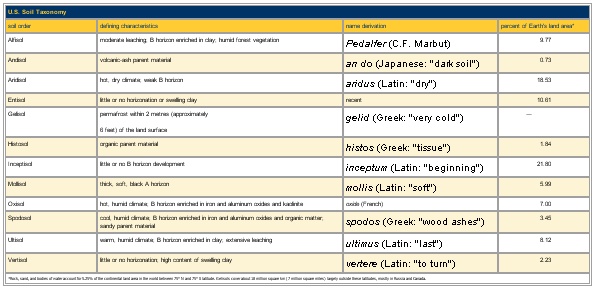

- Vo Chi Cong
- Vocontii
- Vodafone
- vodka
- Vodou
- vodyanoy
- Voegelin, Eric
- Voetius, Gisbertus
- Voevodsky, Vladimir
- Vogel, Hermann Karl
- Vogelsang, Karl, Freiherr (baron) von
- Vogel, Sir Julius
- Voghera
- Vogt, Johan Herman Lie
- Vogtland
- Vogt, Nils Collett
- Vohu Manah
- voice
- Voiceband modem operating standards
- voice identification
- Voice of America
- voir dire
- Voisin-Farman I
- Voisin, Gabriel
- Voit, Carl von