Gondwana
historical region, India
historic region in central India, comprising portions of Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra (Mahārāshtra) states. It is inhabited by the Gonds (Gond), a group of Dravidian peoples exceeding three million in population, first mentioned in 14th-century Muslim chronicles. From the 14th to the 18th century the area was held by powerful Gond dynasties, which during Mughal times remained independent or served as tributary chiefs. When in the 18th century the Gonds were conquered by the Marathas, the greater part of Gondwana was incorporated into the dominions of the Bhonsle rajas of Nagpur or the nizams of Hyderabad. Many Gonds took refuge in relatively inaccessible highlands and became tribal raiders. Between 1818 and 1853 the greater part of the region passed to the British, although in some minor states the Gond rajas continued to rule until Indian independence in 1947.
supercontinent
also called Gondwanaland
 ancient supercontinent that incorporated present-day South America, Africa, Arabia, Madagascar, India, Australia, and Antarctica. It was fully assembled by Late Precambrian (Precambrian time) time, some 600 million years ago, and the first stage of its breakup began in the Early Jurassic (Jurassic Period) Period, about 180 million years ago. The name Gondwanaland was coined by the Austrian geologist Eduard Suess (Suess, Eduard) in reference to Upper Paleozoic (Paleozoic Era) and Mesozoic (Mesozoic Era) formations in the Gondwana region of central India, which are similar to formations of the same age on Southern Hemisphere continents.
ancient supercontinent that incorporated present-day South America, Africa, Arabia, Madagascar, India, Australia, and Antarctica. It was fully assembled by Late Precambrian (Precambrian time) time, some 600 million years ago, and the first stage of its breakup began in the Early Jurassic (Jurassic Period) Period, about 180 million years ago. The name Gondwanaland was coined by the Austrian geologist Eduard Suess (Suess, Eduard) in reference to Upper Paleozoic (Paleozoic Era) and Mesozoic (Mesozoic Era) formations in the Gondwana region of central India, which are similar to formations of the same age on Southern Hemisphere continents.The matching shapes of the coastlines of western Africa and eastern South America were first noted by Francis Bacon (Bacon, Francis, Viscount Saint Alban (or Albans), Baron of Verulam) in 1620 as maps of Africa and the New World first became available. The concept that all of the continents of the Southern Hemisphere were once joined together was set forth in detail by Alfred Wegener (Wegener, Alfred Lothar), a German meteorologist, in 1912. He envisioned a single great landmass, Pangaea (or Pangea). Gondwana comprised the southern half of this supercontinent.
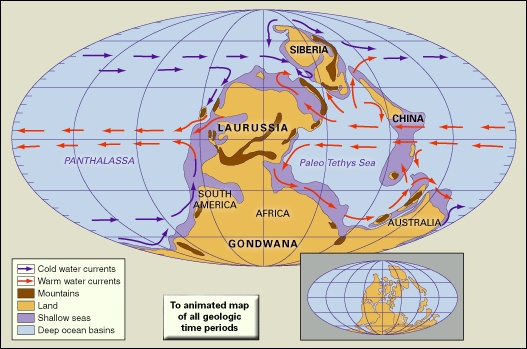 The concept of Gondwana was expanded upon by Alexander Du Toit, a South African geologist, in his 1937 book Our Wandering Continents. Du Toit carefully documented the numerous geologic and paleontological lines of evidence that linked the southern continents. This evidence included the occurrence of glacial deposits—tillites (tillite)—of Permo (Permian Period)-Carboniferous (Carboniferous Period) age (approximately 290 million years old) and similar floras and faunas that are not found in the Northern Hemisphere. The widely distributed seed fern Glossopteris is particularly cited in this regard. The rock strata that contain this evidence are called the Karoo (Karoo System) (Karroo) System in South Africa, the Gondwana System in India, and the Santa Catharina System in South America. It also occurs in the Maitland Group of eastern Australia as well as in the Whiteout conglomerate and Polarstar formations of Antarctica. Though the concept of Gondwana was widely accepted by scientists from the Southern Hemisphere, scientists in the Northern Hemisphere continued to resist the idea of continental mobility until the 1960s, when the theory of plate tectonics demonstrated that the ocean basins are not permanent global features and vindicated Wegener's hypothesis of continental drift.
The concept of Gondwana was expanded upon by Alexander Du Toit, a South African geologist, in his 1937 book Our Wandering Continents. Du Toit carefully documented the numerous geologic and paleontological lines of evidence that linked the southern continents. This evidence included the occurrence of glacial deposits—tillites (tillite)—of Permo (Permian Period)-Carboniferous (Carboniferous Period) age (approximately 290 million years old) and similar floras and faunas that are not found in the Northern Hemisphere. The widely distributed seed fern Glossopteris is particularly cited in this regard. The rock strata that contain this evidence are called the Karoo (Karoo System) (Karroo) System in South Africa, the Gondwana System in India, and the Santa Catharina System in South America. It also occurs in the Maitland Group of eastern Australia as well as in the Whiteout conglomerate and Polarstar formations of Antarctica. Though the concept of Gondwana was widely accepted by scientists from the Southern Hemisphere, scientists in the Northern Hemisphere continued to resist the idea of continental mobility until the 1960s, when the theory of plate tectonics demonstrated that the ocean basins are not permanent global features and vindicated Wegener's hypothesis of continental drift. According to plate tectonic evidence, Gondwana was assembled by continental collisions in the Late Precambrian (Precambrian time) (about 1 billion to 542 million years ago). Gondwana then collided with North America, Europe, and Siberia to form the supercontinent of Pangea. The breakup of Gondwana occurred in stages. Some 180 million years ago, in the Jurassic Period, the western half of Gondwana (Africa and South America) separated from the eastern half (Madagascar, India, Australia, and Antarctica). The South Atlantic Ocean opened about 140 million years ago as Africa separated from South America. At about the same time, India, which was still attached to Madagascar, separated from Antarctica and Australia, opening the central Indian Ocean. During the Late Cretaceous Period, India broke away from Madagascar, and Australia slowly rifted away from Antarctica. India eventually collided with Eurasia some 50 million years ago, forming the Himalayan mountains, while the northward-moving Australian plate had just begun its collision along the southern margin of Southeast Asia—a collision that is still under way today.
According to plate tectonic evidence, Gondwana was assembled by continental collisions in the Late Precambrian (Precambrian time) (about 1 billion to 542 million years ago). Gondwana then collided with North America, Europe, and Siberia to form the supercontinent of Pangea. The breakup of Gondwana occurred in stages. Some 180 million years ago, in the Jurassic Period, the western half of Gondwana (Africa and South America) separated from the eastern half (Madagascar, India, Australia, and Antarctica). The South Atlantic Ocean opened about 140 million years ago as Africa separated from South America. At about the same time, India, which was still attached to Madagascar, separated from Antarctica and Australia, opening the central Indian Ocean. During the Late Cretaceous Period, India broke away from Madagascar, and Australia slowly rifted away from Antarctica. India eventually collided with Eurasia some 50 million years ago, forming the Himalayan mountains, while the northward-moving Australian plate had just begun its collision along the southern margin of Southeast Asia—a collision that is still under way today.- Thjórs River
- Thoburn, Isabella
- Thoinot Arbeau
- tholeiite
- tholos
- Thomas, 1st earl of Dorset Sackville
- Thomas, 1st Marquess of Wharton Wharton
- Thomas, 2nd Earl Of Limerick Dongan
- Thomas Addis Emmet
- Thomas Addison
- Thomas Affleck
- Thomas A Hendricks
- Thomas, Albert
- Thomas Aloysius Dorgan
- Thomas Alva Edison
- Thomas, Ambrose
- Thomas Amory
- Thomas Andrew Dorsey
- Thomas Andrew Knight
- Thomas Andrews
- Thomas Anthony Dooley
- Thomas Aquinas, Saint
- Thomas Archer
- Thomas Arne
- Thomas Arnold