Greek Revival
architectural style
architectural style, based on 5th-century-BC Greek temples, which spread throughout Europe and the United States during the first half of the 19th century.
The main reasons for the style's popularity seem to have been the general intellectual preoccupation with ancient Greek culture at the time, as well as a new awareness of the actual nature of Greek art brought about through widely circulated illustrations of notable ancient temples and the Elgin Marbles. The growing recognition of the Parthenon in Athens as a major monument helped secure the dominance of this Grecian form.
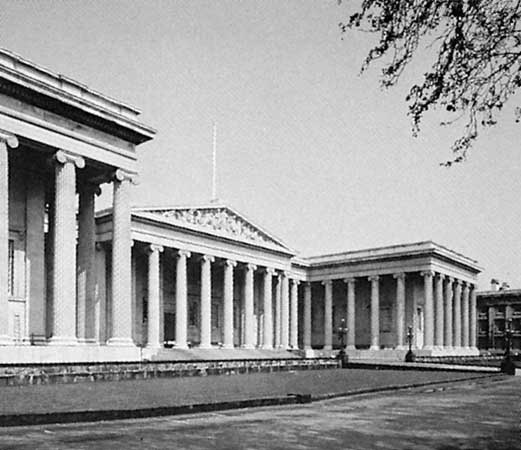

 The British Museum (completed 1847), in London, which utilizes the Greek Ionic order on a massive scale, is the most powerful image of the English version of the style. The Brandenburg Gate in Berlin (1793) was inspired by the Athenian Propylaea, and the Glyptothek sculpture museum in Munich utilized massive Grecian forms, as did the Altes Museum in Berlin by Karl Friedrich Schinkel (1822–30). That there are so many important Greek Revival buildings in Germany is largely due to Ludwig I, king of Bavaria, whose son was king of Greece.
The British Museum (completed 1847), in London, which utilizes the Greek Ionic order on a massive scale, is the most powerful image of the English version of the style. The Brandenburg Gate in Berlin (1793) was inspired by the Athenian Propylaea, and the Glyptothek sculpture museum in Munich utilized massive Grecian forms, as did the Altes Museum in Berlin by Karl Friedrich Schinkel (1822–30). That there are so many important Greek Revival buildings in Germany is largely due to Ludwig I, king of Bavaria, whose son was king of Greece.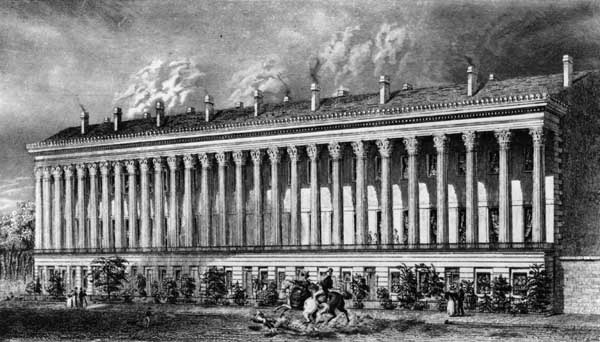 Many major examples of the Greek Revival survive in the United States, where the style was adopted on a large scale. It was also in the United States that, for both practical and ideological reasons, many strange distortions of the style found acceptance.
Many major examples of the Greek Revival survive in the United States, where the style was adopted on a large scale. It was also in the United States that, for both practical and ideological reasons, many strange distortions of the style found acceptance.The Second Bank of the United States (Philadelphia, 1824) was designed with a Doric temple exterior by William Strickland (Strickland, William) with the support of the major patron of the style, Nicholas Biddle (Biddle, Nicholas). It was a dignified example of the style that the two men knew—Biddle from observation and Strickland from reproductions—from the Parthenon. Biddle went further in his pursuit of the style in his own home, Andalusia (Pennsylvania, 1833), for which his architect, Thomas Walter (Walter, Thomas Ustick), created a majestic Doric facade to cover an existing structure. This use of Grecian columns (executed in wood) inspired many similar facades.
Other Walter commissions include the overpowering Founders Hall at Girard College (Philadelphia, 1847) and the wings for the United States Capitol (Washington, D.C., 1865).
- philosophy of mathematics
- philosophy of mind
- philosophy of nature
- philosophy of religion
- philosophy of science
- philosophy, Western
- Philostorgius
- Philostratus, Flavius
- Philostratus the Lemnian
- Philo Taylor Farnsworth
- Philotheos Bryennios
- Philotheus Kokkinos
- Philoxenus Of Mabbug
- Phil Rizzuto
- Phil Spector
- Phineas Fletcher
- Phineas Parkhurst Quimby
- phishing
- Phitsanulok
- phlebitis
- phlebothrombosis
- phloem
- phlogiston
- phlogopite
- phlox