yttrium
chemical element
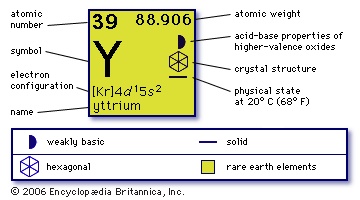 (Y), chemical element, rare-earth metal of transition Group IIIb of the periodic table, used for red phosphors (phosphor) in colour television. Yttrium metal is silvery in colour, ductile, and relatively reactive; turnings of the metal ignite readily in air.
(Y), chemical element, rare-earth metal of transition Group IIIb of the periodic table, used for red phosphors (phosphor) in colour television. Yttrium metal is silvery in colour, ductile, and relatively reactive; turnings of the metal ignite readily in air.Johan Gadolin in 1794 isolated yttria, a new earth or metallic oxide, from a mineral found at Ytterby, Sweden. Yttria, the first rare earth to be discovered, turned out to be a mixture of oxides from which, over a span of more than a century, nine elements, yttrium, scandium (atomic number 21), and the heavy lanthanoid metals from terbium (atomic number 65) to lutetium (atomic number 71), were separated. Yttrium occurs especially in the heavy rare-earth ores, of which gadolinite, euxenite, and xenotime are the most important. In the igneous rocks of the Earth's crust, this element is more plentiful than any of the other rare-earth elements except cerium and is twice as abundant as lead. Yttrium also occurs in the products of nuclear fission. Commercially yttrium is separated from the other rare earths by ion exchange, and the metal is produced by reduction of the fluoride with calcium.
Yttrium is used in alloys and in metallurgical operations. Yttrium compounds are used in optical glasses and in special ceramics, as catalysts, and in electronic and optical devices including phosphors and lasers. Red phosphors containing yttrium and europium have greatly improved colour television. One phosphor is a europium-activated yttrium orthovanadate; another is a europium-activated yttrium oxide. Garnets utilizing yttrium oxide for solid-state microwave devices are used in radar and communication systems; yttrium–iron garnets, for example, transmit shortwave energy with very little loss. Neodymium-doped yttrium–aluminum garnet lasers provide efficient tools for cutting and welding metals. Radioactive yttrium is employed in cancer therapy.
Yttrium behaves chemically as a typical rare-earth element having an oxidation state of +3. Its ionic radius is 0.90 angstrom (Å), near the radii of dysprosium and holmium (0.908 Å and 0.894 Å, respectively); separation from these elements is difficult. It forms a series of nearly white salts including the trioxide, the trisulfate, the trichloride, and the tricarbonate. The Y3+ ion is diamagnetic. Stable yttrium-89 is the only naturally occurring isotope.
atomic number
39
atomic weight
88.905
melting point
1,523° C
boiling point
3,337° C
specific gravity
4.457 (25° C)
oxidation state
+3
electronic config.
【Kr】4d15s2
- Holdheim, Samuel
- holding company
- hole
- Holger Henrik Herholdt Drachmann
- Holger Pedersen
- Holguín
- Holi
- holiday
- Holiday, Billie
- Holiness, Code of
- Holiness movement
- Holinshed, Raphael
- holistic medicine
- Holkar dynasty
- Holland
- holland
- Holland-Dozier-Holland
- Holland, Henry
- Holland, Henry Edmund
- Holland, Henry Fox, 1st Baron
- Holland, Henry Richard Vassall Fox, 3rd Baron
- Holland, John Henry
- Holland, John Philip
- Holland, Parts of
- Holland, Sir Erskine