Principal cosmogenic and uranium-thorium series radioisotopes
Table
Principal cosmogenic and uranium-thorium series radioisotopes
radioisotope half-life in years principal uses
Cosmogenic isotope
beryllium-10 1.5(106) dating marine sediment, manganese nodules, glacial ice, quartz in rock exposures, terrestrial age of meteorites, and petrogenesis of island-arc volcanics
carbon-14 5,730 + or − 40 dating of biogenic carbon, calcium carbonate, terrestrial age of meteorites
aluminum-26 0.716(106) dating marine sediment, manganese nodules, glacial ice, quartz in rock exposures, terrestrial age of meteorites
silicon-32 276 + or − 32 dating biogenic silica, glacial ice
chlorine-36 0.308(106) dating glacial ice, exposures of volcanic rocks, groundwater, terrestrial age of meteorites
argon-39 269 dating glacial ice, groundwater
manganese-53 3.7(106) terrestrial age of meteorites, abundance of extraterrestrial dust in ice and sediment
nickel-59 8(104) terrestrial age of meteorites, abundance of extraterrestrial dust in ice and sediment
krypton-81 0.213(106) dating glacial ice, cosmic-ray exposure age of meteorites
Uranium-thorium series isotope
uranium-234 2.48(105) dating coral and carbonate deposits in oceans and lakes
thorium-230 7.52(104) dating ocean sediments
lead-210 22.26 dating glacial ice and recent sediments
protactinium-231 3.248(104) dating recent sediments
Source: Adapted from Gunter Faure, Principles of Isotope Geology. Copyright 1986 by John Wiley & Sons. Reprinted by permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
See as table: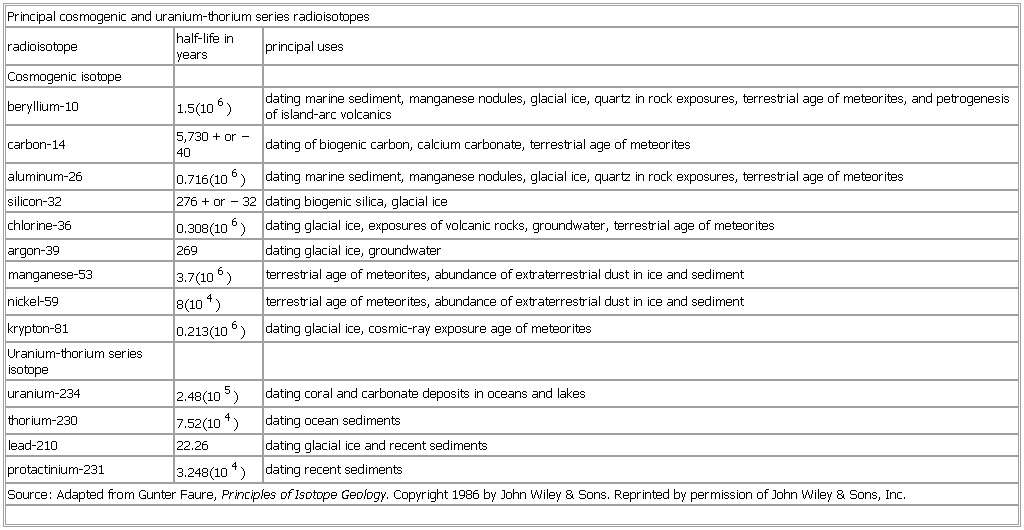

- Nicholas Of Clémanges
- Nicholas Of Cusa
- Nicholas of Damascus
- Nicholas of Flüe, Saint
- Nicholas Of Hereford
- Nicholas Of Lyra
- Nicholas Of Verdun
- Nicholas Oresme
- Nicholas Ray
- Nicholas Ridley
- Nicholas Roerich
- Nicholas Rowe
- Nicholas, Saint
- Nicholas Sanders
- Nicholas Sergeyev
- Nicholas Stone
- Nicholas Udall
- Nicholas (V)
- Nicholas V
- Nicholas Wiseman
- Nicholls, Gwyn
- Nicholls, Rhoda Holmes
- Nichols, Clarina Irene Howard
- Nichols, Herbie
- Nichols, John