American Civil War
United States history
Introduction
also called War Between the States
fratricidal four-year war (1861–65) between the federal government of the United States and 11 Southern states that asserted their right to secede from the Union.
Prelude to war
The secession of the Southern states (in chronological order, South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina) in 1860–61 and the ensuing outbreak of armed hostilities were the culmination of decades of growing sectional friction over the related issues of slavery, trade and tariffs, and the doctrine of states' rights. This friction arose out of fundamental differences between the economies of the Northern and Southern states. The North had a growing manufacturing sector and small farms using free labour, while the South's economy was based on large farms (plantations) using slave labour. In the 1840s and '50s the Northern states wanted to prohibit slavery in the western territories that would eventually become new states. The Southern states opposed all efforts to block the expansion of slavery and feared that the North's stance would eventually endanger existing slaveholdings in the South itself. By the 1850s, some Northerners had begun calling for the complete abolition of slavery, while several Southern states threatened to secede from the Union as a means to protect their right to keep slaves. When Abraham Lincoln (Lincoln, Abraham), the candidate of the antislavery Republican Party, was elected president in late 1860, the Southern states carried out their threat and seceded, organizing as the Confederate States of America.
The flash and dull roar of a 10-inch mortar on April 12, 1861, announced the opening of the American Civil War. After a 34-hour bloodless bombardment, Robert Anderson, in command of a Federal garrison of about 85 soldiers, surrendered Fort Sumter in the harbour of Charleston, South Carolina, to some 5,500 besieging Confederate troops under P.G.T. Beauregard (Beauregard, P.G.T.).
With war upon the land, Union President Abraham Lincoln called for 75,000 militiamen to serve for three months. He proclaimed a naval blockade of the Confederate States, directed the secretary of the treasury to advance $2 million to assist in the raising of troops, and suspended the writ of habeas corpus. The Confederate government had previously authorized a call for 100,000 soldiers for at least six months' service, and this figure was soon increased to 400,000.
The military background of the war
Comparison of North (North, the) and South (South, the)
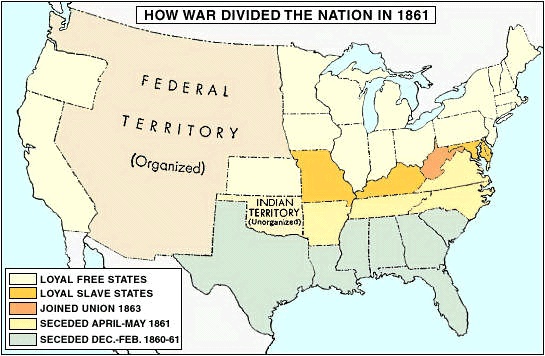 At first glance it seemed that the 23 states of the Union were more than a match for the 11 seceding Southern states. There were approximately 21 million people in the North compared with some 9 million in the South (of whom about 3.5 million were slaves). In addition, the Federals possessed over 100,000 manufacturing plants as against 18,000 south of the Potomac River, and more than 70 percent of the railroads were in the North. Furthermore, the Union had at its command a 30-to-1 superiority in arms production, a 2-to-1 edge in available manpower, and a great preponderance of commercial and financial resources. It had a functioning government and a small but efficient regular army and navy.
At first glance it seemed that the 23 states of the Union were more than a match for the 11 seceding Southern states. There were approximately 21 million people in the North compared with some 9 million in the South (of whom about 3.5 million were slaves). In addition, the Federals possessed over 100,000 manufacturing plants as against 18,000 south of the Potomac River, and more than 70 percent of the railroads were in the North. Furthermore, the Union had at its command a 30-to-1 superiority in arms production, a 2-to-1 edge in available manpower, and a great preponderance of commercial and financial resources. It had a functioning government and a small but efficient regular army and navy.The Confederacy was not predestined to defeat, however. The Southern armies had the advantage of fighting on interior lines, and their military tradition had bulked large in the history of the United States before 1860. Moreover, the long Confederate coastline of 3,500 miles (5,600 km) seemed to defy blockade; and the Confederate president, Jefferson Davis (Davis, Jefferson), hoped to receive decisive foreign aid and intervention. Confederate soldiers were fighting to achieve a separate and independent nation based on what they called “Southern institutions,” the chief of which was the institution of slavery. So the Southern cause was not a lost one; indeed, other nations had won independence against equally heavy odds.
The high commands
Command problems plagued both sides. Of the two rival commanders in chief, most people in 1861 thought Davis to be abler than Lincoln. Davis was a West Point graduate, a hero of the Mexican War, a capable secretary of war under President Franklin Pierce, and a U.S. representative and senator from Mississippi; whereas Lincoln—who had served in the Illinois state legislature and as an undistinguished one-term member of the U.S. House of Representatives—could boast of only a brief period of military service in the Black Hawk War, in which he did not perform well.
As president and commander in chief of the Confederate forces, Davis revealed many fine qualities, including patience, courage, dignity, restraint, firmness, energy, determination, and honesty; but he was flawed by his excessive pride, hypersensitivity to criticism, and inability to delegate minor details to his subordinates. To a large extent Davis was his own secretary of war, although five different men served in that post during the lifetime of the Confederacy. Davis himself also filled the position of general in chief of the Confederate armies until he named Robert E. Lee (Lee, Robert E.) to that position on February 6, 1865, when the Confederacy was near collapse. In naval affairs—an area about which he knew little—the Confederate president seldom intervened directly, allowing the competent secretary of the navy, Stephen Mallory, to handle the Southern naval buildup and operations on the water. Although his position was onerous and perhaps could not have been filled so well by any other Southern political leader, Davis's overall performance in office left something to be desired.
To the astonishment of many, Lincoln grew in stature with time and experience, and by 1864 he had become a consummate war director. But he had much to learn at first, especially in strategic and tactical matters and in his choices of army commanders. With an ineffective first secretary of war—Simon Cameron (Cameron, Simon)—Lincoln unhesitatingly insinuated himself directly into the planning of military movements. Edwin M. Stanton (Stanton, Edwin M), appointed to the secretaryship on January 20, 1862, was equally untutored in military affairs, but he was fully as active a participant as his superior.
Winfield Scott (Scott, Winfield) was the Federal general in chief when Lincoln took office. The 75-year-old Scott—a hero of the War of 1812 (1812, War of) and of the Mexican War (Mexican-American War)—was a magnificent and distinguished soldier whose mind was still keen, but he was physically incapacitated and had to be retired from the service on November 1, 1861. Scott was replaced by young George B. McClellan (McClellan, George B), an able and imaginative general in chief but one who had difficulty in establishing harmonious and effective relations with Lincoln. Because of this and because he had to campaign with his own Army of the Potomac, McClellan was relieved as general in chief on March 11, 1862. He was eventually succeeded on July 11 by the limited Henry W. Halleck (Halleck, Henry W), who held the position until replaced by Ulysses S. Grant (Grant, Ulysses S.) on March 9, 1864. Halleck then became chief of staff under Grant in a long-needed streamlining of the Federal high command. Grant served efficaciously as general in chief throughout the remainder of the war.
After the initial call by Lincoln and Davis for troops and as the war lengthened indeterminately, both sides turned to raising massive armies of volunteers. Local citizens of prominence and means would organize regiments that were uniformed and accoutred at first under the aegis of the states and then mustered into the service of the Union and Confederate governments. As the war dragged on, the two governments had to resort to conscription to fill the ranks being so swiftly thinned by battle casualties.
Strategic plans
In the area of grand strategy, Davis persistently adhered to the defensive, permitting only occasional “spoiling” forays into Northern territory. Yet perhaps the Confederates' best chance of winning would have been an early grand offensive into the Union states before the Lincoln administration could find its ablest generals and bring the preponderant resources of the North to bear against the South.
Lincoln, on the other hand, in order to crush the rebellion and reestablish the authority of the Federal government, had to direct his blue-clad armies to invade, capture, and hold most of the vital areas of the Confederacy. His grand strategy was based on Scott (Scott, Winfield)'s so-called Anaconda plan, a design that evolved from strategic ideas discussed in messages between Scott and McClellan on April 27, May 3, and May 21, 1861. It called for a Union blockade of the Confederacy's littoral as well as a decisive thrust down the Mississippi River and an ensuing strangulation of the South by Federal land and naval forces. But it was to take four years of grim, unrelenting warfare and enormous casualties and devastation before the Confederates could be defeated and the Union preserved.
The land war
The war in 1861
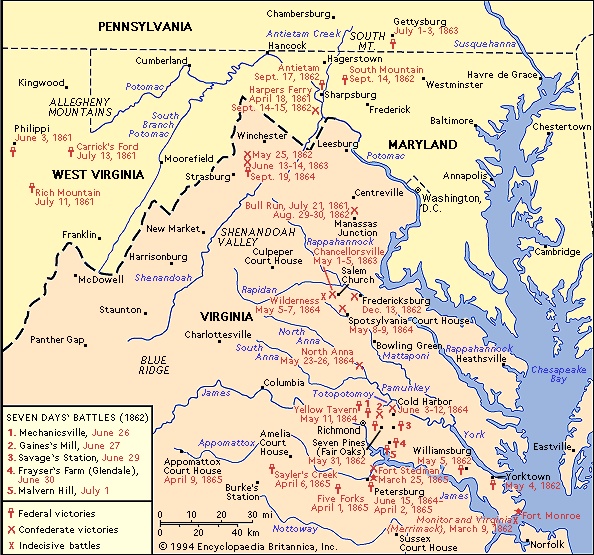 The first military operations took place in northwestern Virginia, where non-slaveholding pro-Unionists sought to secede from the Confederacy. McClellan, in command of Federal forces in southern Ohio, advanced on his own initiative in the early summer of 1861 into western Virginia with about 20,000 men. He encountered smaller forces sent there by Lee, then in Richmond in command of all Virginia troops. Although showing signs of occasional hesitation, McClellan quickly won three small but significant battles: on June 3 at Philippi, on July 11 at Rich Mountain, and on July 13 at Carrick's (or Corrick's) Ford (all now in West Virginia). McClellan's casualties were light, and his victories went far toward eliminating Confederate resistance in northwestern Virginia, which had refused to recognize secession, and toward paving the way for the admittance into the Union of the new state of West Virginia in 1863.
The first military operations took place in northwestern Virginia, where non-slaveholding pro-Unionists sought to secede from the Confederacy. McClellan, in command of Federal forces in southern Ohio, advanced on his own initiative in the early summer of 1861 into western Virginia with about 20,000 men. He encountered smaller forces sent there by Lee, then in Richmond in command of all Virginia troops. Although showing signs of occasional hesitation, McClellan quickly won three small but significant battles: on June 3 at Philippi, on July 11 at Rich Mountain, and on July 13 at Carrick's (or Corrick's) Ford (all now in West Virginia). McClellan's casualties were light, and his victories went far toward eliminating Confederate resistance in northwestern Virginia, which had refused to recognize secession, and toward paving the way for the admittance into the Union of the new state of West Virginia in 1863.Meanwhile, sizable armies were gathering around the Federal capital of Washington, D.C. (Washington), and the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia. Federal forces abandoned positions in Virginia, including, on April 18, Harpers Ferry (now West Virginia), which was quickly occupied by Southern forces, who held it for a time, and the naval base at Norfolk, which was prematurely abandoned to the enemy on April 20. On May 6 Lee ordered a Confederate force—soon to be commanded by P.G.T. Beauregard (Beauregard, P.G.T.)—northward to hold the rail hub of Manassas Junction, Virginia, some 26 miles (42 km) southwest of Washington. With Lincoln's approval, Scott appointed Irvin McDowell to command the main Federal army that was being hastily collected near Washington. But political pressure and Northern public opinion impelled Lincoln, against Scott's advice, to order McDowell's still-untrained army forward to push the enemy back from Manassas. Meanwhile, Federal forces were to hold Confederate soldiers under Joseph E. Johnston (Johnston, Joseph E) in the Shenandoah Valley near Winchester, Virginia, thus preventing them from reinforcing Beauregard along the Bull Run near Manassas.
 McDowell advanced from Washington on July 16 with some 32,000 men and moved slowly toward Bull Run. Two days later a reconnaissance in force was repulsed by the Confederates at Mitchell's and Blackburn's Fords, and when McDowell attacked on July 21 in the First Battle of Bull Run (Bull Run, battles of) (in the South, First Manassas; see photograph-->
McDowell advanced from Washington on July 16 with some 32,000 men and moved slowly toward Bull Run. Two days later a reconnaissance in force was repulsed by the Confederates at Mitchell's and Blackburn's Fords, and when McDowell attacked on July 21 in the First Battle of Bull Run (Bull Run, battles of) (in the South, First Manassas; see photograph--> ), he discovered that Johnston had escaped the Federals in the valley and had joined Beauregard near Manassas just in time, bringing the total Confederate force to around 28,000. McDowell's sharp attacks with green troops forced the equally untrained Southerners back a bit, but a strong defensive stand by Thomas Jonathan Jackson (Jackson, Thomas Jonathan) (who thereby gained the nickname “Stonewall”) enabled the Confederates to check and finally throw back the Federals in the afternoon. The Federal retreat to Washington soon became a rout. McDowell lost 2,708 men—killed, wounded, and missing (including prisoners)—against a Southern loss of 1,981. Both sides now settled down to a long war.
), he discovered that Johnston had escaped the Federals in the valley and had joined Beauregard near Manassas just in time, bringing the total Confederate force to around 28,000. McDowell's sharp attacks with green troops forced the equally untrained Southerners back a bit, but a strong defensive stand by Thomas Jonathan Jackson (Jackson, Thomas Jonathan) (who thereby gained the nickname “Stonewall”) enabled the Confederates to check and finally throw back the Federals in the afternoon. The Federal retreat to Washington soon became a rout. McDowell lost 2,708 men—killed, wounded, and missing (including prisoners)—against a Southern loss of 1,981. Both sides now settled down to a long war.The war in the east in 1862
Fresh from his victories in western Virginia, McClellan was called to Washington to replace Scott. There he began to mold the Army of the Potomac into a resolute, effective shield and sword of the Union. But personality clashes and unrelenting opposition to McClellan from the Radical Republicans in Congress hampered the sometimes tactless, conservative, Democratic general. It took time to drill, discipline, and equip this force of considerably more than 100,000 men, but as fall blended into winter, loud demands arose that McClellan advance against Johnston's Confederate forces at Centreville and Manassas in Virginia. McClellan fell seriously ill with typhoid fever in December, and when he had recovered weeks later he found that Lincoln, desperately eager for action, had ordered him to advance on February 22, 1862. Long debates ensued between president and commander. When in March McClellan finally began his Peninsular Campaign, he discovered that Lincoln and Stanton had withheld large numbers of his command in front of Washington for the defense of the capital—forces that were actually not needed there. Upon taking command of the army in the field, McClellan was relieved of his duties as general in chief.
The Peninsular Campaign (Peninsular Campaign)

 Advancing up the historic peninsula between the York and James rivers in Virginia, McClellan began a month-long siege of Yorktown and captured that stronghold on May 4, 1862. A Confederate rearguard action at Williamsburg the next day delayed the blue-clads, who then slowly moved up through heavy rain to within 4 miles (6 km) of Richmond. Striving to seize the initiative, Johnston attacked McClellan's left wing at Seven Pines (Seven Pines, Battle of) (Fair Oaks) on May 31 and, after scoring initial gains, was checked; Johnston was severely wounded, and Lee, who had been serving as Davis's military adviser, succeeded Johnston in command of the Army of Northern Virginia. McClellan counterattacked on June 1 and forced the Southerners back into the environs of Richmond. The Federals suffered a total of 5,031 casualties out of a force of nearly 100,000, while the Confederates lost 6,134 of about 74,000 men.
Advancing up the historic peninsula between the York and James rivers in Virginia, McClellan began a month-long siege of Yorktown and captured that stronghold on May 4, 1862. A Confederate rearguard action at Williamsburg the next day delayed the blue-clads, who then slowly moved up through heavy rain to within 4 miles (6 km) of Richmond. Striving to seize the initiative, Johnston attacked McClellan's left wing at Seven Pines (Seven Pines, Battle of) (Fair Oaks) on May 31 and, after scoring initial gains, was checked; Johnston was severely wounded, and Lee, who had been serving as Davis's military adviser, succeeded Johnston in command of the Army of Northern Virginia. McClellan counterattacked on June 1 and forced the Southerners back into the environs of Richmond. The Federals suffered a total of 5,031 casualties out of a force of nearly 100,000, while the Confederates lost 6,134 of about 74,000 men.
 As McClellan inched forward toward Richmond in June, Lee (Lee, Robert E.) prepared a counterstroke. He recalled from the Shenandoah Valley Jackson's forces—which had threatened Harpers Ferry and had brilliantly defeated several scattered Federal armies—and, with about 90,000 soldiers, attacked McClellan on June 26 to begin the fighting of the Seven Days' Battles (usually dated June 25–July 1). In the ensuing days at Mechanicsville, Gaines's Mill (Gaines's Mill, Battle of), Savage's Station, Frayser's Farm (Glendale), and Malvern Hill, Lee tried unsuccessfully to crush the Army of the Potomac, which McClellan was moving to another base on the James River; but the Confederate commander had at least saved Richmond. McClellan inflicted 20,614 casualties on Lee while suffering 15,849 himself. McClellan felt he could not move upon Richmond without considerable reinforcement, and against his protests his army was withdrawn from the peninsula to Washington by Lincoln and the new general in chief, Halleck. Many of McClellan's units were given to a new Federal army commander, John Pope (Pope, John), who was directed to move overland against Richmond.
As McClellan inched forward toward Richmond in June, Lee (Lee, Robert E.) prepared a counterstroke. He recalled from the Shenandoah Valley Jackson's forces—which had threatened Harpers Ferry and had brilliantly defeated several scattered Federal armies—and, with about 90,000 soldiers, attacked McClellan on June 26 to begin the fighting of the Seven Days' Battles (usually dated June 25–July 1). In the ensuing days at Mechanicsville, Gaines's Mill (Gaines's Mill, Battle of), Savage's Station, Frayser's Farm (Glendale), and Malvern Hill, Lee tried unsuccessfully to crush the Army of the Potomac, which McClellan was moving to another base on the James River; but the Confederate commander had at least saved Richmond. McClellan inflicted 20,614 casualties on Lee while suffering 15,849 himself. McClellan felt he could not move upon Richmond without considerable reinforcement, and against his protests his army was withdrawn from the peninsula to Washington by Lincoln and the new general in chief, Halleck. Many of McClellan's units were given to a new Federal army commander, John Pope (Pope, John), who was directed to move overland against Richmond.Second Battle of Bull Run (Bull Run, battles of) (Manassas) and Antietam
 Pope (Pope, John) advanced confidently toward the Rappahannock River with his Army of Virginia, while Lee, once McClellan had been pulled back from near Richmond, moved northward to confront Pope before he could be joined by all of McClellan's troops. Daringly splitting his army, Lee sent Jackson to destroy Pope's base at Manassas, while he himself advanced via another route with James Longstreet (Longstreet, James)'s half of the army. Pope opened the Second Battle of Bull Run (Bull Run, battles of) (in the South, Second Manassas) on August 29 with heavy but futile attacks on Jackson. The next day Lee arrived and crushed the Federal left with a massive flank assault by Longstreet, which, combined with Jackson's counterattacks, drove the Northerners back in rout upon Washington. Pope lost 16,054 men out of a force of about 70,000, while Lee lost 9,197 out of about 55,000. With the Federal soldiers now lacking confidence in Pope, Lincoln relieved him and merged his forces into McClellan's Army of the Potomac.
Pope (Pope, John) advanced confidently toward the Rappahannock River with his Army of Virginia, while Lee, once McClellan had been pulled back from near Richmond, moved northward to confront Pope before he could be joined by all of McClellan's troops. Daringly splitting his army, Lee sent Jackson to destroy Pope's base at Manassas, while he himself advanced via another route with James Longstreet (Longstreet, James)'s half of the army. Pope opened the Second Battle of Bull Run (Bull Run, battles of) (in the South, Second Manassas) on August 29 with heavy but futile attacks on Jackson. The next day Lee arrived and crushed the Federal left with a massive flank assault by Longstreet, which, combined with Jackson's counterattacks, drove the Northerners back in rout upon Washington. Pope lost 16,054 men out of a force of about 70,000, while Lee lost 9,197 out of about 55,000. With the Federal soldiers now lacking confidence in Pope, Lincoln relieved him and merged his forces into McClellan's Army of the Potomac. Lee followed up his advantage with his first invasion of the North, pushing as far as Frederick, Maryland. McClellan had to reorganize his army on the march, a task that he performed capably. But he was beset by contradictory orders: Lincoln urged him to pursue Lee more swiftly; Halleck directed him to slow down and to stay closer to Washington. Biding his time, McClellan pressed forward and wrested the initiative from Lee by attacking and defeating a Confederate force at three gaps of the South Mountain between Frederick and Hagerstown on September 14. Lee fell back into a cramped defensive position along the Antietam (Antietam, Battle of) Creek, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, where he was reinforced by Jackson, who had just captured about 11,500 Federals at Harpers Ferry. After a delay, McClellan struck the Confederates on September 17 in the bloodiest single-day's battle of the war. Although gaining some ground, the Federals were unable to drive the Confederate army into the Potomac, but Lee was compelled to retreat back into Virginia. At Antietam, McClellan lost 12,410 of some 69,000 engaged, while Lee lost 13,724 of perhaps 52,000. When McClellan did not pursue Lee as quickly as Lincoln and Halleck thought he should, he was replaced in command by Ambrose E. Burnside (Burnside, Ambrose Everett), who had been an ineffective corps commander at Antietam.
Lee followed up his advantage with his first invasion of the North, pushing as far as Frederick, Maryland. McClellan had to reorganize his army on the march, a task that he performed capably. But he was beset by contradictory orders: Lincoln urged him to pursue Lee more swiftly; Halleck directed him to slow down and to stay closer to Washington. Biding his time, McClellan pressed forward and wrested the initiative from Lee by attacking and defeating a Confederate force at three gaps of the South Mountain between Frederick and Hagerstown on September 14. Lee fell back into a cramped defensive position along the Antietam (Antietam, Battle of) Creek, near Sharpsburg, Maryland, where he was reinforced by Jackson, who had just captured about 11,500 Federals at Harpers Ferry. After a delay, McClellan struck the Confederates on September 17 in the bloodiest single-day's battle of the war. Although gaining some ground, the Federals were unable to drive the Confederate army into the Potomac, but Lee was compelled to retreat back into Virginia. At Antietam, McClellan lost 12,410 of some 69,000 engaged, while Lee lost 13,724 of perhaps 52,000. When McClellan did not pursue Lee as quickly as Lincoln and Halleck thought he should, he was replaced in command by Ambrose E. Burnside (Burnside, Ambrose Everett), who had been an ineffective corps commander at Antietam.Fredericksburg (Fredericksburg, Battle of)
 Burnside delayed for a number of weeks before marching his reinforced army of 120,281 men to a point across the Rappahannock River from Fredericksburg, Virginia. On December 13 he ordered a series of 16 hopeless, piecemeal frontal assaults across open ground against Lee's army of 78,513 troops, drawn up in an impregnable position atop high ground and behind a stone wall. The Federals were repelled with staggering losses; Burnside had lost 12,653 men, compared to Lee's 5,309. The plunging Federal morale was reflected in an increasing number of desertions. Therefore, on January 25, 1863, Lincoln replaced Burnside with a proficient corps commander, Joseph (“Fighting Joe”) Hooker (Hooker, Joseph), who was a harsh critic of other generals and even of the president. Both armies went into winter quarters near Fredericksburg.
Burnside delayed for a number of weeks before marching his reinforced army of 120,281 men to a point across the Rappahannock River from Fredericksburg, Virginia. On December 13 he ordered a series of 16 hopeless, piecemeal frontal assaults across open ground against Lee's army of 78,513 troops, drawn up in an impregnable position atop high ground and behind a stone wall. The Federals were repelled with staggering losses; Burnside had lost 12,653 men, compared to Lee's 5,309. The plunging Federal morale was reflected in an increasing number of desertions. Therefore, on January 25, 1863, Lincoln replaced Burnside with a proficient corps commander, Joseph (“Fighting Joe”) Hooker (Hooker, Joseph), who was a harsh critic of other generals and even of the president. Both armies went into winter quarters near Fredericksburg.The war in the west in 1862
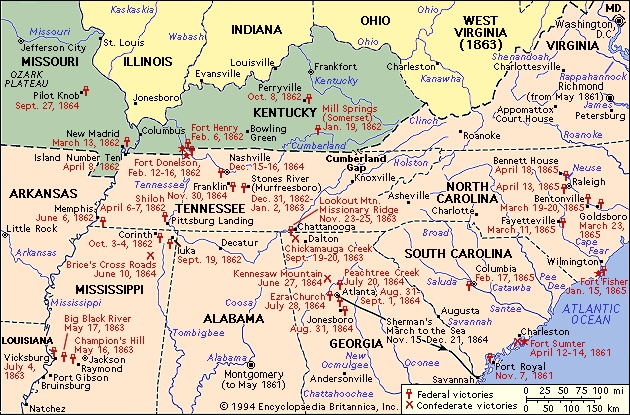 Military events, meanwhile, were transpiring in other arenas.
Military events, meanwhile, were transpiring in other arenas.Trans- Mississippi theatre and Missouri
In the Trans-Mississippi theatre covetous Confederate eyes were cast on California, where ports for privateers could be seized, as could gold and silver to buttress a sagging treasury. Led by Henry Sibley, a Confederate force of some 2,600 invaded the Union's Department of New Mexico, where the Federal commander, Edward Canby, had but 3,810 men to defend the entire vast territory. Although plagued by pneumonia and smallpox, Sibley bettered a Federal force on February 21, 1862, at Valverde, and captured Albuquerque and Santa Fe on March 23. But at the crucial engagement of La Glorieta Pass (known also as Apache Canyon, Johnson's Ranch, or Pigeon's Ranch) a few days later, Sibley was checked and lost most of his wagon train. He had to retreat into Texas, where he reached safety in April but with only 900 men and seven of 337 supply wagons left.
Farther eastward, in the more vital Mississippi valley, operations were unfolding as large and as important as those on the Atlantic seaboard. Missouri and Kentucky were key border states that Lincoln had to retain within the Union orbit. Commanders there—especially on the Federal side—had greater autonomy than those in Virginia. Affairs began inauspiciously for the Federals in Missouri when Union General Nathaniel Lyon's 5,000 troops were defeated at Wilson's Creek on August 10, 1861, by a Confederate force of more than 10,000 under Sterling Price (Price, Sterling) and Benjamin McCulloch, each side losing some 1,200 men. But the Federals under Samuel Curtis decisively set back a gray-clad army under Earl Van Dorn at Pea Ridge (Elkhorn Tavern), Arkansas, on March 7–8, 1862, saving Missouri for the Union and threatening Arkansas.
Operations in Kentucky and Tennessee
The Confederates to the east of Missouri had established a unified command under Albert Sidney Johnston (Johnston, Albert Sidney), who manned, with only 40,000 men, a long line in Kentucky running from near Cumberland Gap on the east through Bowling Green to Columbus on the Mississippi River. Numerically superior Federal forces cracked this line in early 1862. First, George H. Thomas (Thomas, George H) smashed Johnston's right flank at Mill Springs (Somerset), Kentucky, on January 19. Then, in February, Grant, assisted by Federal gunboats commanded by Andrew H. Foote (Foote, Andrew) and acting under Halleck's orders, ruptured the centre of the Southern line in Kentucky by capturing Fort Henry (Fort Henry, Battle of) on the Tennessee River and Fort Donelson (Fort Donelson, Battle of), 11 miles (18 km) to the east on the Cumberland River (both forts located in Tennessee). The Confederates suffered more than 16,000 casualties at the latter stronghold—most of them taken prisoner—as against Federal losses of less than 3,000. Johnston's left anchor fell when Pope seized New Madrid, Missouri, and Island Number Ten in the Mississippi River in March and April. This forced Johnston to withdraw his remnants quickly from Kentucky through Tennessee and to reorganize them for a counterstroke. This seemingly impossible task he performed splendidly.
 The Confederate onslaught came at Shiloh (Shiloh, Battle of), Tennessee, near Pittsburg Landing, a point on the west bank of the Tennessee River to which Grant and William T. Sherman (Sherman, William Tecumseh) had incautiously advanced. In a herculean effort, Johnston had pulled his forces together and, with 40,000 men, suddenly struck a like number of unsuspecting Federals on April 6. Johnston hoped to crush Grant before the arrival of Don Carlos Buell (Buell, Don Carlos)'s 20,000 Federal troops, approaching from Nashville, Tennessee. A desperate combat ensued, with Confederate assaults driving the Unionists perilously close to the river. But at the height of success, Johnston was mortally wounded; the Southern attack then lost momentum, and Grant held on until reinforced by Buell. On the following day the Federals counterattacked and drove the Confederates, now under Beauregard, steadily from the field, forcing them to fall back to Corinth, in northern Mississippi. Grant's victory cost him 13,047 casualties, compared to Southern losses of 10,694. Halleck then assumed personal command of the combined forces of Grant, Buell, and Pope and inched forward to Corinth (Corinth, Battle of) (see photograph-->
The Confederate onslaught came at Shiloh (Shiloh, Battle of), Tennessee, near Pittsburg Landing, a point on the west bank of the Tennessee River to which Grant and William T. Sherman (Sherman, William Tecumseh) had incautiously advanced. In a herculean effort, Johnston had pulled his forces together and, with 40,000 men, suddenly struck a like number of unsuspecting Federals on April 6. Johnston hoped to crush Grant before the arrival of Don Carlos Buell (Buell, Don Carlos)'s 20,000 Federal troops, approaching from Nashville, Tennessee. A desperate combat ensued, with Confederate assaults driving the Unionists perilously close to the river. But at the height of success, Johnston was mortally wounded; the Southern attack then lost momentum, and Grant held on until reinforced by Buell. On the following day the Federals counterattacked and drove the Confederates, now under Beauregard, steadily from the field, forcing them to fall back to Corinth, in northern Mississippi. Grant's victory cost him 13,047 casualties, compared to Southern losses of 10,694. Halleck then assumed personal command of the combined forces of Grant, Buell, and Pope and inched forward to Corinth (Corinth, Battle of) (see photograph--> ), which the Confederates evacuated on May 30.
), which the Confederates evacuated on May 30.Beauregard, never popular with Davis, was superseded by Braxton Bragg (Bragg, Braxton), one of the president's favourites. Bragg was an imaginative strategist and an effective drillmaster and organizer; but he was also a weak tactician and a martinet who was disliked by a number of his principal subordinates. Leaving 22,000 men in Mississippi under Price and Van Dorn, Bragg moved through Chattanooga, Tennessee, with 30,000, hoping to reconquer the state and carry the war into Kentucky. Some 18,000 other Confederate soldiers under Edmund Kirby-Smith (Kirby-Smith, E.) were at Knoxville, Tennessee. Buell led his Federal force northward to save Louisville, Kentucky, and to force Bragg to fight. Occupying Frankfort, Kentucky, Bragg failed to move promptly against Louisville. In the ensuing Battle of Perryville (Perryville, Battle of) on October 8, Bragg, after an early advantage, was halted by Buell and impelled to fall back to a point south of Nashville. Meanwhile, Federal General William S. Rosecrans (Rosecrans, William S) had checked Price and Van Dorn at Iuka, Mississippi, on September 19 and had repelled their attack on Corinth on October 3–4.
Buell—like McClellan a cautious, conservative, Democratic general—was slow in his pursuit of the retreating Confederates and, despite his success at Perryville, was relieved of his command by Lincoln on October 24. His successor, Rosecrans, was able to safeguard Nashville and then to move southeastward against Bragg's army at Murfreesboro, Tennessee. He scored a partial success by bringing on the bloody Battle of Stones River (Stones River, Battle of) (or Murfreesboro, December 31, 1862–January 2, 1863). Again, after first having the better of the combat, Bragg was finally contained and forced to retreat. Of some 41,400 men, Rosecrans lost 12,906, while Bragg suffered 11,739 casualties out of about 34,700 effectives. Although it was a strategic victory for Rosecrans, his army was so shaken that he felt unable to advance again for five months, despite the urgings of Lincoln and Halleck.
The war in the east in 1863
 In the east, after both armies had spent the winter in camp, the arrival of the active 1863 campaign season was eagerly awaited—especially by Hooker (Hooker, Joseph). “Fighting Joe” had capably reorganized and refitted his army, the morale of which was high once again. This massive host numbered around 132,000—the largest formed during the war—and was termed by Hooker “the finest army on the planet.” It was opposed by Lee with about 62,000. Hooker decided to move most of his army up the Rappahannock, cross, and come in upon the Confederate rear at Fredericksburg, while John Sedgwick's smaller force would press Lee in front.
In the east, after both armies had spent the winter in camp, the arrival of the active 1863 campaign season was eagerly awaited—especially by Hooker (Hooker, Joseph). “Fighting Joe” had capably reorganized and refitted his army, the morale of which was high once again. This massive host numbered around 132,000—the largest formed during the war—and was termed by Hooker “the finest army on the planet.” It was opposed by Lee with about 62,000. Hooker decided to move most of his army up the Rappahannock, cross, and come in upon the Confederate rear at Fredericksburg, while John Sedgwick's smaller force would press Lee in front.Chancellorsville (Chancellorsville, Battle of)
Beginning his turning movement on April 27, 1863, Hooker masterfully swung around toward the west of the Confederate army. Thus far he had outmaneuvered Lee; but Hooker was astonished on May 1 when the Confederate commander suddenly moved the bulk of his army directly against him. “Fighting Joe” lost his nerve and pulled back to Chancellorsville (Chancellorsville, Battle of), Virginia, in the Wilderness, where the superior Federal artillery could not be used effectively.
 Lee followed up on May 2 by sending Jackson on a brilliant flanking movement against Hooker's exposed right flank. Bursting like a thunderbolt upon Oliver O. Howard (Howard, Oliver O.)'s 11th Corps late in the afternoon, Jackson crushed this wing; while continuing his advance, however, Jackson was accidentally wounded by his own men and died of complications shortly thereafter. This helped stall the Confederate advance. Lee then resumed the attack on the morning of May 3 and slowly pushed Hooker back; the latter was wounded by Southern artillery fire. That afternoon Sedgwick drove Jubal Early (Early, Jubal A)'s Southerners from Marye's Heights at Fredericksburg, but Lee countermarched his weary troops, fell upon Sedgwick at Salem Church, and forced him back to the north bank of the Rappahannock. Lee then returned to Chancellorsville to resume the main engagement; but Hooker, though he had 37,000 fresh troops available, gave up the contest on May 5 and retreated across the river to his old position opposite Fredericksburg. The Federals suffered 17,278 casualties at Chancellorsville, while the Confederates lost 12,764.
Lee followed up on May 2 by sending Jackson on a brilliant flanking movement against Hooker's exposed right flank. Bursting like a thunderbolt upon Oliver O. Howard (Howard, Oliver O.)'s 11th Corps late in the afternoon, Jackson crushed this wing; while continuing his advance, however, Jackson was accidentally wounded by his own men and died of complications shortly thereafter. This helped stall the Confederate advance. Lee then resumed the attack on the morning of May 3 and slowly pushed Hooker back; the latter was wounded by Southern artillery fire. That afternoon Sedgwick drove Jubal Early (Early, Jubal A)'s Southerners from Marye's Heights at Fredericksburg, but Lee countermarched his weary troops, fell upon Sedgwick at Salem Church, and forced him back to the north bank of the Rappahannock. Lee then returned to Chancellorsville to resume the main engagement; but Hooker, though he had 37,000 fresh troops available, gave up the contest on May 5 and retreated across the river to his old position opposite Fredericksburg. The Federals suffered 17,278 casualties at Chancellorsville, while the Confederates lost 12,764.Gettysburg (Gettysburg, Battle of)
While both armies were licking their wounds and reorganizing, Hooker, Lincoln, and Halleck debated Union strategy. They were thus engaged when Lee launched his second invasion of the North on June 5, 1863. His advance elements moved down the Shenandoah Valley toward Harpers Ferry, brushing aside small Federal forces near Winchester. Marching through Maryland into Pennsylvania, the Confederates reached Chambersburg and turned eastward. They occupied York and Carlisle and menaced Harrisburg. Meanwhile, the dashing Confederate cavalryman J.E.B. (“Jeb”) Stuart (Stuart, Jeb) set off on a questionable ride around the Federal army and was unable to join Lee's main army until the second day at Gettysburg.
Hooker—on unfriendly terms with Lincoln and especially Halleck—ably moved the Federal forces northward, keeping between Lee's army and Washington. Reaching Frederick, Hooker requested that the nearly 10,000-man Federal garrison at Harpers Ferry be added to his field army. When Halleck refused, Hooker resigned his command and was succeeded by the steady George Gordon Meade (Meade, George G), the commander of the 5th Corps. Meade was granted a greater degree of freedom of movement than Hooker had enjoyed, and he carefully felt his way northward, looking for the enemy.
Learning to his surprise on June 28 that the Federal army was north of the Potomac, Lee hastened to concentrate his far-flung legions. Hostile forces came together unexpectedly at the important crossroads town of Gettysburg, in southern Pennsylvania, bringing on the greatest battle ever fought in the Western Hemisphere. Attacking on July 1 from the west and north with 28,000 men, Confederate forces finally prevailed after nine hours of desperate fighting against 18,000 Federal soldiers under John F. Reynolds. When Reynolds was killed, Abner Doubleday (Doubleday, Abner) ably handled the outnumbered Federal troops, and only the sheer weight of Confederate numbers forced him back through the streets of Gettysburg to strategic Cemetery Ridge south of town, where Meade assembled the rest of the army that night.
 On the second day of battle, Meade's 93,000 troops were ensconced in a strong, fishhook-shaped defensive position running northward from the Round Top hills along Cemetery Ridge and thence eastward to Culp's Hill. Lee, with 75,000 troops, ordered Longstreet to attack the Federals diagonally from Little Round Top northward and Richard S. Ewell to assail Cemetery Hill and Culp's Hill. The Confederate attack, coming in the late afternoon and evening, saw Longstreet capture the positions known as the Peach Orchard, Wheat Field, and Devil's Den on the Federal left in furious fighting but fail to seize the vital Little Round Top. Ewell's later assaults on Cemetery Hill were repulsed, and he could capture only a part of Culp's Hill.
On the second day of battle, Meade's 93,000 troops were ensconced in a strong, fishhook-shaped defensive position running northward from the Round Top hills along Cemetery Ridge and thence eastward to Culp's Hill. Lee, with 75,000 troops, ordered Longstreet to attack the Federals diagonally from Little Round Top northward and Richard S. Ewell to assail Cemetery Hill and Culp's Hill. The Confederate attack, coming in the late afternoon and evening, saw Longstreet capture the positions known as the Peach Orchard, Wheat Field, and Devil's Den on the Federal left in furious fighting but fail to seize the vital Little Round Top. Ewell's later assaults on Cemetery Hill were repulsed, and he could capture only a part of Culp's Hill.On the morning of the third day, Meade's right wing drove the Confederates from the lower slopes of Culp's Hill and checked Stuart's cavalry sweep to the east of Gettysburg in midafternoon. Then, in what has been called the greatest infantry charge in American history, Lee—against Longstreet's advice—hurled nearly 15,000 soldiers, under the immediate command of George E. Pickett (Pickett, George Edward), against the centre of Meade's lines on Cemetery Ridge, following a fearful artillery duel of two hours. Despite heroic efforts, only several hundred Southerners temporarily cracked the Federal centre at the so-called High-Water Mark; the rest were shot down by Federal cannoneers and musketrymen, captured, or thrown back, suffering casualties of almost 60 percent. Meade felt unable to counterattack, and Lee conducted an adroit retreat into Virginia. The Confederates had lost 28,063 men at Gettysburg, and the Federals, 23,049. After indecisive maneuvering and light actions in northern Virginia in the fall of 1863, the two armies went into winter quarters. Never again was Lee able to mount a full-scale invasion of the North with his entire army.
The war in the west in 1863
Arkansas and Vicksburg (Vicksburg Campaign)
 In Arkansas, Federal troops under Frederick Steele moved upon the Confederates and defeated them at Prairie Grove, near Fayetteville, on December 7, 1862—a victory that paved the way for Steele's eventual capture of Little Rock the next September.
In Arkansas, Federal troops under Frederick Steele moved upon the Confederates and defeated them at Prairie Grove, near Fayetteville, on December 7, 1862—a victory that paved the way for Steele's eventual capture of Little Rock the next September.More importantly, Grant, back in good graces following his undistinguished performance at Shiloh, was authorized to move against the Confederate “Gibraltar of the West”—Vicksburg (Vicksburg Campaign), Mississippi. This bastion was difficult to approach: Admiral David G. Farragut (Farragut, David), Grant, and Sherman had failed to capture it in 1862. In the early months of 1863, in the so-called Bayou Expeditions, Grant was again frustrated in his efforts to get at Vicksburg from the north. Finally, escorted by Admiral David Dixon Porter (Porter, David Dixon)'s gunboats, which ran the Confederate batteries at Vicksburg, Grant landed his army to the south at Bruinsburg, Mississippi, on April 30, 1863, and pressed northeastward. He won small but sharp actions at Port Gibson, Raymond, and Jackson, while the circumspect Confederate defender of Vicksburg, John C. Pemberton (Pemberton, John Clifford), was unable to link up with a smaller Southern force under Joseph E. Johnston near Jackson.
 Turning due westward toward the rear of Vicksburg's defenses, Grant smashed Pemberton's army at Champion's Hill and the Big Black River (Big Black River, Battle of) and invested the fortress. During his 47-day siege, Grant eventually had an army of 71,000; Pemberton's command numbered 31,000, of whom 18,500 were effectives. After a courageous stand, the outnumbered Confederates were forced to capitulate on July 4. Five days later, 6,000 Confederates yielded to Nathaniel P. Banks at Port Hudson, Louisiana, to the south of Vicksburg, and Lincoln could say, in relief, “The Father of Waters again goes unvexed to the sea.”
Turning due westward toward the rear of Vicksburg's defenses, Grant smashed Pemberton's army at Champion's Hill and the Big Black River (Big Black River, Battle of) and invested the fortress. During his 47-day siege, Grant eventually had an army of 71,000; Pemberton's command numbered 31,000, of whom 18,500 were effectives. After a courageous stand, the outnumbered Confederates were forced to capitulate on July 4. Five days later, 6,000 Confederates yielded to Nathaniel P. Banks at Port Hudson, Louisiana, to the south of Vicksburg, and Lincoln could say, in relief, “The Father of Waters again goes unvexed to the sea.”Chickamauga and Chattanooga (Chattanooga, Battle of)

 Meanwhile, 60,000 Federal soldiers under Rosecrans sought to move southeastward from central Tennessee against the important Confederate rail and industrial centre of Chattanooga, then held by Bragg with some 43,000 troops. In a series of brilliantly conceived movements, Rosecrans maneuvered Bragg out of Chattanooga without having to fight a battle. Bragg was then bolstered by troops from Longstreet's veteran corps, sent swiftly by rail from Lee's army in Virginia. With this reinforcement, Bragg turned on Rosecrans and, in a vicious two-day battle (September 19–20) at Chickamauga Creek (Chickamauga Creek, Battle of), Georgia (see photograph-->
Meanwhile, 60,000 Federal soldiers under Rosecrans sought to move southeastward from central Tennessee against the important Confederate rail and industrial centre of Chattanooga, then held by Bragg with some 43,000 troops. In a series of brilliantly conceived movements, Rosecrans maneuvered Bragg out of Chattanooga without having to fight a battle. Bragg was then bolstered by troops from Longstreet's veteran corps, sent swiftly by rail from Lee's army in Virginia. With this reinforcement, Bragg turned on Rosecrans and, in a vicious two-day battle (September 19–20) at Chickamauga Creek (Chickamauga Creek, Battle of), Georgia (see photograph--> ), just southeast of Chattanooga, gained one of the few Confederate victories in the west. Bragg lost 18,454 of his 66,326 men; Rosecrans, 16,170 out of 53,919 engaged. Rosecrans fell back into Chattanooga, where he was almost encircled by Bragg.
), just southeast of Chattanooga, gained one of the few Confederate victories in the west. Bragg lost 18,454 of his 66,326 men; Rosecrans, 16,170 out of 53,919 engaged. Rosecrans fell back into Chattanooga, where he was almost encircled by Bragg.
 But the Southern success was short-lived. Instead of pressing the siege of Chattanooga, Bragg unwisely sent Longstreet off in a futile attempt to capture Knoxville, then being held by Burnside. When Rosecrans showed signs of disintegration, Lincoln replaced him with Grant and strengthened the hard-pressed Federal army at Chattanooga (Chattanooga, Battle of) by sending, by rail, the remnants of the Army of the Potomac's 11th and 12th Corps, under Hooker's command. Outnumbering Bragg now 56,359 to 46,165, Grant attacked on November 23–25, capturing Lookout Mountain (see photograph-->
But the Southern success was short-lived. Instead of pressing the siege of Chattanooga, Bragg unwisely sent Longstreet off in a futile attempt to capture Knoxville, then being held by Burnside. When Rosecrans showed signs of disintegration, Lincoln replaced him with Grant and strengthened the hard-pressed Federal army at Chattanooga (Chattanooga, Battle of) by sending, by rail, the remnants of the Army of the Potomac's 11th and 12th Corps, under Hooker's command. Outnumbering Bragg now 56,359 to 46,165, Grant attacked on November 23–25, capturing Lookout Mountain (see photograph--> ) and Missionary Ridge, defeating Bragg's army, and driving it southward toward Dalton, Georgia. Grant sustained 5,824 casualties at Chattanooga and Bragg, 6,667. Confidence having been lost in Bragg by most of his top generals, Davis replaced him with Joseph E. Johnston (Johnston, Joseph E). Both armies remained quiescent until the following spring.
) and Missionary Ridge, defeating Bragg's army, and driving it southward toward Dalton, Georgia. Grant sustained 5,824 casualties at Chattanooga and Bragg, 6,667. Confidence having been lost in Bragg by most of his top generals, Davis replaced him with Joseph E. Johnston (Johnston, Joseph E). Both armies remained quiescent until the following spring.The war in 1864–65
Finally dissatisfied with Halleck as general in chief and impressed with Grant's victories, Lincoln appointed Grant to supersede Halleck and to assume the rank of lieutenant general, which Congress had re-created. Leaving Sherman in command in the west, Grant arrived in Washington on March 8, 1864. He was given largely a free hand in developing his grand strategy. He retained Meade in technical command of the Army of the Potomac but in effect assumed direct control by establishing his own headquarters with it. He sought to move this army against Lee in northern Virginia while Sherman marched against Johnston and Atlanta. Several lesser Federal armies were also to advance in May.
Grant's overland campaign
Grant surged across the Rapidan and Rappahannock rivers in Virginia on May 4, hoping to get through the tangled Wilderness before Lee could move. But the Confederate leader reacted instantly and, on May 5, attacked Grant from the west in the Battle of the Wilderness (Wilderness, Battle of the). Two days of bitter, indecisive combat ensued. Although Grant had 115,000 men available against Lee's 62,000, he found both Federal flanks endangered. Moreover, Grant lost 17,666 soldiers compared to a probable Southern loss of about 8,000. Pulling away from the Wilderness battlefield, Grant tried to hasten southeastward to the crossroads point of Spotsylvania Court House (Spotsylvania Court House, Battle of), only to have the Confederates get there first. In savage action (May 8–19), including hand-to-hand fighting at the famous “Bloody Angle,” Grant, although gaining a little ground, was essentially thrown back. He had lost 18,399 men at Spotsylvania. Lee's combined losses at the Wilderness and Spotsylvania were an estimated 17,250.
 Again Grant withdrew, only to move forward in another series of attempts to get past Lee's right flank; again, at the North Anna River and at the Totopotomoy Creek, he found Lee confronting him. Finally at Cold Harbor (Cold Harbor, battles of), just northeast of Richmond, Grant launched several heavy attacks, including a frontal, near-suicidal one on June 3, only to be repelled with grievous total losses of 12,737. Lee's casualties are unknown but were much lighter.
Again Grant withdrew, only to move forward in another series of attempts to get past Lee's right flank; again, at the North Anna River and at the Totopotomoy Creek, he found Lee confronting him. Finally at Cold Harbor (Cold Harbor, battles of), just northeast of Richmond, Grant launched several heavy attacks, including a frontal, near-suicidal one on June 3, only to be repelled with grievous total losses of 12,737. Lee's casualties are unknown but were much lighter.Grant, with the vital rail centre of Petersburg (Petersburg Campaign)—the southern key to Richmond—as his objective, made one final effort to swing around Lee's right and finally outguessed his opponent and stole a march on him. But several blunders by Federal officers, swift action by Beauregard, and Lee's belated though rapid reaction enabled the Confederates to hold Petersburg. Grant attacked on June 15 and 18, hoping to break through before Lee could consolidate the Confederate lines east of the city, but he was contained with 8,150 losses.
 Unable to admit defeat but having failed to destroy Lee's army and capture Richmond, Grant settled down to a nine-month active siege of Petersburg. The summer and fall of 1864 were highlighted by the Federal failure with a mine explosion under the gray lines at Petersburg on July 30, the near capture of Washington by the Confederate Jubal Early in July, and Early's later setbacks in the Shenandoah Valley at the hands of Philip H. Sheridan (Sheridan, Philip H.).
Unable to admit defeat but having failed to destroy Lee's army and capture Richmond, Grant settled down to a nine-month active siege of Petersburg. The summer and fall of 1864 were highlighted by the Federal failure with a mine explosion under the gray lines at Petersburg on July 30, the near capture of Washington by the Confederate Jubal Early in July, and Early's later setbacks in the Shenandoah Valley at the hands of Philip H. Sheridan (Sheridan, Philip H.).Sherman (Sherman, William Tecumseh)'s Georgia campaigns
 Meanwhile, Sherman was pushing off toward Atlanta (Atlanta Campaign) from Dalton, Georgia, on May 7, 1864, with 110,123 men against Johnston's 55,000. This masterly campaign comprised a series of cat-and-mouse moves by the rival commanders. Nine successive defensive positions were taken up by Johnston. Trying to outguess his opponent, Sherman attempted to swing around the Confederate right flank twice and around the left flank the other times, but each time Johnston divined which way Sherman was moving and each time pulled back in time to thwart him. At one point Sherman's patience snapped and he frontally assaulted the Southerners at Kennesaw Mountain, Georgia, on June 27; Johnston threw him back with heavy losses. All the while Sherman's lines of communication in his rear were being menaced by audacious Confederate cavalry raids conducted by Nathan Bedford Forrest (Forrest, Nathan Bedford) and Joseph Wheeler (Wheeler, Joseph). Forrest administered a crushing defeat to Federal troops under Samuel D. Sturgis at Brice's Cross Roads, Mississippi, on June 10. But these Confederate forays were more annoying than decisive, and Sherman pressed forward.
Meanwhile, Sherman was pushing off toward Atlanta (Atlanta Campaign) from Dalton, Georgia, on May 7, 1864, with 110,123 men against Johnston's 55,000. This masterly campaign comprised a series of cat-and-mouse moves by the rival commanders. Nine successive defensive positions were taken up by Johnston. Trying to outguess his opponent, Sherman attempted to swing around the Confederate right flank twice and around the left flank the other times, but each time Johnston divined which way Sherman was moving and each time pulled back in time to thwart him. At one point Sherman's patience snapped and he frontally assaulted the Southerners at Kennesaw Mountain, Georgia, on June 27; Johnston threw him back with heavy losses. All the while Sherman's lines of communication in his rear were being menaced by audacious Confederate cavalry raids conducted by Nathan Bedford Forrest (Forrest, Nathan Bedford) and Joseph Wheeler (Wheeler, Joseph). Forrest administered a crushing defeat to Federal troops under Samuel D. Sturgis at Brice's Cross Roads, Mississippi, on June 10. But these Confederate forays were more annoying than decisive, and Sherman pressed forward. When Johnston finally informed Davis that he could not realistically hope to annihilate Sherman's mighty army, the Confederate president replaced him with John B. Hood, who had already lost two limbs in the war. Hood inaugurated a series of premature offensive battles at Peachtree Creek, Atlanta, Ezra Church, and Jonesboro, but he was repulsed in each of them. With his communications threatened, Hood evacuated Atlanta on the night of August 31–September 1. Sherman pursued only at first. Then, on November 15, he commenced his great March to the Sea with more than 60,000 men, laying waste to the economic resources of Georgia in a 50-mile- (80-km-) wide swath of destruction. He captured Savannah on December 21.
When Johnston finally informed Davis that he could not realistically hope to annihilate Sherman's mighty army, the Confederate president replaced him with John B. Hood, who had already lost two limbs in the war. Hood inaugurated a series of premature offensive battles at Peachtree Creek, Atlanta, Ezra Church, and Jonesboro, but he was repulsed in each of them. With his communications threatened, Hood evacuated Atlanta on the night of August 31–September 1. Sherman pursued only at first. Then, on November 15, he commenced his great March to the Sea with more than 60,000 men, laying waste to the economic resources of Georgia in a 50-mile- (80-km-) wide swath of destruction. He captured Savannah on December 21. Hood had sought unsuccessfully to lure Sherman out of Georgia and back into Tennessee by marching northwestward with nearly 40,000 men toward the key city of Nashville (Nashville, Battle of) (see photograph-->
Hood had sought unsuccessfully to lure Sherman out of Georgia and back into Tennessee by marching northwestward with nearly 40,000 men toward the key city of Nashville (Nashville, Battle of) (see photograph--> ), the defense of which had been entrusted by Sherman to George H. Thomas. At Franklin, Hood was checked for a day with severe casualties by a Federal holding force under John M. Schofield. This helped Thomas to retain Nashville, where, on December 15–16, he delivered a crushing counterstroke against Hood's besieging army, cutting it up so badly that it was of little use thereafter.
), the defense of which had been entrusted by Sherman to George H. Thomas. At Franklin, Hood was checked for a day with severe casualties by a Federal holding force under John M. Schofield. This helped Thomas to retain Nashville, where, on December 15–16, he delivered a crushing counterstroke against Hood's besieging army, cutting it up so badly that it was of little use thereafter.Western campaigns
 Sherman's force might have been larger and his Atlanta-Savannah Campaign consummated much sooner had not Lincoln approved the Red River Campaign in Louisiana led by Banks in the spring of 1864. Accompanied by Porter's warships, Banks moved up the Red River with some 40,000 men. He had two objectives: to capture cotton and to defeat Southern forces under Kirby-Smith (Kirby-Smith, E.) and Richard Taylor. Not only did he fail to net much cotton but he was also checked with loss on April 8 at Sabine Cross Roads, Louisiana, and forced to retreat. Porter lost several gunboats, and the campaign amounted to a costly debacle.
Sherman's force might have been larger and his Atlanta-Savannah Campaign consummated much sooner had not Lincoln approved the Red River Campaign in Louisiana led by Banks in the spring of 1864. Accompanied by Porter's warships, Banks moved up the Red River with some 40,000 men. He had two objectives: to capture cotton and to defeat Southern forces under Kirby-Smith (Kirby-Smith, E.) and Richard Taylor. Not only did he fail to net much cotton but he was also checked with loss on April 8 at Sabine Cross Roads, Louisiana, and forced to retreat. Porter lost several gunboats, and the campaign amounted to a costly debacle.That fall Kirby-Smith ordered the reconquest of Missouri. Sterling Price's Confederate army advanced on a broad front into Missouri but was set back temporarily by Thomas Ewing at Pilot Knob on September 27. Resuming the advance toward St. Louis, Price was forced westward along the south bank of the Missouri River by pursuing Federal troops under A.J. Smith, Alfred Pleasonton, and Samuel Curtis. Finally, on October 23, at Westport, near Kansas City, Price was decisively defeated and forced to retreat along a circuitous route, arriving back in Arkansas on December 2. This ill-fated raid cost Price most of his artillery as well as the greater part of his army, which numbered about 12,000.
Sherman's Carolina campaigns
 On January 10, 1865, with Tennessee and Georgia now securely in Federal hands, Sherman's 60,000-man force began to march northward into the Carolinas. It was only lightly opposed by much smaller Confederate forces. Sherman captured Columbia, South Carolina, on February 17 and compelled the Confederates to evacuate Charleston (including Fort Sumter). When Lee was finally named Confederate general in chief, he promptly reinstated Johnston as commander of the small forces striving to oppose the Federal advance. Nonetheless, Sherman pushed on into North Carolina, capturing Fayetteville on March 11 and, after an initial setback, repulsing the counterattacking Johnston at Bentonville on March 19–20. Goldsboro fell to the Federals on March 23, and Raleigh on April 13. Finally, perceiving that he no longer had any reasonable chance of containing the relentless Federal advance, Johnston (Johnston, Joseph E) surrendered to Sherman at the Bennett House near Durham Station on April 18. When Sherman's generous terms proved unacceptable to Secretary of War Stanton (Lincoln had been assassinated on April 14), the former submitted new terms that Johnston signed on April 26.
On January 10, 1865, with Tennessee and Georgia now securely in Federal hands, Sherman's 60,000-man force began to march northward into the Carolinas. It was only lightly opposed by much smaller Confederate forces. Sherman captured Columbia, South Carolina, on February 17 and compelled the Confederates to evacuate Charleston (including Fort Sumter). When Lee was finally named Confederate general in chief, he promptly reinstated Johnston as commander of the small forces striving to oppose the Federal advance. Nonetheless, Sherman pushed on into North Carolina, capturing Fayetteville on March 11 and, after an initial setback, repulsing the counterattacking Johnston at Bentonville on March 19–20. Goldsboro fell to the Federals on March 23, and Raleigh on April 13. Finally, perceiving that he no longer had any reasonable chance of containing the relentless Federal advance, Johnston (Johnston, Joseph E) surrendered to Sherman at the Bennett House near Durham Station on April 18. When Sherman's generous terms proved unacceptable to Secretary of War Stanton (Lincoln had been assassinated on April 14), the former submitted new terms that Johnston signed on April 26.The final land operations
 Grant and Meade were continuing their siege of Petersburg and Richmond early in 1865. For months the Federals had been lengthening their left (southern) flank while operating against several important railroads supplying the two Confederate cities. This stretched Lee's dwindling forces very thin. The Southern leader briefly threatened to break the siege when he attacked and captured Fort Stedman on March 25. But an immediate Federal counterattack regained the strongpoint, and Lee, when his lines were subsequently pierced, evacuated both Petersburg and Richmond on the night of April 2–3.
Grant and Meade were continuing their siege of Petersburg and Richmond early in 1865. For months the Federals had been lengthening their left (southern) flank while operating against several important railroads supplying the two Confederate cities. This stretched Lee's dwindling forces very thin. The Southern leader briefly threatened to break the siege when he attacked and captured Fort Stedman on March 25. But an immediate Federal counterattack regained the strongpoint, and Lee, when his lines were subsequently pierced, evacuated both Petersburg and Richmond on the night of April 2–3. An 88-mile (142-km) pursuit west-southwestward along the Appomattox River in Virginia ensued, with Grant and Meade straining every nerve to bring Lee to bay. The Confederates were detained at Amelia Court House, awaiting delayed food supplies, and were badly cut up at Five Forks and Sayler's Creek, with their only avenue of escape now cut off by Sheridan and George A. Custer (Custer, George Armstrong). When Lee's final attempt to break out failed, he surrendered the remnants of his gallant Army of Northern Virginia at the McLean house at Appomattox Court House on April 9. The lamp of magnanimity was reflected in Grant's unselfish terms.
An 88-mile (142-km) pursuit west-southwestward along the Appomattox River in Virginia ensued, with Grant and Meade straining every nerve to bring Lee to bay. The Confederates were detained at Amelia Court House, awaiting delayed food supplies, and were badly cut up at Five Forks and Sayler's Creek, with their only avenue of escape now cut off by Sheridan and George A. Custer (Custer, George Armstrong). When Lee's final attempt to break out failed, he surrendered the remnants of his gallant Army of Northern Virginia at the McLean house at Appomattox Court House on April 9. The lamp of magnanimity was reflected in Grant's unselfish terms.On the periphery of the Confederacy, 43,000 gray-clad soldiers in Louisiana under Kirby-Smith surrendered to Canby on May 26. The port of Galveston, Texas, yielded to the Federals on June 2, and the greatest war on American soil was over.
The naval war
While the Federal armies actually stamped out Confederate land resistance, the increasingly effective Federal naval effort must not be overlooked. If Union sea power did not win the war, it enabled the war to be won. When hostilities opened, the U.S. Navy (United States Navy, The) numbered 90 warships, of which only 42 were in commission, and many of these were on foreign station. Fortunately for the Federals, Lincoln had, in the person of Gideon Welles (Welles, Gideon), a wise secretary of the navy and one of his most competent cabinet members. Welles was ably seconded by his assistant, Gustavus Vasa Fox.
By the time of Lee's surrender, Lincoln's navy numbered 626 warships, of which 65 were ironclads. From a tiny force of nearly 9,000 seamen in 1861, the Union navy increased by war's end to about 59,000 sailors, whereas naval appropriations per year leaped from approximately $12 million to perhaps $123 million. The blockade of about 3,500 miles (5,600 km) of Confederate coastline was a factor of incalculable value in the final defeat of the Davis government, although the blockade did not become truly effective before the end of 1863.
The Confederates, on the other hand, had to start from almost nothing in building a navy. That they did so well was largely because of untiring efforts by the capable secretary of the navy, Stephen Mallory. He dispatched agents to Europe to purchase warships, sought to refurbish captured or scuttled Federal vessels, and made every effort to arm and employ Southern-owned ships then in Confederate ports. Mallory's only major omission was his delay in seeing the advantage of Confederate government control of blockade runners bringing in strategic supplies; not until later in the war did the government begin closer supervision of blockade-running vessels. Eventually, the government commandeered space on all privately owned blockade runners and even built and operated some of its own late in the war.
The naval side of the Civil War was a revolutionary one. In addition to their increasing use of steam power, the screw propeller, shell guns, and rifled ordnance, both sides built and employed ironclad warships. The notable clash on March 9, 1862, between the North's Monitor and the South's Virginia (formerly the Merrimack) was the first battle ever waged between ironclads. Also, the first sinking of a warship by a submarine occurred on February 17, 1864, when the Confederate submersible Hunley sank the blockader USS Housatonic.
Daring Confederate sea raiders preyed upon Union commerce. Especially successful were the Sumter, commanded by Raphael Semmes, which captured 18 Northern merchantmen early in the war; the Florida, captained by John Maffit, which, in 1863, seized 37 Federal prizes in the North and South Atlantic; and the Shenandoah, with James Waddell as skipper, which took 38 Union merchant ships, mostly in the Pacific. But the most famous of all the Confederate cruisers was the Alabama, commanded by Semmes, which captured 69 Federal ships in two years; not until June 19, 1864, was the Alabama intercepted and sunk off Cherbourg, France, by the Federal warship Kearsarge, captained by John Winslow. A great many other Federal ships were captured, and marine insurance rates were driven to a prohibitive high by these Southern depredations. This led to a serious deterioration of the American merchant marine, the effects of which lasted into the 20th century.
Besides fighting efficaciously with ironclads on the inland rivers, Lincoln's navy also played an important role in a series of coastal and amphibious operations, some in conjunction with the Federal army. As early as November 7, 1861, a Federal flotilla under Samuel Francis du Pont seized Port Royal, South Carolina, and another squadron under Louis M. Goldsborough assisted Burnside's army in capturing Roanoke Island and New Bern on the North Carolina littoral in February–March 1862. One month later, Savannah, Georgia, was closed to Confederate blockade runners when the Federal navy reduced Fort Pulaski guarding the city; and on April 25 David Glasgow Farragut, running the forts near the mouth of the Mississippi, took New Orleans, which was subsequently occupied by Benjamin F. Butler's army.
But in April 1863 and again in July and August, Federal warships were repelled at Fort Sumter when they descended upon Charleston, and a Federal army under Quincy A. Gillmore fared little better when it tried to assist. Farragut had better luck, however, when he rendered Mobile, Alabama, useless by reducing Fort Morgan and destroying several defending Confederate ships on August 5, 1864, in the hardest-fought naval action of the war. The Confederacy's last open Atlantic port, Wilmington, North Carolina, successfully withstood a Federal naval attack by Porter on defending Fort Fisher when Butler's army failed to coordinate its attack properly in December 1864, but it fell one month later to Porter and to an ably conducted army assault led by Alfred H. Terry. Only Galveston remained open to the Confederates in the last months of the war. In short, “Uncle Sam's web feet,” as Lincoln termed the Union navy, played a decisive role in helping to crush the Confederacy.
The cost and significance of the Civil War
The triumph of the North, above and beyond its superior naval forces, numbers, and industrial and financial resources, was due in part to the statesmanship of Lincoln, who by 1864 had become a masterful war leader, to the pervading valour of Federal soldiers, and to the increasing skill of their officers. The victory can also be attributed in part to failures of Confederate transportation, matériel, and political leadership. Only praise can be extended to the continuing bravery of Confederate soldiers and to the strategic and tactical dexterity of such generals as Lee, Jackson, and Joseph E. Johnston.

 While there were some desertions on both sides, the personal valour and the enormous casualties—both in absolute numbers and in percentage of numbers engaged—have not yet ceased to astound scholars and military historians. Based on the three-year standard of enlistment, about 1,556,000 soldiers served in the Federal armies, which suffered a total of 634,703 casualties (359,528 dead and 275,175 wounded). There were probably about 800,000 men serving in the Confederate forces, which sustained approximately 483,000 casualties (about 258,000 dead and perhaps 225,000 wounded).
While there were some desertions on both sides, the personal valour and the enormous casualties—both in absolute numbers and in percentage of numbers engaged—have not yet ceased to astound scholars and military historians. Based on the three-year standard of enlistment, about 1,556,000 soldiers served in the Federal armies, which suffered a total of 634,703 casualties (359,528 dead and 275,175 wounded). There were probably about 800,000 men serving in the Confederate forces, which sustained approximately 483,000 casualties (about 258,000 dead and perhaps 225,000 wounded). The American Civil War has been called by some the last of the old-fashioned wars; others have termed it the first of the modern wars of history. Actually it was a transitional war, and it had a profound impact, technologically, on the development of modern weapons and techniques. There were many innovations. It was the first war in history in which ironclad warships clashed; the first in which the telegraph and railroad played significant roles (see photograph-->
The American Civil War has been called by some the last of the old-fashioned wars; others have termed it the first of the modern wars of history. Actually it was a transitional war, and it had a profound impact, technologically, on the development of modern weapons and techniques. There were many innovations. It was the first war in history in which ironclad warships clashed; the first in which the telegraph and railroad played significant roles (see photograph--> ); the first to use, extensively, rifled ordnance and shell guns and to introduce a machine gun; the first to have widespread newspaper coverage, voting by servicemen in national elections, and photographic recordings; the first to organize medical care of troops systematically; and the first to use land and water mines and to employ a submarine that could sink a warship. It was also the first war in which armies widely employed aerial reconnaissance (by means of balloons).
); the first to use, extensively, rifled ordnance and shell guns and to introduce a machine gun; the first to have widespread newspaper coverage, voting by servicemen in national elections, and photographic recordings; the first to organize medical care of troops systematically; and the first to use land and water mines and to employ a submarine that could sink a warship. It was also the first war in which armies widely employed aerial reconnaissance (by means of balloons).The Civil War has been written about as have few other wars in history. More than 60,000 books and articles give eloquent testimony to the accuracy of Walt Whitman's prediction that “a great literature will … arise out of the era of those four years.” The events of the war left a rich heritage for future generations, and that legacy was summed up by the martyred Lincoln as showing that the reunited sections of the United States constituted “the last best hope of earth.”
Additional Reading
Civil War literature is vast, refined, and good. The following suggestions for further information are divided into four groups: overviews of the war, books on individual personalities and campaigns, works dealing with the social and cultural impact of the war, and documentaries covering the conflict.
Overviews
Essential multivolume works include Shelby Foote, The Civil War: A Narrative, 3 vol. (1958–74; reissued in 14 vol., 1998–2000); Allan Nevins, The War for the Union, 4 vol. (1959–71, reissued 2000); and Bruce Catton, The Centennial History of the Civil War, 3 vol. (1961–65). Two books by James M. McPherson, Ordeal by Fire: The Civil War and Reconstruction, 3rd ed. (2000), and Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era (1988), are excellent; the former places the war into broad context, while the later focuses on the war years. Russell F. Weigley, A Great Civil War: A Military and Political History, 1861–1865 (2000), is equally good. Frank E. Vandiver, Their Tattered Flags: The Epic of the Confederacy (1970, reprinted 1987); and Emory M. Thomas, The Confederate Nation, 1861–1865 (1979, reissued 1993), concentrate on the South. Charles P. Roland, An American Iliad: The Story of the Civil War, 2nd ed. (2002), is a fine survey of the conflict. William M. Fowler, Jr., Under Two Flags: The American Navy in the Civil War (1990, reprinted 2001), covers sea combat.
Personalities and campaigns
Sketches of all generals can be found in Ezra J. Warner, Generals in Gray: Lives of the Confederate Commanders (1959, reissued 1987), and Generals in Blue: Lives of the Union Commanders (1964, reissued 1993). Individual biographies of major personalities are numerous; some of the better include William C. Davis, Jefferson Davis: The Man and His Hour (1991, reissued 1996); Stephen B. Oates, With Malice Toward None: The Life of Abraham Lincoln (1977, reissued 1994); Douglas Southall Freemen, R.E. Lee: A Biography, 4 vol. (1934–35, reissued 1962), and Lee's Lieutenants: A Study in Command, 3 vol. (1942–44, reissued 1997); Craig L. Symonds, Joseph E. Johnston: A Civil War Biography (1992); John F. Marszalek, Sherman: A Soldier's Passion for Order (1993); James I. Robertson, Jr., Stonewall Jackson: The Man, the Soldier, the Legend (1997); and Gene Smith, Lee and Grant (1984, reissued 1991), which offers a dual look at the leading generals of the war.Historians have chronicled all the war's campaigns and battles. Prominent works include Bruce Catton, The Army of the Potomac, 3 vol. (1951–53, reissued 1990); William C. Davis, Battle at Bull Run: A History of the First Major Campaign of the Civil War, 2nd ed. (1995); Wiley Sword, Shiloh: Bloody April, rev. ed. (1983); Robert G. Tanner, Stonewall in the Valley: Thomas J. “Stonewall” Jackson's Shenandoah Valley Campaign, Spring 1862, updated and rev. ed. (1996); James V. Murfin, The Gleam of Bayonets: The Battle of Antietam and the Maryland Campaign of 1862 (1965, reissued 1993); Alvin M. Josephy, Jr., The Civil War in the American West (1991); Albert Castel, Decision in the West: The Atlanta Campaign of 1864 (1992); and Joseph T. Glatthaar, The March to the Sea and Beyond: Sherman's Troops in the Savannah and Carolinas Campaigns (1985, reissued 1995). Archer Jones, Civil War Command and Strategy: The Process of Victory and Defeat (1992), examines how and why the North prevailed in the fight. Michael Shaara, The Killer Angels (1974, reissued 2001), is an outstanding fictionalized account of the Battle of Gettysburg.
Social and cultural impact
Scholars have also examined the lives of ordinary combatants and civilians during the Civil War. Bell Irvin Wiley, The Life of Johnny Reb (1943, reissued 1997), and The Life of Billy Yank (1952, reprinted 1993), are standard sources; and James I. Robertson, Jr., Soldiers Blue and Gray (1988, reissued 1998), updates Wiley's look at the common soldier. Gerald F. Linderman, Embattled Courage: The Experience of Combat in the American Civil War (1987), is exceptionally good. See also Michael Fellman, Inside War; The Guerrilla Conflict in Missouri During the American Civil War (1989); Stephen V. Ash, Middle Tennessee Society Transformed, 1860–1870: War and Peace in the Upper South (1988); and Mark Grimsley, The Hard Hand of War: Union Military Policy Toward Southern Civilians, 1861–1865 (1995).
Documentaries
The Civil War (1989), produced by Ken Burns for the Public Broadcasting System, is incomparable; it covers most of the war's aspects. Civil War Combat (1999), directed by Jim Lindsey and David DeVries for the Arts and Entertainment Television Networks, examines the war's major battles. Civil War Journal (1993), and Civil War Journal II (1994), produced by Greystone Communications, Inc., and the Arts and Entertainment Television Networks for the History Channel, is a broader look at the people and the events of the war. Lincoln (1992), directed by Peter W. Kunhardt, is the best look at the Union president; the Arts and Entertainment Television Networks produced fine single-volume treatments of many of the war's other personalities.
- satrap
- Sattahip
- Satu Mare
- Satun
- saturation
- Saturday
- Saturday Night Live
- Saturn
- Saturnian verse
- saturniid moth
- Saturninus, Lucius Appuleius
- satyagraha
- Satyajit Ray
- Satyasiddhi-śāstra
- Satyendra Nath Bose
- Satyendra Prassano, 1st Baron Sinha of Raipur Sinha
- Satyendra Prassano Sinha, 1st Baron Sinha of Raipur
- Satyr and Silenus
- satyr butterfly
- Satyricon
- satyr play
- Satō Eisaku
- Satō Haruo
- Satō Nobuhiro
- Saubel, Katherine Siva