lemur
primate suborder
Introduction
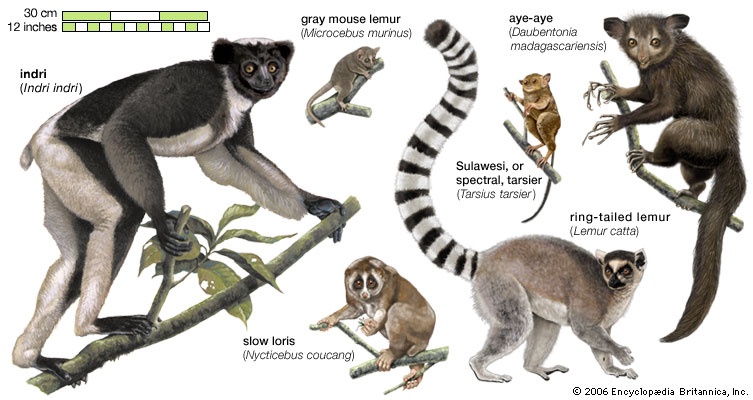 generally, any primitive primate except the tarsier; more specifically, any of the indigenous primates of Madagascar. In the broad sense, the term lemur applies not only to the typical lemurs (family Lemuridae) but also to the avahis, sifakas, indri, and aye-aye of Madagascar, in addition to the lorises, potto, and bush babies (bush baby) of Southeast Asia and Africa. Defined more narrowly, it excludes the last three (the Lorisiformes).
generally, any primitive primate except the tarsier; more specifically, any of the indigenous primates of Madagascar. In the broad sense, the term lemur applies not only to the typical lemurs (family Lemuridae) but also to the avahis, sifakas, indri, and aye-aye of Madagascar, in addition to the lorises, potto, and bush babies (bush baby) of Southeast Asia and Africa. Defined more narrowly, it excludes the last three (the Lorisiformes).General features
 Most lemurs of Madagascar and the nearby Comoros Islands have large eyes, foxlike faces, monkeylike bodies, and long hind limbs. Lemurs range in length (excluding the tail) from about 9 cm (3.5 inches) in Madame Berthe's mouse lemur (Microcebus berthae) to nearly 70 cm for the indri (Indri indri). The bushy tails of lemurs can be longer than their bodies; the indri, however, has only a stub of a tail. Except for the aye-aye, lemurs have woolly fur that is reddish, gray, brown, or black; some species are variously patterned with white. Among other markings, they may also have eye-rings or crown patches.
Most lemurs of Madagascar and the nearby Comoros Islands have large eyes, foxlike faces, monkeylike bodies, and long hind limbs. Lemurs range in length (excluding the tail) from about 9 cm (3.5 inches) in Madame Berthe's mouse lemur (Microcebus berthae) to nearly 70 cm for the indri (Indri indri). The bushy tails of lemurs can be longer than their bodies; the indri, however, has only a stub of a tail. Except for the aye-aye, lemurs have woolly fur that is reddish, gray, brown, or black; some species are variously patterned with white. Among other markings, they may also have eye-rings or crown patches.Lemurs are less intelligent than monkeys. Their sense of smell is more acute but their vision less so. Although some species are at times active during the day, their eyes seem to be adapted for nocturnal life, trading acuity for increased sensitivity in low light conditions. All lemurs are characterized by a reflective layer (tapetum) behind the retina in the eye, but no fovea or macula lutea; a hairless, moist tip to the muzzle; a noninvasive (epitheliochorial) placenta; comblike forward-directed lower front teeth (with the exception of the aye-aye); and a claw (“toilet claw”) on the second toe of the foot.
Lemurs are docile, gregarious animals; some species live in groups of 10 or more. Most of their time is spent in the trees eating fruit, leaves, buds, insects, and small birds and birds' eggs, but diet varies among different species. Some, for example, are mainly insectivorous, whereas others feed almost exclusively on foliage. All breed seasonally, and females may have only one fertile day during the entire year. Single offspring are usually born after two to five months' gestation. The newborn lemur then clings to its mother's underside until it is old enough to ride on her back.
A number of lemurs are rare or endangered (endangered species). Several either were not discovered until the late 20th century or were rediscovered after having been thought extinct. Remains exist of species larger than any of today's lemurs. Some of these may have survived until only 500 years ago. They were probably exterminated by overhunting or habitat modification by the Malagasy people, who arrived on the island less than 2,000 years ago.
Lemur diversity
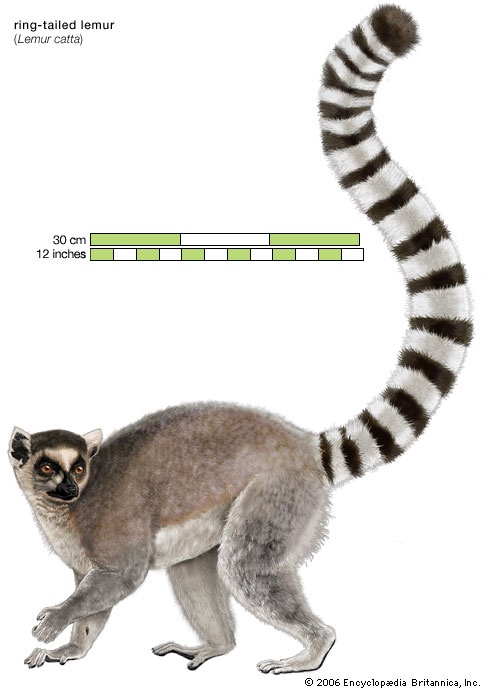 The “true lemurs” (family Lemuridae) include five genera and about 18 species. The best known of these is the ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta), commonly seen in zoos. It is unique both in its habitat (some dry and rocky areas of Madagascar) and for its striped tail (all other lemurs have solid-coloured tails). Troops are made up of several males and females, and the females are the dominant sex. A male marks the troop's territory by slashing the trunk of a small tree with a horny spur on his wrist, making an audible click, and leaving a scented scar on the tree. Members of the related genus Eulemur include the black lemur (E. macaco), in which the male is black and the female is reddish brown. The rare black-and-white or black-and-red ruffed lemurs (genus Varecia) live in rainforests on the eastern side of Madagascar. The gentle lemurs, or lesser bamboo lemurs (genus Hapalemur), and the highly endangered greater bamboo lemurs (Prolemur simus) feed on bamboo stems in the eastern and northwestern rainforests of the island.
The “true lemurs” (family Lemuridae) include five genera and about 18 species. The best known of these is the ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta), commonly seen in zoos. It is unique both in its habitat (some dry and rocky areas of Madagascar) and for its striped tail (all other lemurs have solid-coloured tails). Troops are made up of several males and females, and the females are the dominant sex. A male marks the troop's territory by slashing the trunk of a small tree with a horny spur on his wrist, making an audible click, and leaving a scented scar on the tree. Members of the related genus Eulemur include the black lemur (E. macaco), in which the male is black and the female is reddish brown. The rare black-and-white or black-and-red ruffed lemurs (genus Varecia) live in rainforests on the eastern side of Madagascar. The gentle lemurs, or lesser bamboo lemurs (genus Hapalemur), and the highly endangered greater bamboo lemurs (Prolemur simus) feed on bamboo stems in the eastern and northwestern rainforests of the island.There are at least 10 species of sportive lemurs (family Megaladapidae) that live throughout Madagascar in both rainforests and dry forests. They are solitary and nocturnal, feeding on leaves and flowers, which are digested in their enormous cecum with the aid of bacteria. Bacterial fermentation enables energy to be extracted from the large quantity of otherwise indigestible cellulose in the lemur's diet.
 The dwarf lemurs (Cheirogaleus), along with the mouse (Microcebus), Coquerel's (Mirza), hairy-eared (Allocebus), and fork-crowned (Phaner) lemurs, make up the family Cheirogaleidae, which in many respects are the most primitive living lemurs. Dwarf lemurs store fat in their tails and are dormant (estivate) during dry periods; they live in monogamous pairs. Mouse lemurs, which eat insects and fruit, are the smallest living primates.
The dwarf lemurs (Cheirogaleus), along with the mouse (Microcebus), Coquerel's (Mirza), hairy-eared (Allocebus), and fork-crowned (Phaner) lemurs, make up the family Cheirogaleidae, which in many respects are the most primitive living lemurs. Dwarf lemurs store fat in their tails and are dormant (estivate) during dry periods; they live in monogamous pairs. Mouse lemurs, which eat insects and fruit, are the smallest living primates.Strepsirrhine primates first emerged in the Early Eocene Epoch (some 50 million years ago), though their origins may be traced to the preceding Paleocene Epoch. These Eocene lemuroids were abundant in North America and Europe, and some are known from complete skeletons. By the close of the Eocene (approximately 34 million years ago), strepsirrhines had practically disappeared from the Northern Hemisphere. The lemur lineage continued in tropical forests, however, and they were particularly successful in Madagascar, where they were relatively free from competition with more-advanced primates. No fossil deposits are known in Madagascar between the Mesozoic Era and recent times, so the fossil history of the island's lemurs is unknown.
Additional Reading
Russel A. Mittermeier, Lemurs of Madagascar (1994), is a field guide including maps and 36 colour plates; Spirits of the Forest (1987), produced by WNET as part of the Nature television series, portrays several species and behaviours.
- Portulacaceae
- Portus
- Port-Vila
- Port Washington
- Porus
- Porvoo
- Posada, José Guadalupe
- Posadas
- Poseidon
- Poseidonius
- Poseidon missile
- position
- position vector
- positive organ
- Positivism
- positron
- positron emission tomography
- positronium
- posse comitatus
- possession
- possum
- postal system
- post-and-lintel system
- post chaise
- Post, C W