Prominent metabolic diseases
Table
Prominent metabolic diseases
disorder cause signs and symptoms treatment
cystinosis lysosomal cystine transporter defect rickets, dehydration, stunted growth, kidney disease, corneal deposits supportive therapy, cysteamine, kidney transplantation
cystinuria cystine and dibasic amino acid transporter defect kidney stones high fluid intake, urine alkalinization, oral sulfhydryl agents
Fabry disease (Fabry's disease) deficiency of alpha-galactosidase A kidney failure, pain, skin lesions, cloudy corneas and lenses, heart disease pain management, dialysis, kidney transplantation, enzyme replacement therapy (experimental)
galactosemia deficiency of galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase jaundice, liver dysfunction, lethargy, weight loss, kidney disease, susceptibility to infection, cataracts exclusion of galactose from the diet
Gaucher disease (type I) defect of beta-glucocerebrosidase enlarged liver and spleen, bone disease, lipid-laden cells in bone marrow enzyme replacement therapy, splenectomy, orthopedic procedures
Hartnup disease neutral amino acid transport defect ataxia, rash, mental and psychiatric abnormalities supplementation of nicotinamide, high-protein diet
homocystinuria defect in cystathionine beta-synthase pronounced flush of the cheeks, thin, tall frame, lens dislocation, vascular disease, osteoporosis, possible mental retardation, psychiatric abnormalities vitamin B6, folic acid, vitamin B12, betaine, low-dose aspirin, dietary restriction of protein and methionine
Hunter syndrome (Hunter's syndrome) deficiency of iduronate 2-sulfatase coarse features, enlarged liver and spleen, growth deficiency, probable mental deficiency, heart disease, bone abnormalities supportive therapy, enzyme replacement therapy (experimental)
Hurler syndrome (Hurler's syndrome) deficiency of alpha-L-iduronidase mental retardation, cloudy corneas, enlarged liver and spleen, coarse features, cardiac failure, stiff joints, bone abnormalities supportive therapy, enzyme replacement therapy
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase neurological impairment, mental retardation, gout, kidney stones, kidney failure, self-mutilation high fluid intake, urine alkalinization, allopurinol, extraction of teeth, protective physical devices
maple syrup urine disease deficiency of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex neurological deterioration, maple syrup smell to urine, muscular tension, mental retardation protein restriction, formulas deficient in branched-chain amino acids, thiamin for milder forms
Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome deficiency of arylsulfatase B coarse features, stiff joints, cloudy corneas, enlarged liver and spleen, skeletal involvement supportive therapy, enzyme replacement therapy (experimental)
Morquio syndrome deficiency of N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase or beta-galactosidase coarse features, cloudy corneas, spinal curvature, knock-knees and other severe skeletal abnormalities, severe short stature supportive therapy
Niemann-Pick disease (type A) deficiency of sphingomyelinase neurological deterioration, “cherry-red” spot on the retina of the eye, enlarged liver and spleen, lipid-laden cells in bone marrow, pulmonary disease, liver dysfunction supportive therapy
phenylketonuria low activity of phenylalanine hydroxlase developmental delay, light features, behaviour disturbances, mental retardation if untreated diet low in phenylalanine and protein, including special formula
Pompe disease (Pompe's disease) lack of alpha-1,4-glucosidase diminished muscle tone, heart failure, enlarged tongue supportive therapy, enzyme replacement therapy (experimental)
porphyria heme biosynthesis defects abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dark or red urine, rashes, neurological symptoms administration of heme, high-carbohydrate diet, avoidance of exacerbating factors
Scheie syndrome (Scheie's syndrome) mild deficiency of alpha-L-iduronidase cloudy corneas, joint limitation supportive therapy, enzyme replacement therapy
Tay-Sachs disease deficiency of beta-hexosaminidase A neurological deterioration, startle reaction to sound, seizures, “cherry-red” spot on the retina of the eye supportive therapy
tyrosinemia (hepatorenal) defect in fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase liver disease, liver cancer, peripheral nerve disease, kidney defects NTBC, a dietary restriction of phenylalanine and tyrosine, liver transplantation if necessary
von Gierke disease (von Gierke's disease) deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase hypoglycemia, enlarged liver, dwarfism, gout, short stature, high blood lipids frequent feedings of glucose, liver transplantation if necessary
See as table: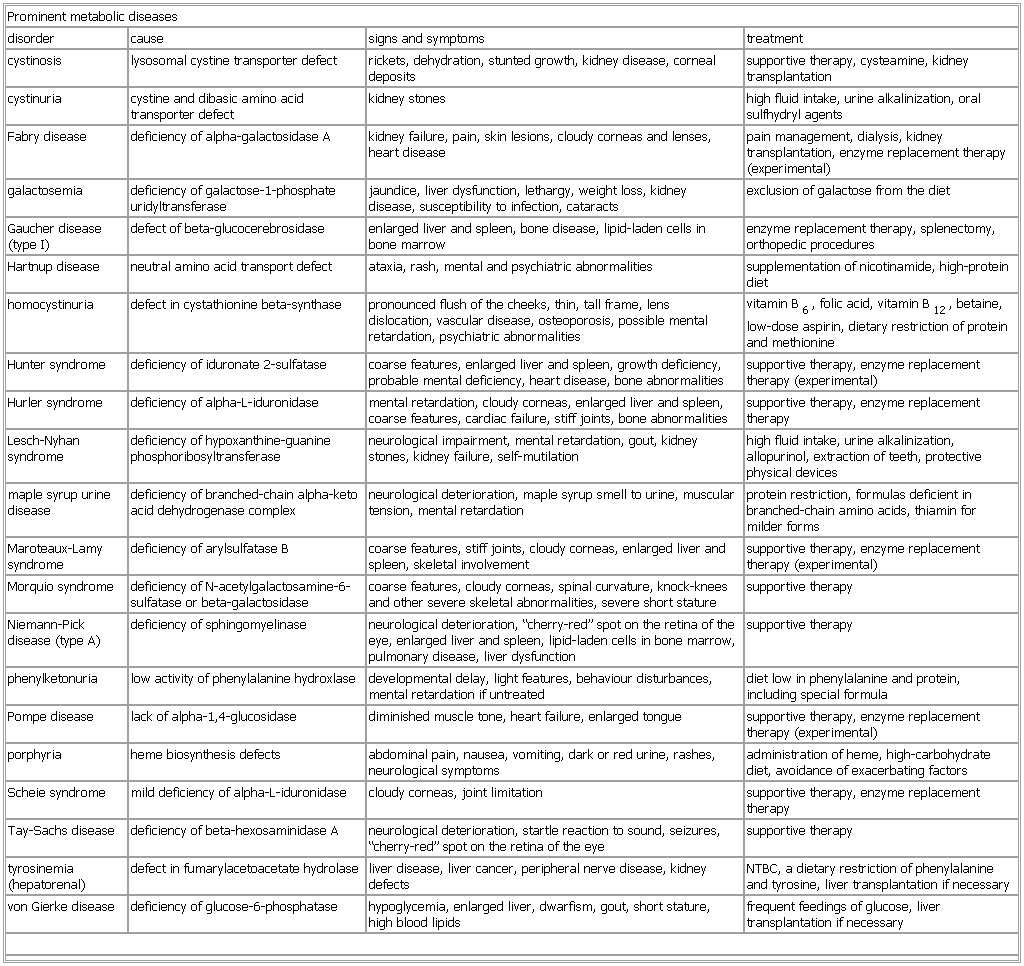

- Champagne-Ardenne
- Champagny, Jean-Baptiste Nompère de, Duc De Cadore
- Champaign
- Champaigne, Philippe de
- Champasak
- Champ Clark
- Champerico
- Champfleury
- Champigny-sur-Marne
- champion
- Champion International Corporation
- Champlain, Lake
- Champlain, Samuel de
- champlevé
- Champmeslé, Marie
- Champollion-Figeac, Jacques-Joseph
- Champollion, Jean-François
- Champs-Élysées
- Ch'an
- Chanba, Samson
- chancel
- Chancelade skeleton
- chancellor
- Chancellor, Richard
- Chancellorsville, Battle of