Lockheed Martin Corporation
American corporation
Introduction
major American diversified company with core business concentrations in aerospace products—including aircraft, space launchers, satellites, and defense systems—and other advanced-technology systems and services. About half of the company's annual sales are to the U.S. Department of Defense. Lockheed Martin is also a leading contractor for the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). It was formed in 1995 through the merger of Lockheed Corporation and Martin Marietta Corporation, the second and third largest American defense contractors at the time. In 1996 the new company grew further with the acquisition of Loral Corporation's defense electronics and systems (itself comprising nine separate aerospace and defense units of major American corporations such as IBM, Xerox, and Ford). Headquarters are in Bethesda, Maryland.
Lockheed Martin manufactures, among other aircraft, the F-16 Fighting Falcon multirole fighter, the C-130 Hercules military transport, and the P-3 Orion maritime patrol aircraft. Additional projects include, in partnership with Boeing Company, the F-22 Raptor stealth fighter and, in competition with Boeing, the Joint Strike Fighter (JSF). The company also conducts upgrades, modifications, and refurbishing of its older aircraft. In the space sector, Lockheed Martin builds the Titan (Titan rocket) IV, the largest American expendable launch vehicle; the commercial Atlas (Atlas rocket) families of expendable launchers; the Centaur upper-stage rocket; the Trident (Trident missile) II submarine-launched ballistic missile; and smaller tactical missile systems for aircraft and ground-based platforms. It also makes military satellites (e.g., for the Milstar communications satellite system) and numerous scientific, weather, and telecommunications satellites. Lockheed Martin supplies the external propellant tank for the U.S. space shuttle, and, in a joint venture with Boeing called United Space Alliance, it conducts day-to-day operation and management of the shuttle fleet for NASA. As part of International Launch Services, a joint venture formed in 1995 with the Russian firms Energia and Khrunichev, it markets commercial Atlas and Proton launch services worldwide. The company also produces fire-control systems, radars, and other elements of the U.S. Navy's Aegis Combat System, which automatically tracks hostile targets and directs missile defense. It is managing contractor of the Oak Ridge (Tennessee) National Laboratory and the Sandia National Laboratories in New Mexico and California. In 2000 Lockheed Martin had a workforce of about 150,000 employees worldwide.
Lockheed Corporation
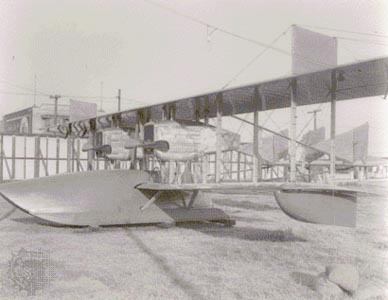 Lockheed Corporation dates to 1912 when Allan Loughead, his brother Malcolm, and Max Mamlock, who at the time was head of Alco Cab Company, founded Alco Hydro-Aeroplane Company to build the Loughead brothers' floatplane design, the Model G. After a year the company became dormant, but in 1915 the Loughead brothers bought out the interests of other investors to acquire control of the ModelG and successfully flew paying passengers at the Panama-Pacific Exposition in San Francisco that year. Using their profits and capital from investors, the brothers organized Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Company in 1916. Although its F-1 flying boat was well designed, sales were poor, and in 1921 the company was liquidated.
Lockheed Corporation dates to 1912 when Allan Loughead, his brother Malcolm, and Max Mamlock, who at the time was head of Alco Cab Company, founded Alco Hydro-Aeroplane Company to build the Loughead brothers' floatplane design, the Model G. After a year the company became dormant, but in 1915 the Loughead brothers bought out the interests of other investors to acquire control of the ModelG and successfully flew paying passengers at the Panama-Pacific Exposition in San Francisco that year. Using their profits and capital from investors, the brothers organized Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Company in 1916. Although its F-1 flying boat was well designed, sales were poor, and in 1921 the company was liquidated.In 1926 Allan Loughead returned to aviation and established the Lockheed Aircraft Company (the spelling of Loughead was changed to match its pronunciation) with brick and tile manufacturer Fred E. Keeler as president and majority stockholder. The next year, with John K. Northrop (Northrop, John Knudsen) as chief engineer, Lockheed developed the trend-setting Vega, a four-passenger, wooden monoplane. This highly successful aircraft achieved several records including completion of the first successful solo flight around the world (by Wiley Post (Post, Wiley) in 1933). the first solo flight around the world, by Wiley Post (Post, Wiley) in 1933.In 1929 Keeler sold the company to Detroit Aircraft Corporation, which made it a division. While Lockheed itself remained profitable during the Great Depression, the rising losses of its parent company drained its own profits, and in 1932 Detroit Aircraft was liquidated. Within a short time, four investors led by the banker Robert Ellsworth Gross acquired Lockheed's assets for $40,000 and revived Lockheed Aircraft Company. In 1934 the company delivered its first Electra, a twin-engine, all-metal airliner whose sales brought the business to profitability.
 With the advent of World War II, Lockheed began its close association with the U.S. military by producing the twin-engine, twin-tailboom P-38 Lightning fighter-interceptor, the only American pursuit plane to remain in continuous production throughout the war. In 1943, under the leadership of the aircraft engineer and designer Clarence L. (“Kelly”) Johnson (Johnson, Kelly), Lockheed established a highly secret section, Advanced Development Projects (ADP), to design a fighter around a British De Havilland jet engine. The result was the P-80 Shooting Star, the first American jet aircraft to enter operational service (1945).
With the advent of World War II, Lockheed began its close association with the U.S. military by producing the twin-engine, twin-tailboom P-38 Lightning fighter-interceptor, the only American pursuit plane to remain in continuous production throughout the war. In 1943, under the leadership of the aircraft engineer and designer Clarence L. (“Kelly”) Johnson (Johnson, Kelly), Lockheed established a highly secret section, Advanced Development Projects (ADP), to design a fighter around a British De Havilland jet engine. The result was the P-80 Shooting Star, the first American jet aircraft to enter operational service (1945).
 After the war, ADP—popularly known as the Skunk Works—became the American aerospace industry's leading military aircraft developer. It produced the F-104 Starfighter (first flown as the XF-104 in 1954), the first operational aircraft capable of sustained speeds more than twice that of sound; the U-2 high-altitude spy plane (1955); and the twin-engine reconnaissance plane SR-71 Blackbird (1964), capable of more than three times the speed of sound. In 1977 ADP flew the first stealth aircraft, an experimental prototype code-named Have Blue, which was designed to be almost invisible to radar. Its stealth research culminated in the development of the F-117A (F-117) Nighthawk, which first flew in 1981. In 1991 ADP became a separate company within Lockheed, and, after the merger of Lockheed with Martin Marietta in 1995, its official name was changed to Lockheed Martin Skunk Works.
After the war, ADP—popularly known as the Skunk Works—became the American aerospace industry's leading military aircraft developer. It produced the F-104 Starfighter (first flown as the XF-104 in 1954), the first operational aircraft capable of sustained speeds more than twice that of sound; the U-2 high-altitude spy plane (1955); and the twin-engine reconnaissance plane SR-71 Blackbird (1964), capable of more than three times the speed of sound. In 1977 ADP flew the first stealth aircraft, an experimental prototype code-named Have Blue, which was designed to be almost invisible to radar. Its stealth research culminated in the development of the F-117A (F-117) Nighthawk, which first flew in 1981. In 1991 ADP became a separate company within Lockheed, and, after the merger of Lockheed with Martin Marietta in 1995, its official name was changed to Lockheed Martin Skunk Works. In the decades after World War II, Lockheed also produced several transport aircraft for the military. In 1955 the production version of the C-130 Hercules, a tactical troop and cargo transport plane, made its maiden flight. With manufacturing continuing into the early 21st century, the Hercules family of military and civil transports became the most successful and long-lived series of cargo lifters in the world. Lockheed also built the world's first turbojet airlifter, the C-141 StarLifter (first flown in 1963), and the C-5 Galaxy military cargo plane (first flown in 1968), which at the start of the 21st century remained the heaviest and largest American aircraft. In the late 1950s the company developed the four-turboprop P-3 Orion, a land-based antisubmarine patrol aircraft derived from an airliner design.
In the decades after World War II, Lockheed also produced several transport aircraft for the military. In 1955 the production version of the C-130 Hercules, a tactical troop and cargo transport plane, made its maiden flight. With manufacturing continuing into the early 21st century, the Hercules family of military and civil transports became the most successful and long-lived series of cargo lifters in the world. Lockheed also built the world's first turbojet airlifter, the C-141 StarLifter (first flown in 1963), and the C-5 Galaxy military cargo plane (first flown in 1968), which at the start of the 21st century remained the heaviest and largest American aircraft. In the late 1950s the company developed the four-turboprop P-3 Orion, a land-based antisubmarine patrol aircraft derived from an airliner design.In the civilian sector following World War II, Lockheed introduced several propeller-driven airliners, including the famous triple-tailed Constellation (entered commercial service in 1946) and Super Constellation (entered commercial service in 1951), and the first business jet, the four-engine JetStar (first flown as a twin-engine craft in 1957). Although it missed entering the commercial jetliner field in the formative years, the advent of wide-bodied airliners in the 1960s provided the company with a new opportunity to penetrate the market. Its L-1011 TriStar began development in 1966 and made its first flight in 1970. To power the TriStar, Lockheed selected the British engine maker Rolls-Royce (Rolls-Royce PLC)'s new RB211 turbofan. In 1971, however, several poor business decisions related to the RB211 forced Rolls-Royce into bankruptcy. Lockheed considered it too costly to modify the TriStar for a different engine, and it, too, was on the verge of bankruptcy because of delays with the L-1011, cost overruns on its C-5 program, and reduced military contracts in the waning years of the Vietnam War. The L-1011 and its manufacturer were saved only through coordinated efforts of the U.S. government (with a massive loan guarantee), the British government (by nationalizing Rolls-Royce), other consolidated lenders, and committed customers.

 Lockheed lagged behind other aerospace companies (e.g., Douglas and the Convair division of General Dynamics) in entering the field of missile development, and a missile systems division was not formed until late 1953. Organized later as Lockheed Missiles & Space Company, it was responsible for the development of several generations of U.S. Navy submarine-launched strategic ballistic missiles—the Polaris (Polaris missile) (deployed in 1960), Poseidon (Poseidon missile) (1971), Trident (Trident missile) I (1979), and Trident II (1990). Lockheed's space activities included the development in the late 1950s of the Agena rocket, which served as a second stage and a spacecraft for numerous space missions. In the late 1970s and '80s the company was responsible for the construction and systems integration of the Hubble Space Telescope, which was carried by space shuttle into orbit in 1990. During the late 1950s Lockheed also expanded into electronics with the formation of an electronics and avionics division and branched out into marine systems with its purchase of a major construction, shipbuilding, and ship-repair firm. By 1977, when the company changed its name to Lockheed Corporation, aircraft and related services accounted for little more than 50 percent of sales.
Lockheed lagged behind other aerospace companies (e.g., Douglas and the Convair division of General Dynamics) in entering the field of missile development, and a missile systems division was not formed until late 1953. Organized later as Lockheed Missiles & Space Company, it was responsible for the development of several generations of U.S. Navy submarine-launched strategic ballistic missiles—the Polaris (Polaris missile) (deployed in 1960), Poseidon (Poseidon missile) (1971), Trident (Trident missile) I (1979), and Trident II (1990). Lockheed's space activities included the development in the late 1950s of the Agena rocket, which served as a second stage and a spacecraft for numerous space missions. In the late 1970s and '80s the company was responsible for the construction and systems integration of the Hubble Space Telescope, which was carried by space shuttle into orbit in 1990. During the late 1950s Lockheed also expanded into electronics with the formation of an electronics and avionics division and branched out into marine systems with its purchase of a major construction, shipbuilding, and ship-repair firm. By 1977, when the company changed its name to Lockheed Corporation, aircraft and related services accounted for little more than 50 percent of sales.In the early 1990s Lockheed expanded its lines of military aircraft with the acquisition of the Fort Worth (Texas) Division of General Dynamics (General Dynamics Corp.), whose major product was the F-16 fighter. The roots of that division reach back to the formation of Consolidated Aircraft Corporation in 1923 by the American military pilot and aircraft maker Reuben Hollis Fleet. Consolidated Aircraft started out by building training aircraft. During World War II it was one of the leading airplane manufacturers in the United States; its production included the B-24 Liberator bomber and PB4Y flying boat. In 1943 Consolidated merged with Vultee Aircraft Inc. (founded 1939) to form Consolidated Vultee Aircraft Corporation, which in the postwar period produced both the largest piston-engine-powered American bomber, the B-36 Peacekeeper (which in later versions incorporated four auxiliary turbojets in addition to its six radial piston engines), and the fastest jet bomber of the time, the delta-wing B-58 Hustler.
In 1953 General Dynamics acquired a stock majority in Consolidated Vultee and established it as its Convair division. Eight years later the name Convair was dropped, and most aircraft-manufacturing activity was concentrated at the former Consolidated Fort Worth plant. This division developed the twin-engine F-111 fighter-bomber (deployed in 1967), the world's first production variable-wing aircraft, and the compact, lightweight F-16 (deployed in 1979), which featured fly-by-wire (electronic rather than mechanical) flight controls. Generous contracts with several NATO countries to coproduce the F-16 contributed to the international success of the aircraft. In 1991 the U.S. Air Force chose a design offered by a consortium comprising Lockheed, Boeing (Boeing Company), and General Dynamics for a twin-engine advanced tactical fighter with stealth features. The aircraft was named the F-22 Raptor and first flew in 1997.
Martin Marietta Corporation
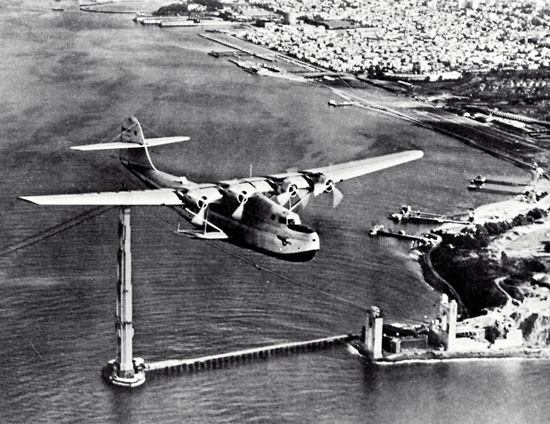

 Lockheed Martin's second line of heritage, Martin Marietta Corporation, began in 1912 when the American aviation pioneer Glenn L. Martin (Martin, Glenn L) organized a company to manufacture and sell airplanes. Four years later, Wright Company acquired the enterprise to form Wright-Martin Aircraft Corporation. Wright Company had been reformed in 1915 after Orville Wright (Wright, Wilbur and Orville) sold his sagging business (founded in 1909) to Wall Street investors. In 1917, with the help of several American industrialists, Martin incorporated a new Glenn L. Martin Company, which supplied its MB-1 bomber to the U.S. military. In 1928 Glenn Martin sold that company's manufacturing facilities and bought a 90 percent interest in pioneer automobile designer Louis Chevrolet (Chevrolet, Louis)'s small airplane-engine company, incorporating as Martin Company. The firm's four-engine flying boat, the M-130, became a pre-World War II mainstay for transatlantic and transpacific Clipper service. During the war the company produced numerous small bomber aircraft, such as the twin-engine B-26 Marauder, and several rather unsuccessful commercial transports. In the 1950s Martin Company began work on the Pershing ballistic missile and the Titan (Titan rocket) intercontinental ballistic missile, the latter of which it later developed into a space launch vehicle. In 1960 Martin's last airplane rolled off the production line, and the company devoted itself to missiles and space launchers.
Lockheed Martin's second line of heritage, Martin Marietta Corporation, began in 1912 when the American aviation pioneer Glenn L. Martin (Martin, Glenn L) organized a company to manufacture and sell airplanes. Four years later, Wright Company acquired the enterprise to form Wright-Martin Aircraft Corporation. Wright Company had been reformed in 1915 after Orville Wright (Wright, Wilbur and Orville) sold his sagging business (founded in 1909) to Wall Street investors. In 1917, with the help of several American industrialists, Martin incorporated a new Glenn L. Martin Company, which supplied its MB-1 bomber to the U.S. military. In 1928 Glenn Martin sold that company's manufacturing facilities and bought a 90 percent interest in pioneer automobile designer Louis Chevrolet (Chevrolet, Louis)'s small airplane-engine company, incorporating as Martin Company. The firm's four-engine flying boat, the M-130, became a pre-World War II mainstay for transatlantic and transpacific Clipper service. During the war the company produced numerous small bomber aircraft, such as the twin-engine B-26 Marauder, and several rather unsuccessful commercial transports. In the 1950s Martin Company began work on the Pershing ballistic missile and the Titan (Titan rocket) intercontinental ballistic missile, the latter of which it later developed into a space launch vehicle. In 1960 Martin's last airplane rolled off the production line, and the company devoted itself to missiles and space launchers. In 1961 Martin Company diversified through its merger with American-Marietta Company (incorporated 1930) to form Martin Marietta Corporation. American-Marietta had been founded in 1913 as American Asphalt Paint Company and was a leading supplier of building and road construction materials. Martin Marietta retained most aspects of its antecedent companies' production. Its space activities included the construction of the two Viking landers, which touched down on Mars in 1976, and the Magellan spacecraft, which mapped the surface of Venus in the early 1990s, and the design and production of the space shuttle's external fuel tank. In the early 1990s Martin Marietta made two large-scale additions to its space-related assets. In 1993 it acquired General Electric's aerospace business, a move that was followed a year later by the purchase of the space systems division of General Dynamics (General Dynamics Corp.), producer of the Atlas launcher and Centaur upper-stage vehicle.
In 1961 Martin Company diversified through its merger with American-Marietta Company (incorporated 1930) to form Martin Marietta Corporation. American-Marietta had been founded in 1913 as American Asphalt Paint Company and was a leading supplier of building and road construction materials. Martin Marietta retained most aspects of its antecedent companies' production. Its space activities included the construction of the two Viking landers, which touched down on Mars in 1976, and the Magellan spacecraft, which mapped the surface of Venus in the early 1990s, and the design and production of the space shuttle's external fuel tank. In the early 1990s Martin Marietta made two large-scale additions to its space-related assets. In 1993 it acquired General Electric's aerospace business, a move that was followed a year later by the purchase of the space systems division of General Dynamics (General Dynamics Corp.), producer of the Atlas launcher and Centaur upper-stage vehicle.- indicator species
- indiction
- indictment
- Indic writing systems
- Indies, Council of the
- Indies, Laws of the
- indifference
- indifference curve
- Indigenismo
- indigestion
- Indigirka River
- indigo
- indigo snake
- Indio
- Indira Gandhi
- indium
- individualism
- individual psychology
- Indo-Aryan languages
- Indochina
- Indochina wars
- Indo-European languages
- Indo-Eṣfahān carpet
- Indo-Gangetic Plain
- Indo-Hittite languages