loop of Henle
anatomy
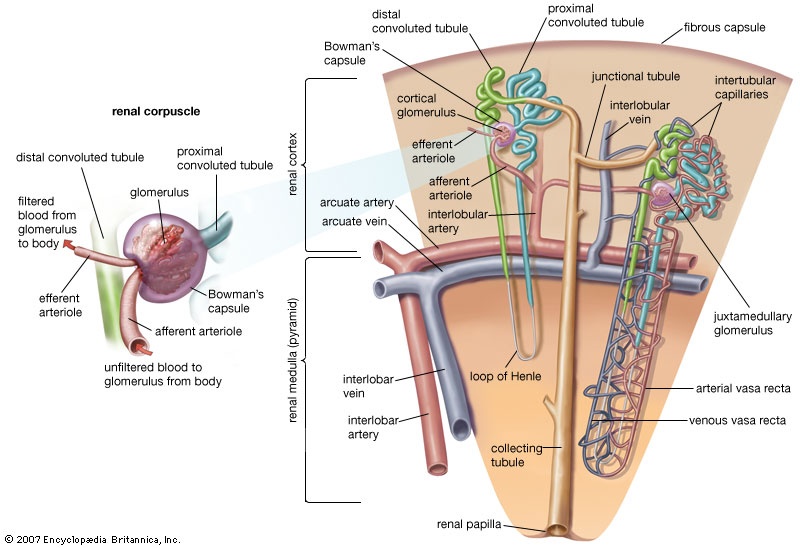 long, U-shaped portion of the tubule that conducts urine within each nephron (q.v.) of the kidney of reptiles, birds, and mammals. The principal function of the loop of Henle appears to be the recovery of water and sodium chloride from the urine. This function allows production of urine that is far more concentrated than blood, limiting the amount of water needed as intake for survival. Many species that live in arid environments such as deserts have highly efficient loops of Henle.
long, U-shaped portion of the tubule that conducts urine within each nephron (q.v.) of the kidney of reptiles, birds, and mammals. The principal function of the loop of Henle appears to be the recovery of water and sodium chloride from the urine. This function allows production of urine that is far more concentrated than blood, limiting the amount of water needed as intake for survival. Many species that live in arid environments such as deserts have highly efficient loops of Henle.The liquid entering the loop is the solution of salt, urea, and other substances passed along by the proximal convoluted tubule, from which most of the dissolved components needed by the body—particularly glucose, amino acids, and sodium bicarbonate—have been reabsorbed into the blood. The first segment of the loop, the descending limb, is permeable to water, and the liquid reaching the bend of the loop is much richer than the blood plasma in salt and urea. As the liquid returns through the ascending limb, sodium chloride diffuses out of the tubule into the surrounding tissue, where its concentration is lower. In the third segment of the loop, the tubule wall can, if necessary, effect further removal of salt, even against the concentration gradient, in an active-transport process requiring the expenditure of energy. In a healthy person the reabsorption of salt from the urine exactly maintains the bodily requirement: during periods of low salt intake, virtually none is allowed to escape in the urine, but, in periods of high salt intake, the excess is excreted.
- Hisarlık
- Hishida Shunsō
- Hishikawa Moronobu
- Hishām ibn al-Kalbī
- Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Malik
- Hispania
- Hispaniola
- Hispano-Moresque ware
- Hisperic style
- Hiss, Alger
- Histadrut
- histamine
- hister beetle
- Histiaeus
- histidine
- histogenesis
- histology
- histone
- histoplasmosis
- historical criticism
- Historical determinations of the Earth's radius and flattening
- historical geography
- historical linguistics
- historical novel
- historical school of economics