mitosis
biology
a process of cell duplication, or reproduction, during which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells. Strictly applied, the term mitosis is used to describe the duplication and distribution of chromosomes (chromosome), the structures that carry the genetic information.
A brief treatment of mitosis follows. For a full treatment, see growth: In cells (growth); cell: Mitosis and cytokinesis (cell).
Prior to the onset of mitosis, the chromosomes have replicated and the proteins that will form the mitotic spindle have been synthesized. Mitosis begins at prophase with the thickening and coiling of the chromosomes. The nucleolus, a rounded structure, shrinks and disappears. The end of prophase is marked by the beginning of the organization of a group of fibres to form a spindle and the disintegration of the nuclear membrane.
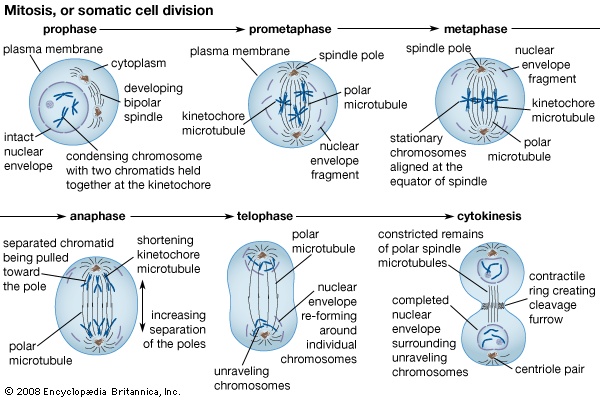 The chromosomes, each of which is a double structure consisting of duplicate chromatids, line up along the midline of the cell at metaphase. In anaphase each chromatid pair separates into two identical chromosomes that are pulled to opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibres. During telophase, the chromosomes begin to decondense, the spindle breaks down, and the nuclear membranes and nucleoli re-form. The cytoplasm of the mother cell divides to form two daughter cells, each containing the same number and kind of chromosomes as the mother cell. The stage, or phase, after the completion of mitosis is called interphase.
The chromosomes, each of which is a double structure consisting of duplicate chromatids, line up along the midline of the cell at metaphase. In anaphase each chromatid pair separates into two identical chromosomes that are pulled to opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibres. During telophase, the chromosomes begin to decondense, the spindle breaks down, and the nuclear membranes and nucleoli re-form. The cytoplasm of the mother cell divides to form two daughter cells, each containing the same number and kind of chromosomes as the mother cell. The stage, or phase, after the completion of mitosis is called interphase.Mitosis is absolutely essential to life because it provides new cells for growth and for replacement of worn-out cells. Mitosis may take minutes or hours, depending upon the kind of cells and species of organisms. It is influenced by time of day, temperature, and chemicals.