Clinton, Bill
president of United States
Introduction
byname of William Jefferson Clinton, original name William Jefferson Blythe III
born August 19, 1946, Hope, Arkansas, U.S.
 42nd president of the United States (1993–2001), who oversaw the country's longest peacetime economic expansion. In 1998 he became only the second U.S. president to be impeached (impeachment); he was acquitted by the Senate in 1999. (For a discussion of the history and nature of the presidency, see presidency of the United States of America.)
42nd president of the United States (1993–2001), who oversaw the country's longest peacetime economic expansion. In 1998 he became only the second U.S. president to be impeached (impeachment); he was acquitted by the Senate in 1999. (For a discussion of the history and nature of the presidency, see presidency of the United States of America.)Early life
Bill Clinton's father was a traveling salesman who died in an automobile accident three months before his son was born. His widow, Virginia Dell Blythe, married Roger Clinton, and, despite their unstable union (they divorced and then remarried) and her husband's alcoholism, her son eventually took his stepfather's name. Reared in part by his maternal grandmother, Bill Clinton developed political aspirations at an early age; they were solidified (by his own account) in July 1963, when he met and shook hands with President John F. Kennedy (Kennedy, John F.).
Clinton enrolled at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C., in 1964 and graduated in 1968 with a degree in international affairs. During his freshman and sophomore years he was elected student president, and during his junior and senior years he worked as an intern for Senator J. William Fulbright (Fulbright, J. William), the Arkansas Democrat who chaired the U.S. Senate Committee on Foreign Relations. Fulbright was a vocal critic of the Vietnam War, and Clinton, like many young men of his generation, opposed the war as well. He received a draft deferment for the first year of his studies as a Rhodes (Rhodes scholarship) scholar at the University of Oxford in 1968 and later attempted to extend the deferment by applying to the Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) program at the University of Arkansas School of Law. Although he soon changed his plans and returned to Oxford, thus making himself eligible for the draft, he was not chosen. While at Oxford, Clinton wrote a letter to the director of the Arkansas ROTC program thanking the director for “saving” him from the draft and explaining his concern that his opposition to the war could ruin his future “political viability.” During this period Clinton also experimented with marijuana; his later claim that he “didn't inhale” would become the subject of much ridicule.
After graduating from Yale University Law School in 1973, Clinton joined the faculty of the University of Arkansas School of Law, where he taught until 1976. In 1974 he ran unsuccessfully for a seat in the U.S. House of Representatives. In 1975 he married a fellow Yale Law graduate, attorney Hillary Rodham (Hillary Clinton (Clinton, Hillary Rodham)), who thereafter took an active role in his political career. In the following year he was elected attorney general of Arkansas, and in 1978 he won the governorship, becoming the youngest governor the country had seen in 40 years.
Governor of Arkansas
After an eventful two-year term as governor, Clinton failed in his reelection bid in 1980, the year his daughter and only child, Chelsea, was born. After apologizing to voters for unpopular decisions he had made as governor (such as highway-improvement projects funded by increases in the state gasoline tax and automobile licensing fees), he regained the governor's office in 1982 and was successively reelected three more times by substantial margins. A pragmatic, centrist Democrat, he imposed mandatory competency testing for teachers and students and encouraged investment in the state by granting tax breaks to industries. He became a prominent member of the Democratic Leadership Council, a group that sought to recast the party's agenda away from its traditional liberalism and move it closer to the centre of American political life.
 Clinton declared his candidacy for president while still governor of Arkansas. Just before the New Hampshire presidential primary, his campaign was nearly derailed by widespread press coverage of his alleged 12-year affair with an Arkansas woman, Gennifer Flowers. In an interview watched by millions of viewers on the television news program 60 Minutes, Clinton and his wife subsequently admitted to having marital problems. Clinton's popularity soon rebounded, and he scored a strong second-place showing in New Hampshire—a performance for which he labeled himself the “Comeback Kid.” On the strength of his middle-of-the-road approach, his apparent sympathy for the concerns of ordinary Americans (his statement “I feel your pain” was an often-mocked phrase), and his personal warmth, he eventually won the Democratic presidential nomination in 1992. Facing incumbent President George Bush (Bush, George), Clinton and his running mate, Tennessee Senator Al Gore (Gore, Al), argued that 12 years of Republican leadership had led to political and economic stagnation. In November the Clinton-Gore ticket defeated both Bush and independent candidate Ross Perot (Perot, Ross) with 43 percent of the popular vote to 37 percent for Bush and 19 percent for Perot; Clinton defeated Bush in the electoral college by a vote of 370 to 168. (See primary source document: First Inaugural Address (Bill Clinton: Inaugural Address).)
Clinton declared his candidacy for president while still governor of Arkansas. Just before the New Hampshire presidential primary, his campaign was nearly derailed by widespread press coverage of his alleged 12-year affair with an Arkansas woman, Gennifer Flowers. In an interview watched by millions of viewers on the television news program 60 Minutes, Clinton and his wife subsequently admitted to having marital problems. Clinton's popularity soon rebounded, and he scored a strong second-place showing in New Hampshire—a performance for which he labeled himself the “Comeback Kid.” On the strength of his middle-of-the-road approach, his apparent sympathy for the concerns of ordinary Americans (his statement “I feel your pain” was an often-mocked phrase), and his personal warmth, he eventually won the Democratic presidential nomination in 1992. Facing incumbent President George Bush (Bush, George), Clinton and his running mate, Tennessee Senator Al Gore (Gore, Al), argued that 12 years of Republican leadership had led to political and economic stagnation. In November the Clinton-Gore ticket defeated both Bush and independent candidate Ross Perot (Perot, Ross) with 43 percent of the popular vote to 37 percent for Bush and 19 percent for Perot; Clinton defeated Bush in the electoral college by a vote of 370 to 168. (See primary source document: First Inaugural Address (Bill Clinton: Inaugural Address).)Presidency
The Clinton administration got off to a shaky start, the victim of what some critics called ineptitude and bad judgment. His attempt to fulfill a campaign promise to end discrimination against gay men and lesbians (homosexuality) in the military was met with criticism from conservatives and some military leaders—including General Colin Powell (Powell, Colin), the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. In response, Clinton proposed a compromise policy—summed up by the phrase “Don't ask, don't tell”—that failed to satisfy either side of the issue. Clinton's first two nominees for attorney general withdrew after questions were raised about domestic workers they had hired. Clinton's efforts to sign campaign-finance-reform legislation were quashed by a Republican filibuster in the Senate, as was his economic-stimulus package.
Clinton had promised during the campaign to institute a system of universal health insurance. His appointment of his wife to chair the Task Force on National Health Care Reform, a novel role for the country's first lady, was criticized by conservatives, who objected both to the propriety of the arrangement and to Hillary Rodham Clinton's feminist views. They joined lobbyists for the insurance industry, small-business organizations, and the American Medical Association to campaign vehemently against the task force's eventual proposal, the Health Security Act. Despite protracted negotiations with Congress, all efforts to pass compromise legislation failed.
Despite these early missteps, Clinton's first term was marked by numerous successes, including the passage by Congress of the North American Free Trade Agreement, which created a free-trade (free trade) zone for the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Clinton also appointed several women and minorities to significant government posts throughout his administration, including Janet Reno (Reno, Janet) as attorney general, Donna Shalala as secretary of Health and Human Services, Joycelyn Elders as surgeon general, Madeleine Albright (Albright, Madeleine) as the first woman secretary of state, and Ruth Bader Ginsburg (Ginsburg, Ruth Bader) as the second woman justice on the United States Supreme Court (Supreme Court of the United States). During Clinton's first term, Congress enacted a deficit-reduction package—which passed the Senate with a tie-breaking vote from Gore—and some 30 major bills related to education, crime prevention, the environment, and women and family issues, including the Violence Against Women Act and the Family and Medical Leave Act.
In January 1994 Attorney General Reno approved an investigation into business dealings by Clinton and his wife with an Arkansas housing development corporation known as Whitewater. Led from August by independent counsel Kenneth Starr, the Whitewater inquiry consumed several years and more than $50 million but did not turn up conclusive evidence of wrongdoing by the Clintons.
The renewal of the Whitewater investigation under Starr, the continuing rancorous debate in Congress over Clinton's health care initiative, and the liberal character of some of Clinton's policies—which alienated significant numbers of mainstream American voters—all contributed to Republican electoral victories in November 1994, when the party gained a majority in both houses of Congress for the first time in 40 years. A chastened Clinton subsequently tempered some of his policies and accommodated some Republican proposals, eventually embracing a more aggressive deficit-reduction plan and a massive overhaul of the country's welfare system while continuing to oppose Republican efforts to slow the growth of government spending on social programs. Ultimately, mainstream American voters found themselves more alienated by the uncompromising and confrontational behaviour of the new Republicans in Congress than they had been by Clinton, who won considerable public sympathy for his more moderate approach.
 Clinton's initiatives in foreign policy during his first term included a successful effort in September–October 1994 to reinstate Haitian President Jean-Bertrand Aristide (Aristide, Jean-Bertrand), who had been ousted by a military coup in 1991; the sponsorship of peace talks and the eventual Dayton Accords (1995) aimed at ending the ethnic conflict in Bosnia and Herzegovina; and a leading role in the ongoing attempt to bring about a permanent resolution of the dispute between Palestinians and Israelis. In 1993 he invited Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin (Rabin, Yitzhak) and Palestine Liberation Organization chairman Yāsir ʿArafāt (Arafāt, Yāsirʿ) to Washington to sign a historic agreement that granted limited Palestinian self-rule in the Gaza Strip and Jericho. (See primary source document: The Oklahoma City Bombing (Bill Clinton: The Oklahoma City Bombing).)
Clinton's initiatives in foreign policy during his first term included a successful effort in September–October 1994 to reinstate Haitian President Jean-Bertrand Aristide (Aristide, Jean-Bertrand), who had been ousted by a military coup in 1991; the sponsorship of peace talks and the eventual Dayton Accords (1995) aimed at ending the ethnic conflict in Bosnia and Herzegovina; and a leading role in the ongoing attempt to bring about a permanent resolution of the dispute between Palestinians and Israelis. In 1993 he invited Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin (Rabin, Yitzhak) and Palestine Liberation Organization chairman Yāsir ʿArafāt (Arafāt, Yāsirʿ) to Washington to sign a historic agreement that granted limited Palestinian self-rule in the Gaza Strip and Jericho. (See primary source document: The Oklahoma City Bombing (Bill Clinton: The Oklahoma City Bombing).)
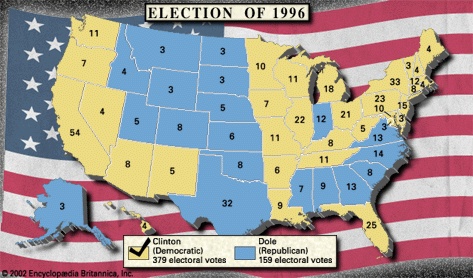 Although scandal was never far from the White House—a fellow Arkansan who had been part of the administration committed suicide; there were rumours of financial irregularities that had occurred in Little Rock; former associates were indicted and convicted of crimes; and rumours of sexual impropriety involving the president persisted—Clinton was handily reelected in 1996, buoyed by a recovering and increasingly strong economy. He captured 49 percent of the popular vote to Republican Bob Dole (Dole, Bob)'s 41 percent and Perot's 8 percent; the electoral vote was 379 to 159. Strong economic growth continued during Clinton's second term, eventually setting a record for the country's longest peacetime expansion. By 1998 the Clinton administration was overseeing the first balanced budget since 1969 and the largest budget surpluses in the country's history. The vibrant economy also produced historically high levels of home ownership and the lowest unemployment rate in nearly 30 years.
Although scandal was never far from the White House—a fellow Arkansan who had been part of the administration committed suicide; there were rumours of financial irregularities that had occurred in Little Rock; former associates were indicted and convicted of crimes; and rumours of sexual impropriety involving the president persisted—Clinton was handily reelected in 1996, buoyed by a recovering and increasingly strong economy. He captured 49 percent of the popular vote to Republican Bob Dole (Dole, Bob)'s 41 percent and Perot's 8 percent; the electoral vote was 379 to 159. Strong economic growth continued during Clinton's second term, eventually setting a record for the country's longest peacetime expansion. By 1998 the Clinton administration was overseeing the first balanced budget since 1969 and the largest budget surpluses in the country's history. The vibrant economy also produced historically high levels of home ownership and the lowest unemployment rate in nearly 30 years.In 1998 Starr was granted permission to expand the scope of his investigation to determine whether Clinton had encouraged a 24-year-old White House intern, Monica Lewinsky, to state falsely under oath that she and Clinton had not had an affair. Clinton repeatedly and publicly denied that the affair had taken place. His compelled testimony, which appeared evasive and disingenuous even to Clinton's supporters (he responded to one question by stating, “It depends on what the meaning of the word is is”), prompted renewed criticism of Clinton's character from conservatives and liberals alike. After conclusive evidence of the affair came to light, Clinton apologized to his family and to the American public. On the basis of Starr's 445-page report and supporting evidence, the House of Representatives in 1998 approved two articles of impeachment, for perjury and obstruction of justice. Clinton was acquitted of the charges by the Senate in 1999. Despite his impeachment, Clinton's job-approval rating remained high.

 In foreign affairs, Clinton ordered a four-day bombing campaign against Iraq in December 1998 in response to Iraq's failure to cooperate fully with United Nations weapons inspectors (the bombing coincided with the start of full congressional debate on Clinton's impeachment). In 1999 U.S.-led forces of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) conducted a successful three-month bombing campaign against Yugoslavia designed to end Serbian attacks on ethnic Albanians in the province of Kosovo. In 1998 and 2000 Clinton was hailed as a peacemaker in visits to Ireland and Northern Ireland, and in 2000 he became the first U.S. president to visit Vietnam since the end of the Vietnam War. He spent the last weeks of his presidency in an unsuccessful effort to broker a final peace agreement between the Israelis and the Palestinians.
In foreign affairs, Clinton ordered a four-day bombing campaign against Iraq in December 1998 in response to Iraq's failure to cooperate fully with United Nations weapons inspectors (the bombing coincided with the start of full congressional debate on Clinton's impeachment). In 1999 U.S.-led forces of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) conducted a successful three-month bombing campaign against Yugoslavia designed to end Serbian attacks on ethnic Albanians in the province of Kosovo. In 1998 and 2000 Clinton was hailed as a peacemaker in visits to Ireland and Northern Ireland, and in 2000 he became the first U.S. president to visit Vietnam since the end of the Vietnam War. He spent the last weeks of his presidency in an unsuccessful effort to broker a final peace agreement between the Israelis and the Palestinians.Shortly before he left office, Clinton was roundly criticized by Democrats as well as Republicans for having issued a number of questionable pardons, including one to the former spouse of a major Democratic Party contributor. In subsequent years Clinton remained active in political affairs and was a popular speaker on the lecture circuit. His autobiography, My Life, was published in 2004. Later that year the William J. Clinton Presidential Library and Museum opened in Little Rock. In 2005, after a tsunami in the Indian Ocean (Indian Ocean tsunami) had caused widespread death and devastation, Clinton was appointed by United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan to serve as a special envoy for relief efforts. In Giving: How Each of Us Can Change the World (2007), Clinton encouraged readers to become involved in various worthy causes.
 In 1999 Hillary Rodham Clinton launched her candidacy for the New York Senate seat being vacated by Democrat Daniel Patrick Moynihan (Moynihan, Daniel Patrick). After a hard-fought race, she defeated Republican Representative Rick Lazio to become the first wife of a U.S. president to win elected office. In 2007 Hillary announced that she would seek the Democratic Party's presidential nomination the following year. However, she lost to Barack Obama (Obama, Barack) in the closely contested primary race.
In 1999 Hillary Rodham Clinton launched her candidacy for the New York Senate seat being vacated by Democrat Daniel Patrick Moynihan (Moynihan, Daniel Patrick). After a hard-fought race, she defeated Republican Representative Rick Lazio to become the first wife of a U.S. president to win elected office. In 2007 Hillary announced that she would seek the Democratic Party's presidential nomination the following year. However, she lost to Barack Obama (Obama, Barack) in the closely contested primary race.Cabinet of President Bill Clinton
Cabinet of President Bill Clinton Cabinet of President Bill ClintonThe table provides a list of cabinet members in the administration of President Bill Clinton.
Additional Reading
Clinton's speeches and statements are collected in Public Papers of the Presidents of the United States, William J. Clinton (1994– ). Biographical works include David Gallen and Philip Martin, Bill Clinton as They Know Him (1994), comprising comments and anecdotes from friends, reporters, and politicians; David Maraniss, First in His Class (1995), which covers his life up to the announcement of his presidential candidacy and is based on almost 400 interviews; and Nigel Hamilton, Bill Clinton: An American Journey (2003).The 1992 presidential campaign is chronicled in John Hohenberg, The Bill Clinton Story: Winning the Presidency (1994), with a brief discussion of Clinton's first year in office. Bob Woodward, The Agenda: Inside the Clinton White House (1994), is a critical study focusing mainly on the economic policy of Clinton's early presidency. Other critical works include Elizabeth Drew, On the Edge (1994); William Bennett, Death of Outrage: Bill Clinton and the Assault on American Ideals (1998); Barbara Olson, The Final Days: The Last Desperate Abuses of Power by the Clinton White House (2001); and, from a different perspective, Christopher Hitchens, No One Left to Lie To: The Triangulations of William Jefferson Clinton (1999). A qualified defense of Clinton's presidency is Joe Klein, The Natural: The Misunderstood Presidency of Bill Clinton (2002). William C. Berman, From the Center to the Edge: The Politics and Policies of the Clinton Presidency (2001), considers the domestic and foreign policies of the Clinton administration in historical perspective.Peter Baker, The Breach: Inside the Impeachment and Trial of William Jefferson Clinton (2001), is a well-researched account by a veteran Washington journalist. Kenneth Starr, The Starr Report: The Findings of Independent Counsel Kenneth W. Starr on President Clinton and the Lewinsky Affair (1998), outlines the case for impeachment and describes Clinton's encounters with Lewinsky in somewhat lurid detail. Critical discussions of the conservative opposition to Clinton include Joe Conason and Gene Lyons, The Hunting of the President: The Ten-Year Campaign to Destroy Bill and Hillary Clinton (2000); and Sidney Blumenthal, The Clinton Wars (2003).
- thing
- Thingvalla, Lake
- Thingvellir
- thin-layer chromatography
- thiol
- Thionville
- thiophene
- thiourea
- Third Department
- Third Estate
- Third International
- Third Punic War
- Third Reich
- Thirkell, Angela
- Thirteen Articles of Faith
- Thirteen Years' War
- Thirty, Battle of the
- Thirty-nine Articles
- thirtysomething
- Thirty Years' War
- Thiruvananthapuram
- Thiry, Marcel
- Thisted
- thistle
- Thistle, The Most Ancient and Most Noble Order of the