coccidioidomycosis
pathology
also called San Joaquin fever or Valley fever
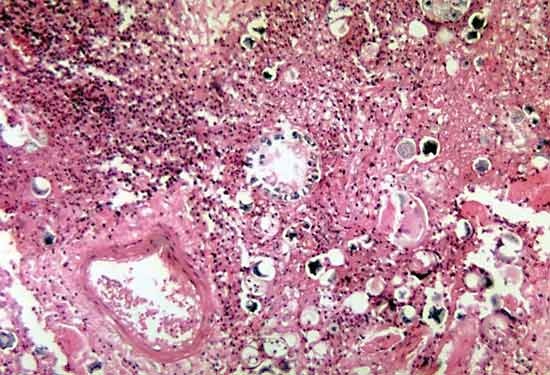 an infectious disease caused by inhalation of spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis. C. immitis can be found in the soil, and most infections occur during dry spells in semiarid regions of the southwestern United States, especially around the San Joaquin Valley, and in the Chaco region of Argentina; dust storms have caused outbreaks of the infection in humans.
an infectious disease caused by inhalation of spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis. C. immitis can be found in the soil, and most infections occur during dry spells in semiarid regions of the southwestern United States, especially around the San Joaquin Valley, and in the Chaco region of Argentina; dust storms have caused outbreaks of the infection in humans.Coccidioidomycosis may be benign and self-limiting, or it may be progressive, spreading throughout the body. In about 50 percent of the cases of benign coccidioidomycosis there are no symptoms. When symptoms occur, they resemble symptoms of influenza or pneumonia: fever, chills, headache, severe pain in the joints, chest pain, and coughing. In a few instances after recovery there are solid lesions or cavities in the lungs. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis, or coccidioidal granuloma, is a progressive form of infection that can result in skin ulcers, many nodules or cavities in the lungs, widespread involvement of lymph nodes, lesions of the bones, and osteomyelitis (infection of the bone). meningitis is usually the immediate cause of death.
Diagnosis of coccidioidomycosis is made by serologic tests or by culture of the organism. Most cases do not require treatment, but patients with widespread disease can be treated with amphotericin B. See also cryptococcosis.
- carbon dioxide
- carbon disulfide
- carbon group element
- carbonic anhydrase
- Carboniferous Period
- Carbon in Earth's crust
- carbonium ion
- carbon monoxide
- carbon monoxide poisoning
- carbon steel
- carbon tetrachloride
- carbonyl group
- carborane
- carboxylic acid
- carbuncle
- carburetor
- carburizing
- Carcassonne
- carcharhinid
- Carchemish
- carcinogen
- carcinoma
- cardamom
- Cardamom Hills
- Cardano, Girolamo