stability
solution of equations
in mathematics, condition in which a slight disturbance in a system does not produce too disrupting an effect on that system. In terms of the solution of a differential equation, a function f(x) is said to be stable if any other solution of the equation that starts out sufficiently close to it when x = 0 remains close to it for succeeding values of x. If the difference between the solutions approaches zero as x increases, the solution is called asymptotically stable. If a solution does not have either of these properties, it is called unstable.
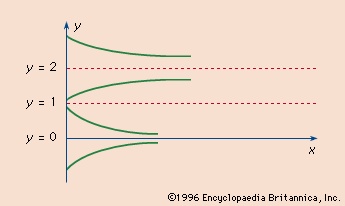 For example, the solution y = ce-x of the equation y′ = -y is asymptotically stable, because the difference of any two solutions c1e-x and c2e-x is (c1 - c2)e-x, which always approaches zero as x increases. The solution y = cex of the equation y′ = y, on the other hand, is unstable, because the difference of any two solutions is (c1 - c2)ex, which increases without bound as x increases. A given equation can have both stable and unstable solutions. For example, the equation y′ = -y(1 - y)(2 - y) has the solutions y = 1, y = 0, y = 2, y = 1 + (1 + c2e-2x)-1/2, and y = 1 - (1 + c2e-2x)-1/2 (see Graph-->
For example, the solution y = ce-x of the equation y′ = -y is asymptotically stable, because the difference of any two solutions c1e-x and c2e-x is (c1 - c2)e-x, which always approaches zero as x increases. The solution y = cex of the equation y′ = y, on the other hand, is unstable, because the difference of any two solutions is (c1 - c2)ex, which increases without bound as x increases. A given equation can have both stable and unstable solutions. For example, the equation y′ = -y(1 - y)(2 - y) has the solutions y = 1, y = 0, y = 2, y = 1 + (1 + c2e-2x)-1/2, and y = 1 - (1 + c2e-2x)-1/2 (see Graph--> ). All these solutions except y = 1 are stable because they all approach the lines y = 0 or y = 2 as x increases for any values of c that allow the solutions to start out close together. The solution y = 1 is unstable because the difference between this solution and other nearby ones is (1 + c2e-2x)-1/2, which increases to 1 as x increases, no matter how close it is initially to the solution y = 1.
). All these solutions except y = 1 are stable because they all approach the lines y = 0 or y = 2 as x increases for any values of c that allow the solutions to start out close together. The solution y = 1 is unstable because the difference between this solution and other nearby ones is (1 + c2e-2x)-1/2, which increases to 1 as x increases, no matter how close it is initially to the solution y = 1.Stability of solutions is important in physical problems because if slight deviations from the mathematical model caused by unavoidable errors in measurement do not have a correspondingly slight effect on the solution, the mathematical equations describing the problem will not accurately predict the future outcome. Thus, one of the difficulties in predicting population growth is the fact that it is governed by the equation y = axce, which is an unstable solution of the equation y′ = ay. Relatively slight errors in the initial population count, c, or in the breeding rate, a, will cause quite large errors in prediction, even if no disturbing influences occur.
- crown and anchor
- Crown Court
- crown gall
- crown glass
- Crown, Henry
- crown jewels
- crown land
- crown of thorns
- Crown of Thorns
- crown-of-thorns starfish
- Crown Point
- crowns of Egypt
- crown vetch
- Crowsnest Pass
- Crowther, Samuel
- Croydon
- Crozet Islands
- Cruces
- crucible
- crucible furnace
- crucible process
- crucifixion
- crucifixion thorn
- Crucé, Émeric
- Cruden Bay