Gaza Strip
territory, Middle East
Introduction
Arabic Qiṭāʿ Ghazzah, Hebrew Reẓuʿat ʿAzza
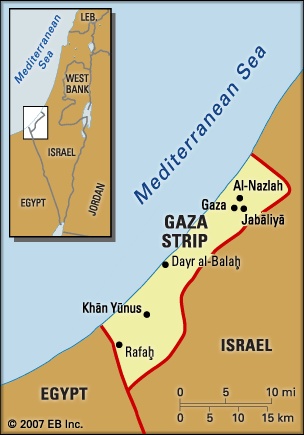 territory occupying 140 square miles (363 square km) along the Mediterranean Sea just northeast of the Sinai Peninsula. The Gaza Strip is unusual in being a densely settled area not recognized as a de jure part of any extant country. The first accurate census, conducted in September 1967, showed a population smaller than had previously been estimated by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) or by Egypt, with nearly half of the people living in refugee camps. Pop. (2006 est.) 1,444,000.
territory occupying 140 square miles (363 square km) along the Mediterranean Sea just northeast of the Sinai Peninsula. The Gaza Strip is unusual in being a densely settled area not recognized as a de jure part of any extant country. The first accurate census, conducted in September 1967, showed a population smaller than had previously been estimated by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) or by Egypt, with nearly half of the people living in refugee camps. Pop. (2006 est.) 1,444,000.Geography
The Gaza Strip is situated on a relatively flat coastal plain. Temperatures average in the mid-50s F (about 13 °C) in the winter and in the upper 70s to low 80s F (mid- to upper 20s C) in summer. The area receives an average of about 12 inches (300 mm) of precipitation annually.
Living conditions in the Gaza Strip are typically poor for a number of reasons: the region's dense and rapidly increasing population (the area's growth rate is one of the highest in the world); inadequate water, sewage, and electrical services; high rates of unemployment; and, from September 2007, sanctions imposed by Israel on the region. Agriculture is the economic mainstay of the employed population, and nearly three-fourths of the land area is under cultivation. The chief crop, citrus fruit, is raised on irrigated lands and is exported to Europe and other markets under arrangement with Israel. Truck crops, wheat, and olives also are produced. Light industry and handicrafts are centred in Gaza, the chief city of the area. In politically stable times, as much as one-tenth of the Palestinian population travels daily to Israel (where they are not allowed to stay overnight) to work in menial jobs. Political tension and outbreaks of violence often led Israeli authorities to close the border for extended periods, putting many Palestinians out of work. As a result, a thriving smuggling industry emerged, based on a network of subterranean tunnels linking parts of the Gaza Strip with neighbouring Egypt. The tunnels provided Palestinians with access to goods such as food, fuel, medicine, electronics, and weapons.
History
After rule by the Ottoman Empire ended there in World War I (1914–18), the Gaza area became part of the League of Nations (Nations, League of) mandate of Palestine under British rule. Before this mandate ended, the General Assembly of the United Nations (UN) in November 1947 accepted a plan for the Arab-Jewish partition of Palestine under which the town of Gaza and an area of surrounding territory were to be allotted to the Arabs. The British mandate ended on May 15, 1948, and on that same day the first Arab-Israeli war (Six-Day War) began. Egyptian forces soon entered the town of Gaza, which became the headquarters of the Egyptian expeditionary force in Palestine. As a result of heavy fighting in autumn 1948, the area around the town under Arab occupation was reduced to a strip of territory 25 miles (40 km) long and 4–5 miles (6–8 km) wide. This area became known as the Gaza Strip. Its boundaries were demarcated in the Egyptian-Israeli armistice agreement of February 24, 1949.
The Gaza Strip was under Egyptian military rule from 1949 to 1956 and again from 1957 to 1967. From the beginning, the area's chief economic and social problem was the presence of large numbers of Palestinian Arab refugees (refugee) living in extreme poverty in squalid camps. The Egyptian government did not consider the area part of Egypt and did not allow the refugees to become Egyptian citizens or to migrate to Egypt or to other Arab countries where they might be integrated into the population. Israel did not allow them to return to their former homes or to receive compensation for their loss of property. The refugees were maintained largely through the aid of the UNRWA (United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East). Many of the younger refugees became fedayeen (Arab guerrillas operating against Israel); their attacks on Israel were one of the causes precipitating the Sinai campaign during the Suez Crisis of 1956, when the strip was taken by Israel. The strip reverted to Egyptian control in 1957 following strong international pressures on Israel.
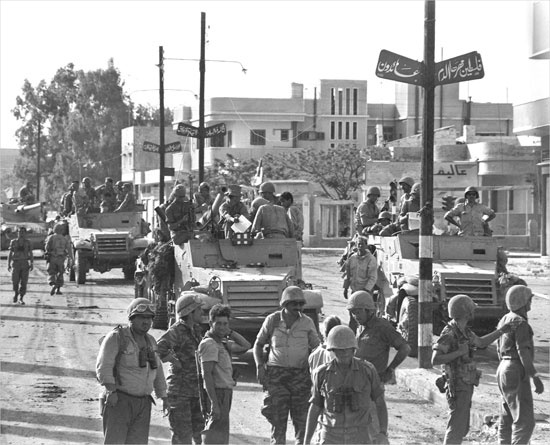

 In the Six-Day War of June 1967, the Gaza Strip was again taken by Israel, which occupied the region for the next quarter century. In December 1987 rioting and violent street clashes between Gaza's Palestinians and occupying Israeli troops marked the birth of an uprising that came to be known as the intifāḍah (Arabic: “shaking off”). In 1994 Israel began a phased transfer of governmental authority in the Gaza Strip to the Palestinian Authority (PA) under the terms of the Oslo Accords that were signed by Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). The fledgling Palestinian government, led by Yāsir ʿArafāt (Arafāt, Yāsirʿ), struggled with such problems as a stagnant economy, divided popular support, stalled negotiations with Israel over further troop withdrawals and territoriality, and the threat of terrorism from militant Muslim groups such as Islamic Jihad and Ḥamās, which refused to compromise with Israel and were intent on derailing the peace process. Beginning in late 2000, a breakdown in negotiations between the PA and Israel was followed by a further, more extreme outbreak of violence, termed the second, or Aqṣā, intifāḍah. In an effort to end the fighting, Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon (Sharon, Ariel) announced in late 2003 a plan that centred on withdrawing Israeli soldiers and settlers from the Gaza Strip. In September 2005 Israel completed the pullout from the territory, and control of the Gaza Strip was transferred to the PA, although Israel continued to patrol its borders and airspace.
In the Six-Day War of June 1967, the Gaza Strip was again taken by Israel, which occupied the region for the next quarter century. In December 1987 rioting and violent street clashes between Gaza's Palestinians and occupying Israeli troops marked the birth of an uprising that came to be known as the intifāḍah (Arabic: “shaking off”). In 1994 Israel began a phased transfer of governmental authority in the Gaza Strip to the Palestinian Authority (PA) under the terms of the Oslo Accords that were signed by Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). The fledgling Palestinian government, led by Yāsir ʿArafāt (Arafāt, Yāsirʿ), struggled with such problems as a stagnant economy, divided popular support, stalled negotiations with Israel over further troop withdrawals and territoriality, and the threat of terrorism from militant Muslim groups such as Islamic Jihad and Ḥamās, which refused to compromise with Israel and were intent on derailing the peace process. Beginning in late 2000, a breakdown in negotiations between the PA and Israel was followed by a further, more extreme outbreak of violence, termed the second, or Aqṣā, intifāḍah. In an effort to end the fighting, Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon (Sharon, Ariel) announced in late 2003 a plan that centred on withdrawing Israeli soldiers and settlers from the Gaza Strip. In September 2005 Israel completed the pullout from the territory, and control of the Gaza Strip was transferred to the PA, although Israel continued to patrol its borders and airspace.In the 2006 PA parliamentary elections, Fatah—which had dominated Palestinian politics since its founding in the 1950s—suffered a decisive loss to Ḥamās, reflecting years of dissatisfaction with Fatah's governance, which was criticized as corrupt and inefficient. Ḥamās's victory prompted sanctions by Israel, the United States, and the European Union, all of which had placed the organization on its official list of terrorist groups. The Gaza Strip was the site of escalating violence between the competing groups, and a short-lived coalition government was ended in June 2007 after Ḥamās took control of the Gaza Strip and a Fatah-led emergency cabinet took control of the West Bank. Despite calls by PA Pres. Mahmoud Abbas (Abbas, Mahmoud) for Ḥamās to relinquish its position in the Gaza Strip, the territory remained under Ḥamās's control.
 In fall 2007 Israel declared the Gaza Strip under Ḥamās a hostile entity and approved a series of sanctions that included power cuts, heavily restricted imports, and border closures. In January 2008, facing sustained rocket assaults into its southern settlements, Israel broadened its sanctions, completely sealing its border with the Gaza Strip and temporarily preventing fuel imports. Later that month, after nearly a week of the intensified Israeli blockade, Ḥamās's forces demolished portions of the barrier along the Gaza Strip–Egypt border (closed since Ḥamās's mid-2007 takeover), opening gaps through which, according to some estimates, hundreds of thousands of Gazans passed into Egypt to purchase food, fuel, and goods unavailable under the blockade. Egyptian Pres. Hosnī Mubārak (Mubārak, Hosnī) temporarily permitted the breach to alleviate civilian hardship in Gaza before efforts could begin to restore the border.
In fall 2007 Israel declared the Gaza Strip under Ḥamās a hostile entity and approved a series of sanctions that included power cuts, heavily restricted imports, and border closures. In January 2008, facing sustained rocket assaults into its southern settlements, Israel broadened its sanctions, completely sealing its border with the Gaza Strip and temporarily preventing fuel imports. Later that month, after nearly a week of the intensified Israeli blockade, Ḥamās's forces demolished portions of the barrier along the Gaza Strip–Egypt border (closed since Ḥamās's mid-2007 takeover), opening gaps through which, according to some estimates, hundreds of thousands of Gazans passed into Egypt to purchase food, fuel, and goods unavailable under the blockade. Egyptian Pres. Hosnī Mubārak (Mubārak, Hosnī) temporarily permitted the breach to alleviate civilian hardship in Gaza before efforts could begin to restore the border.In June 2008, after months of negotiations, Israel and Ḥamās agreed to implement a truce scheduled to last six months; however, this was threatened shortly thereafter as each accused the other of violations, which escalated in the last months of the agreement. When the truce officially expired on December 19, Ḥamās announced that they did not intend to extend it. Broader hostilities erupted shortly thereafter as Israel, responding to sustained rocket fire, mounted a series of air strikes across the region—among the strongest in years—meant to target Ḥamās. After a week of air strikes, Israeli forces initiated a ground campaign into the Gaza Strip amid calls from the international community for a cease-fire. Following more than three weeks of hostilities—in which perhaps more than 1,000 were killed and tens of thousands left homeless—Israel and Ḥamās each declared a unilateral cease-fire.
- RJR Nabisco, Inc.
- R. Kelly
- R.K. Narayan
- Barbara C. Jordan
- Barbara Clementine Harris
- Barbara Hauer Frietschie
- Barbara Heinemann
- Barbara Juliane, Freifrau von Krüdener
- Barbara Juliane Krüdener, Freifrau von
- Barbara Kingsolver
- Barbara Kruger
- Barbara Leigh Smith Bodichon
- Barbara McClintock
- Barbara Pym
- Barbara, Saint
- Barbara Stanwyck
- Barbara Tuchman
- Barbara Walters
- Barbari, Jacopo de'
- Barbarossa
- Barbary
- Barbary macaque
- Barbary pirate
- Barbasetti, Luigi
- barbastelle