Harding, Warren G.
president of United States
in full Warren Gamaliel Harding
born November 2, 1865, Caledonia 【now Blooming Grove】, Ohio, U.S.
died August 2, 1923, San Francisco, California
 29th president of the United States (1921–23). Pledging a nostalgic “return to normalcy” following World War I, Harding won the presidency by the greatest popular vote margin to that time. He died during his third year in office and was succeeded by Vice President Calvin Coolidge. His brief administration accomplished little of lasting value, however, and soon after his death a series of scandals doomed the Harding presidency to be judged among the worst in American history. (For a discussion of the history and nature of the presidency, see presidency of the United States of America.)
29th president of the United States (1921–23). Pledging a nostalgic “return to normalcy” following World War I, Harding won the presidency by the greatest popular vote margin to that time. He died during his third year in office and was succeeded by Vice President Calvin Coolidge. His brief administration accomplished little of lasting value, however, and soon after his death a series of scandals doomed the Harding presidency to be judged among the worst in American history. (For a discussion of the history and nature of the presidency, see presidency of the United States of America.)Born on a farm, Harding was the eldest of eight children of George Tryon and Phoebe Dickerson Harding; his ancestry combined English, Scottish, and Dutch stock. His father later left farming to become a physician. Following a mediocre education at local schools in Ohio and three years at Ohio Central College, Harding tried his hand at several vocations until in 1884 he bought a struggling weekly newspaper in Marion, Ohio, to which he devoted himself. Seven years thereafter, he married Florence Kling De Wolfe (Florence Harding (Harding, Florence)), and she proved instrumental in transforming the Marion Star into a financially successful daily paper. Soon Harding, a man of little discernible intellect or imagination, found himself invited to join leading corporate boards and fraternal organizations. As he began to associate with the state's movers and shakers, he was drawn into Republican Party politics. A handsome man who was always well dressed and well groomed, Harding looked like a leader. It was his outward appearance rather than any internal qualities that contributed most strongly to his political success.
Harding was elected a state senator (1899–1902) and lieutenant governor (1903–04), but he was defeated in his bid for the governorship in 1910. On most issues he allied himself with the conservative (“Old Guard”) wing of the Republican Party, standing firm against U.S. membership in the League of Nations (Nations, League of) and always supporting legislation friendly to business. He achieved national visibility when he was chosen to nominate William Howard Taft at the 1912 Republican Convention, and in his next campaign he was elected U.S. senator (1915–21).

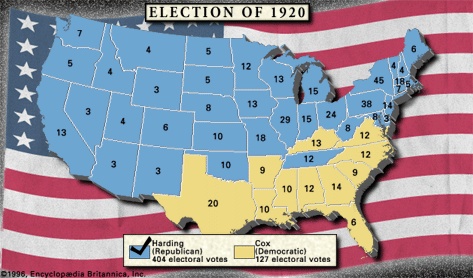 Cabinet of President Warren G. HardingWhen the 1920 Republican Convention deadlocked over its selection of a presidential nominee, party leaders turned—supposedly in a smoke-filled room in Chicago's Blackstone Hotel—to the handsome, genial Ohioan as a compromise candidate. Paired with vice presidential candidate Calvin Coolidge (Coolidge, Calvin), Harding eschewed a speaking tour in favour of a “front porch” campaign in which he read carefully scripted speeches to delegations of visitors at his Marion home. After eight years of the administrations of President Woodrow Wilson (Wilson, Woodrow), during which Americans had been asked to sacrifice greatly to reform the United States and to aid the Allied cause in World War I, Harding's undemanding call for a return to normalcy was precisely what war-weary, disillusioned voters wanted to hear. Harding won the election by the largest landslide to date, capturing some 60 percent of the popular vote. (See primary source documents: Inaugural Address (Warren G. Harding: Inaugural Address) and “Return to Normalcy” (Warren G. Harding: The Return to Normalcy) speech. See also Cabinet of President Warren G. Harding. (Cabinet of President Warren G. Harding))
Cabinet of President Warren G. HardingWhen the 1920 Republican Convention deadlocked over its selection of a presidential nominee, party leaders turned—supposedly in a smoke-filled room in Chicago's Blackstone Hotel—to the handsome, genial Ohioan as a compromise candidate. Paired with vice presidential candidate Calvin Coolidge (Coolidge, Calvin), Harding eschewed a speaking tour in favour of a “front porch” campaign in which he read carefully scripted speeches to delegations of visitors at his Marion home. After eight years of the administrations of President Woodrow Wilson (Wilson, Woodrow), during which Americans had been asked to sacrifice greatly to reform the United States and to aid the Allied cause in World War I, Harding's undemanding call for a return to normalcy was precisely what war-weary, disillusioned voters wanted to hear. Harding won the election by the largest landslide to date, capturing some 60 percent of the popular vote. (See primary source documents: Inaugural Address (Warren G. Harding: Inaugural Address) and “Return to Normalcy” (Warren G. Harding: The Return to Normalcy) speech. See also Cabinet of President Warren G. Harding. (Cabinet of President Warren G. Harding))President-elect Harding appointed to his cabinet a mixture of outstanding leaders and unscrupulous politicians waiting for an opportunity to line their pockets. In the first category were Secretary of State Charles Evans Hughes (Hughes, Charles Evans) and Secretary of Commerce Herbert Hoover (Hoover, Herbert); in the second were Attorney General Harry Daugherty (Daugherty, Harry Micajah) and Secretary of the Interior Albert B. Fall (Fall, Albert Bacon). Harding was a notoriously poor judge of character who expected his appointees to repay his trust with integrity. He was to be deeply disappointed.
The administration got off to a good start when Congress completed an initiative begun in the Wilson administration and established a budget system for the federal government; Charles G. Dawes (Dawes, Charles G.) was appointed first director of the budget. Then in 1921–22, the United States hosted the Washington Naval Disarmament Conference (Washington Conference). Under the leadership of Secretary Hughes, the conference succeeded in getting the world's major powers to agree to halt the arms race in production of large naval vessels.
It was by far the most important achievement of the Harding presidency. Other achievements were more in keeping with the Old Guard Republican views with which Harding had long been associated: a higher protective tariff (Fordney-McCumber), lower taxes on business, and a sharp reduction in the number of immigrants allowed to enter the United States from southern and eastern Europe.
Early in 1923, Attorney General Daugherty (Daugherty, Harry Micajah) disclosed to Harding that Charles Forbes, director of the Veterans Bureau, had been illegally selling government medical supplies to private contractors. After violently berating Forbes in the White House, Harding allowed him to leave the country to escape prosecution. Shortly thereafter Charles Cranmer, general counsel of the Veterans Bureau, committed suicide. Ten weeks later Jesse Smith, Daugherty's private secretary, also committed suicide—one day after a long conversation with Harding in the White House. Rumours had been circulating that Smith and a group known as the “ Ohio Gang” had been profiting from a variety of corrupt activities.
By the spring of 1923, Harding was visibly distraught at what he regarded as the betrayal of his friends who were taking advantage of his kindliness and lax administration. He sought escape from Washington in mid-June by taking a trip to Alaska with his wife and a large entourage. On his way home at the end of July, the president complained of abdominal pain, but he seemed to rally as he rested at a San Francisco hotel. On the evening of August 2, however, as his wife read to him from a magazine, Harding suddenly died from either a heart attack or stroke.
The nation plunged into mourning, little suspecting that the beloved leader they eulogized as “an ideal American” would soon be revealed to be head of the most corrupt administration in the nation's history. Senate investigations uncovered Forbes's illegal financial dealings at the Veterans Bureau and pointed to Daugherty's collusion with the Ohio Gang. Far more serious was the unfolding of the Teapot Dome Scandal. In 1921 Interior Secretary Albert Fall (Fall, Albert Bacon) had persuaded Harding to transfer authority over two of the nation's most important oil reserves—Elk Hills in California and Teapot Dome in Wyoming—from the Navy Department to the Department of the Interior. Fall then leased these reserves to private oil companies, netting for himself several hundreds of thousands of dollars in gifts and loans. Fall and Forbes later received jail sentences for their crimes; Daugherty twice went on trial, the first resulting in a hung jury and the second in a not guilty verdict.
Harding was never personally implicated in the scandals, but he was aware of the actions of Forbes, Smith, and the Ohio Gang and failed to bring their corruption to light. By the mid-1920s, the public began to regard Harding as a man who simply did not measure up to the responsibilities of his high office. Rumours of his heavy drinking in the White House (at a time when Prohibition was the law of the land) and of his involvement in extramarital affairs further degraded his reputation. In 1927 Nan Britton published The President's Daughter, in which she claimed that in 1919 she had given birth to a child fathered by the future president. While historians have challenged the veracity of this and other allegations made against Harding, most of them agree that he was the least capable of the nation's chief executives.
Additional Reading
Samuel Hopkins Adams, Incredible Era: The Life and Times of Warren Gamaliel Harding (1939, reprinted 1979), although dated, remains a highly useful biography. More recent treatments are Andrew Sinclair, The Available Man (1965); Francis Russell, The Shadow of Blooming Grove (1968); and Robert K. Murray, The Harding Era (1969). Harding's administration is assessed in Robert K. Murray, The Politics of Normalcy: Governmental Theory and Practice in the Harding-Coolidge Era (1973); Eugene P. Trani and David L. Wilson, The Presidency of Warren G. Harding (1977, reissued 1985); and Charles L. Mee, Jr., The Ohio Gang (1981). Richard G. Frederick (compiler), Warren G. Harding: A Bibliography (1992), contains over 3,000 annotated entries.
- Reiyū-kai
- Reizei Tamechika
- Rejang
- Rejlander, O.G.
- rejoneo
- relapsing fever
- Relationship of a Performer to His Audience, Table
- Relationship of positions in the zodiac to aspects of life
- Relationship of the Medium to the Performance, Table
- Relative abundances of the elements
- relative aperture
- Relative composition of plasma and urine in normal men
- relative humidity
- relative volumes occupied by some cellular compartments in a typical liver cell
- relativistic mass
- relativistic mechanics
- relativity
- relaxation phenomenon
- relaxin
- relay
- relay race
- R.E. Lee: Letter of Resignation
- Reles, Abe
- relic
- relief