Hess's law of heat summation
chemistry
rule first enunciated by Germain Henri Hess (Hess, Germain Henri), a Swiss-born Russian chemist, in 1840, stating that the heat absorbed or evolved in any chemical reaction is a fixed quantity and is independent of the path of the reaction or the number of steps taken to obtain the reaction. Hess's law is a consequence of the first law of thermodynamics and need not be considered a separate thermodynamic law; in thermochemistry, however, it retains its identity because of its importance as the basis for calculating heats of reactions. Hess's law is exemplified by the calculation of the heat of formation of carbon dioxide from its elements (carbon 【C】 and oxygen 【O】). This reaction is represented by
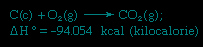
In the equation (c) and (g) denote crystalline and gaseous, respectively; ΔH° is called the heat of formation.
In accordance with Hess's law, the heat of formation of carbon dioxide is the same, whether it occurs in one reaction as represented by the equation above or in two steps as represented by the equations given below:
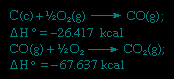
The sum of the above equations is:
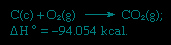
Thus Hess's law allows the calculation of the heats of various reactions from the heats of other reactions.
- tabby
- Tabernacle
- tabes dorsalis
- Tabinshwehti
- tabl
- tabla
- Tablas de Daimiel National Park
- tablature
- table
- Table 1 Annual Average Rates of Growth of Manufacturing Output, 1980-94
- Table 1 Changes in Consumer Prices in Less-Developed Countries
- Table 1 Changes in Output in Less-Developed Countries
- Table 1 Consumer Prices in OECD Countries
- Table 1 Livestock Inventories and Meat Production in Major Producing Countries
- Table 1 Real Gross Domestic Product per Employed Person
- Table 1 Real Gross Domestic Products of Selected OECD Countries
- Table 1 Selected Indexes of World Agricultural and Food Production
- Table 1 Selected Major World Stock Market Indexes
- Table 1 Selected Major World Stock Market Indexes 8
- Table 1 Shipment of Food Aid in Cereals
- Table 1 Standardized Unemployment Rates in Selected Developed Countries
- Table 1 U.S. Corporate Bond Yields
- Table 1 U.S. Government Long-Term Bond Yields
- Table 1 U.S. Stock Market Prices
- Table 1 World Cereal Supply and Distribution