pressure gauge
instrument
instrument for measuring the condition of a fluid (liquid or gas) that is specified by the force that the fluid would exert, when at rest, on a unit area, such as pounds per square inch or newtons per square centimetre.
The reading on a gauge, which is the difference between two pressures, is known as the gauge pressure. If the lower of the pressures is the pressure of the atmosphere, the total, or absolute, pressure is the sum of the gauge and atmospheric pressures.
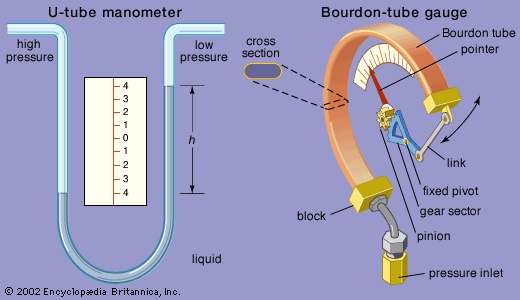 The simplest device for measuring static pressures up to about 90 pounds per square inch (62 newtons per square cm) is a U-tube manometer (shown in the figure-->
The simplest device for measuring static pressures up to about 90 pounds per square inch (62 newtons per square cm) is a U-tube manometer (shown in the figure--> ), in which one column of a liquid in the tube is open to a region of high pressure and the other column to a region of low pressure. The differential pressure is indicated by the difference in level between the two columns of liquid, and it is calculated as the difference in level multiplied by the density of the liquid. The manometer liquids most commonly used are mercury, oil, alcohol, and water.
), in which one column of a liquid in the tube is open to a region of high pressure and the other column to a region of low pressure. The differential pressure is indicated by the difference in level between the two columns of liquid, and it is calculated as the difference in level multiplied by the density of the liquid. The manometer liquids most commonly used are mercury, oil, alcohol, and water. The Bourdon-tube gauge, invented about 1850, is still one of the most widely used instruments for measuring the pressure of liquids and gases of all kinds, including steam, water, and air up to pressures of 100,000 pounds per square inch (70,000 newtons per square cm). The device (also shown in the figure-->
The Bourdon-tube gauge, invented about 1850, is still one of the most widely used instruments for measuring the pressure of liquids and gases of all kinds, including steam, water, and air up to pressures of 100,000 pounds per square inch (70,000 newtons per square cm). The device (also shown in the figure--> ) consists of a flattened circular tube coiled into a circular arc. One end is soldered to a central block and is open to the fluid whose pressure is to be measured; the other end is sealed and coupled to the pointer spindle. When the pressure inside the tube is greater than the outside pressure, the tube tends to straighten, thus turning the pointer. The pressure is read on a circular scale.
) consists of a flattened circular tube coiled into a circular arc. One end is soldered to a central block and is open to the fluid whose pressure is to be measured; the other end is sealed and coupled to the pointer spindle. When the pressure inside the tube is greater than the outside pressure, the tube tends to straighten, thus turning the pointer. The pressure is read on a circular scale.Metal bellows and diaphragms are also used as pressure-sensing elements. Because of the large deflections for small pressure changes, bellows instruments are particularly suitable for pressures below atmospheric. Two corrugated diaphragms sealed at their edges to form a capsule, which is evacuated, are used in aneroid barometers to measure atmospheric pressure (see altimeter).
These instruments employ mechanical linkages and so are primarily useful for measuring static pressures or pressures that change slowly. For rapidly changing pressures, electrical pressure transducers that convert pressure to an electrical signal are more suitable. These include strain gauges; moving contact resistance elements; and inductance, reluctance, capacitative, and piezoelectric devices. Electromechanical transducers (electromechanical transducer), which are used in hydraulic controllers, where speed and power are needed, convert changes in pressure of fluid to electrical signals.
- Dhyan Chand
- dhyāna
- Dhyāni-Buddha
- Dhū al-faqār
- Dhū an-Nūnid Dynasty
- di
- diabase
- Diabelli, Anton
- diabetes
- diabetes insipidus
- diabetes mellitus
- diablerie
- Diablo
- Diablo Range
- Dia Center for the Arts
- diaconate
- Diadectes
- Diadochus Of Photice
- diadochy
- diaeresis
- diagenesis
- Diaghilev, Sergey Pavlovich
- diagnosis
- diagnostic imaging
- Diaguita