Botswana
Introduction
officially Republic of Botswana, formerly Bechuanaland,
Botswana, flag of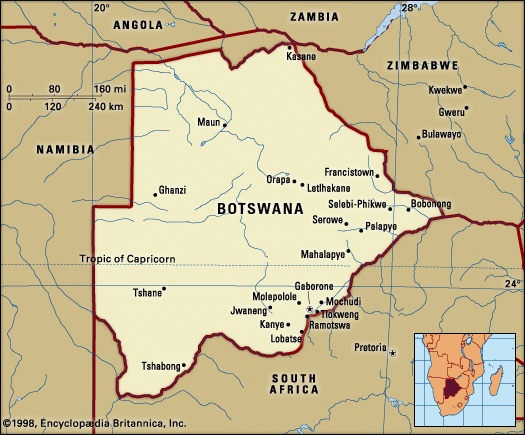
 country in the centre of southern Africa. The territory is roughly square—approximately 600 miles from north to south and 600 miles from east to west—with its eastern side protruding into a sharp point. Its eastern and southern borders are marked by river courses and an old wagon road; its western borders are lines of longitude and latitude through the Kalahari, and its northern borders combine straight lines with a river course. The capital is Gaborone (until 1969 spelled Gaberones—i.e., Gaborone's town), which was founded in 1964.
country in the centre of southern Africa. The territory is roughly square—approximately 600 miles from north to south and 600 miles from east to west—with its eastern side protruding into a sharp point. Its eastern and southern borders are marked by river courses and an old wagon road; its western borders are lines of longitude and latitude through the Kalahari, and its northern borders combine straight lines with a river course. The capital is Gaborone (until 1969 spelled Gaberones—i.e., Gaborone's town), which was founded in 1964.

 country in the centre of southern Africa. The territory is roughly square—approximately 600 miles from north to south and 600 miles from east to west—with its eastern side protruding into a sharp point. Its eastern and southern borders are marked by river courses and an old wagon road; its western borders are lines of longitude and latitude through the Kalahari, and its northern borders combine straight lines with a river course. The capital is Gaborone (until 1969 spelled Gaberones—i.e., Gaborone's town), which was founded in 1964.
country in the centre of southern Africa. The territory is roughly square—approximately 600 miles from north to south and 600 miles from east to west—with its eastern side protruding into a sharp point. Its eastern and southern borders are marked by river courses and an old wagon road; its western borders are lines of longitude and latitude through the Kalahari, and its northern borders combine straight lines with a river course. The capital is Gaborone (until 1969 spelled Gaberones—i.e., Gaborone's town), which was founded in 1964.
 Botswana is bounded by Namibia to the west and north (the Caprivi Strip), Zambia and Zimbabwe to the northeast, and South Africa to the southeast and south. The Zambezi River border with Zambia is only several hundred yards long. The border along the main channel of the Chobe River up to the Zambezi is disputed with Namibia. The point at which the borders of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe meet in the middle of the river has therefore never been precisely determined. Within the confines of Botswana's borders is a rich variety of wildlife, including many species of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
Botswana is bounded by Namibia to the west and north (the Caprivi Strip), Zambia and Zimbabwe to the northeast, and South Africa to the southeast and south. The Zambezi River border with Zambia is only several hundred yards long. The border along the main channel of the Chobe River up to the Zambezi is disputed with Namibia. The point at which the borders of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe meet in the middle of the river has therefore never been precisely determined. Within the confines of Botswana's borders is a rich variety of wildlife, including many species of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.Before its independence in 1966, Botswana was a British protectorate known as Bechuanaland. It was also one of the poorest and least-developed states in the world. The country is named after its dominant ethnic group, the Tswana, or Batswana (“Bechuana” in older variant orthography). The national language is Setswana (or Sechuana), and the official language is English.
Since its independence the Republic of Botswana has gained international stature as a peaceful and increasingly prosperous democratic state. It is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth, the African Union (AU), and the Southern African Development Community (SADC). The secretariat of SADC is housed in Gaborone. Botswana is also a member (with South Africa) of the Southern African Customs Union.
The land
Relief and drainage
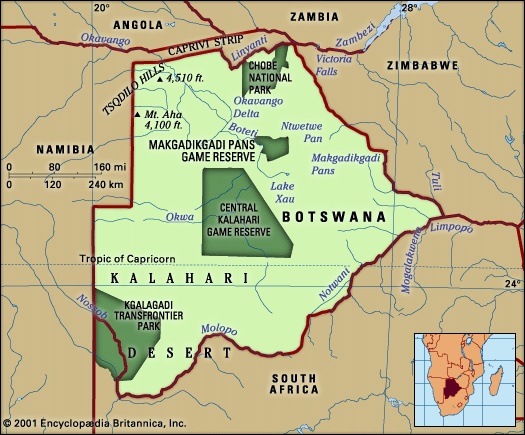 Botswana extends from the Chobe River (which drains through the Zambezi to the Indian Ocean) in the north to the Molopo River (part of the Orange River system, which flows into the Atlantic) in the south. To the east it is bordered by the Limpopo River and its tributaries, the Ngotwane (Notwani), Marico (Madikwe), and Shashe.
Botswana extends from the Chobe River (which drains through the Zambezi to the Indian Ocean) in the north to the Molopo River (part of the Orange River system, which flows into the Atlantic) in the south. To the east it is bordered by the Limpopo River and its tributaries, the Ngotwane (Notwani), Marico (Madikwe), and Shashe.The country has a mean altitude of 3,300 feet and consists largely of a sand-filled basin, with gently undulating plains rising to highlands in neighbouring countries. The highest point is 4,888 feet (1,490 metres) in the hills north of Lobatse in southeastern Botswana; the lowest point is 2,170 feet at the country's easternmost point, in the Limpopo valley.
The country is divided into three main environmental regions. The hardveld region consists of rocky hill ranges and areas of shallow sand cover in eastern Botswana. The sandveld region is the area of deep Kalahari sand covering the rest of the country. The third region consists of ancient lake beds superimposed on the northern sandveld in the lowest part of the Kalahari Basin.
Geologic exploration has been limited by the depth and extent of Kalahari sand covering the surface geology. The rock groups underlying most of the sandveld are therefore the least-known but appear to be the youngest, belonging to the Karoo (Karroo) System (Karoo System), formed 290 to 208 million years ago. Elsewhere, Precambrian rock formations predominate. The surface geology of the eastern hardveld, exposed in its hill ranges, largely consists of basement complex rocks (more than 2.5 billion years old) intruding from northern South Africa and southern Zimbabwe. This complex is known to extend into younger rock formations (2.5 to 1.2 billion years old) in the extreme southern sandveld, while rocks of the Ghanzi and Damara groups (1.2 billion to 570 million years old) extend across the northwest corner of the country into northern Namibia.
 Drainage through the marshes of the Okavango delta is complex and imperfectly understood. The perennial Okavango River runs southward into its delta across the Caprivi Strip from the highlands of Angola. Most of its water evaporates from the 4,000 square miles of the delta wetlands. Floodwater reaches down through the eastern side of the marshes to the Boteti River, which flows sporadically to Lake Xau (Dow) and the Makgadikgadi Pans (also roughly 4,000 square miles in area). Less and less water has been flowing through the western side of the Okavango marshes during the 20th century, so that 70-square-mile Lake Ngami (Ngami, Lake)—famous a century ago—is today dry and almost unrecognizable as a lake. Meanwhile, the eastern Makgadikgadi Pans are annually flooded by the otherwise ephemeral Nata River from the Zimbabwe highlands, while the southern tributaries of the pans are now dry fossil valleys.
Drainage through the marshes of the Okavango delta is complex and imperfectly understood. The perennial Okavango River runs southward into its delta across the Caprivi Strip from the highlands of Angola. Most of its water evaporates from the 4,000 square miles of the delta wetlands. Floodwater reaches down through the eastern side of the marshes to the Boteti River, which flows sporadically to Lake Xau (Dow) and the Makgadikgadi Pans (also roughly 4,000 square miles in area). Less and less water has been flowing through the western side of the Okavango marshes during the 20th century, so that 70-square-mile Lake Ngami (Ngami, Lake)—famous a century ago—is today dry and almost unrecognizable as a lake. Meanwhile, the eastern Makgadikgadi Pans are annually flooded by the otherwise ephemeral Nata River from the Zimbabwe highlands, while the southern tributaries of the pans are now dry fossil valleys.The Molopo River and its Ramatlhabama tributary, on the southern border of Botswana with a course flowing into the Orange River, today rarely flood more than 50 miles from their sources. Most rivers in Botswana are ephemeral channels, usually not flowing above ground except in the summer rainy season. The two great exceptions to this rule are vigorous channels fed by the rains of central Africa—the Okavango River above its delta and the Chobe River flowing through its marshes along the northern border to join the Zambezi above the Victoria Falls.
Soils
The soils of the eastern hardveld consist of moderately dry red loamy mokata soils on the plains, or mixed chalky and sandy chawana soils, with brownish rocky seloko soils on and around hills. Seloko soils are considered best for grain crops. The fertility of all soils is limited by the amount of rainfall, which is sometimes inadequate on the hardveld and regularly unable to support any cultivation on the sandveld.
The alluvial soils of the ancient lake beds include gray loamy soils in the wetlands, gray-green saline soils on the pans, gray clayish soils to yellowish sandy soils around the wetlands, and very chalky light gray soils around the pans. There are also areas of gray to black cracking clay in former wet areas, such as those around Pandamatenga.
Climate
The annual climate ranges from months of dry temperate weather during winter to humid subtropical weather interspersed with drier periods of hot weather during summer. In summer (which lasts from October to March) temperatures rise to about 93 °F (34 °C) in the extreme north and southwest, the warmest parts of the country. In winter (which lasts from April to September), there is frequent frost at night, and temperatures may fall to near freezing in some high-altitude areas during the day. Summer is heralded by a windy season, carrying dust from the Kalahari, from about late August to early October. Annual rainfall, brought by winds from the Indian Ocean, averages 18 inches (460 millimetres), representing a range from 25 inches in the extreme northeast to less than 5 inches in the extreme southwest. The rains are almost entirely limited to summer downpours between December and April, which also mark the season for plowing and planting. Cyclic droughts, often lasting up to five or six years in every two decades, can limit or eliminate harvests and reduce livestock to starvation.
Plant and animal life
The Kalahari sandveld has often been called “thirstland” to distinguish it from true desert. Even in its southwestern corner, where there are some bare sand dunes, the vegetation is more characteristic of dry steppe than desert.
 The general vegetation of the country is savanna grassland with yellow or light brown grass cover (turning green after rains) and woody plants. The savanna ranges from acacia shrub savanna in the southwest through acacia thornbush and tree savanna “parkland” into denser woodland and eventually forest as one moves north and east. Croton and Combretum tree savanna is found on the rocky hills of the eastern hardveld. Acacia tree savanna merges northward into mopane (African ironwood) savanna woodland. Mopane woodland covers most of the northern and eastern third of the country, with the exception of the open grasslands immediately surrounding the Okavango delta and Makgadikgadi Pans.
The general vegetation of the country is savanna grassland with yellow or light brown grass cover (turning green after rains) and woody plants. The savanna ranges from acacia shrub savanna in the southwest through acacia thornbush and tree savanna “parkland” into denser woodland and eventually forest as one moves north and east. Croton and Combretum tree savanna is found on the rocky hills of the eastern hardveld. Acacia tree savanna merges northward into mopane (African ironwood) savanna woodland. Mopane woodland covers most of the northern and eastern third of the country, with the exception of the open grasslands immediately surrounding the Okavango delta and Makgadikgadi Pans. Animal life is extremely varied in a thirstland environment. About 150 species of mammals are found in Botswana. These range from 30 species of bats and 27 of rodents to more than 30 species of large mammals. Birdlife is prolific, with more than 460 species. Botswana has a great variety of reptiles and amphibians, of which more than 200 species have been described in detail. The principal fish, in the rivers of the north, are tilapia (African bream), catfish, and the tigerfish, which is famous for its ferocious resistance to being caught on a line.
Animal life is extremely varied in a thirstland environment. About 150 species of mammals are found in Botswana. These range from 30 species of bats and 27 of rodents to more than 30 species of large mammals. Birdlife is prolific, with more than 460 species. Botswana has a great variety of reptiles and amphibians, of which more than 200 species have been described in detail. The principal fish, in the rivers of the north, are tilapia (African bream), catfish, and the tigerfish, which is famous for its ferocious resistance to being caught on a line. There are several national parks and game reserves in Botswana, including the Central Kalahari Game Reserve—the largest reserve in the country and home to such animals as lions, black-backed jackals, elephants, foxes, ostriches, springboks, and zebras. Others include Chobe National Park, the Makgadikgadi Pans Game Reserve, and the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, a conservation area jointly managed by Botswana and South Africa.
There are several national parks and game reserves in Botswana, including the Central Kalahari Game Reserve—the largest reserve in the country and home to such animals as lions, black-backed jackals, elephants, foxes, ostriches, springboks, and zebras. Others include Chobe National Park, the Makgadikgadi Pans Game Reserve, and the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, a conservation area jointly managed by Botswana and South Africa.Settlement patterns
The human and livestock population of Botswana is concentrated around the hill ranges of the eastern hardveld and along the perennial rivers of the north. Almost half of the population is rural and lives in settlements that range from small, scattered sites that are sparsely populated to villages of more than 1,000 people to traditional towns with tens of thousands of people.
The typical rural settlement and land use pattern of the eastern hardveld in the past may be characterized as having been concentric circles around a concentrated village nucleus. The family had a home base in the village, where the majority of its members spent most of the year. In the appropriate season it cultivated lands (fields) within one or two days' walk from the village. The family cattle, on the other hand, were pastured for most of the year at “cattle-posts” a number of days' walk from the village. Finally, beyond the cattle-posts there were hunting lands.
The villages and traditional towns of Botswana are still basically laid out around the kgotla (courtyard) and cattle kraal (corral) of traditional rulers and are subdivided into wards, each of which mimics the village or town plan with its own central kgotla and kraal. But, especially since the 1970s, traditional settlements have been sliced through by modern roads and facilities such as schools and offices, as well as shopping malls and bars. Traditional architecture of thatch roofing and clay walls has given way to corrugated metal roofing and brick walls.
Two of the seven larger towns of Botswana, Francistown (1897) and Lobatse (1902), originated as small urban centres on the railway for white farming communities. Both began to develop in size and function in the 1950s, as employment in nonagricultural services expanded. Gaborone, the capital city, was founded in 1964; since then its population has grown to more than 150,000. Selebi-Phikwe (1971) and Jwaneng (1979) constitute the only substantial mining towns; the smaller diamond town of Orapa (1971) is under company control behind high security fences. The newest mining town, Sua (1991), is based on the soda-ash deposits of the eastern Makgadikgadi Pans.
The people
Ethnic groups
The dominant ethnic identity in Botswana is Tswana. The country's whole population is characterized as Batswana (singular, Motswana) whatever their ethnic origin. Though no attempt to count population by ethnic origin has been made since 1946, probably less than half the population is “ethnic Tswana” by origin. There are far greater numbers of ethnic Tswana in South Africa.
Tswana ethnic dominance (“Tswanadom”) in Botswana can be dated to the eight Tswana states which ruled most of the area in the 19th century. Under British colonial rule, the populations of these states were given the official status of “tribes,” a term still used officially today.
Within southeastern Botswana the other main ethnic identity besides Tswana, that of the Khalagari (Western Sotho), has become so incorporated as to be almost indistinguishable from the Tswana. Even their name is now usually rendered in the Tswana form as “Kgalagadi.”
The Ngwato of east-central Botswana constitute the largest traditional “tribal” state but are probably less than one-fifth ethnic Tswana by origin. The major incorporated ethnic groups are Khalagari, Tswapong and Birwa (both Northern Sotho), and Kalanga (Western Shona). With larger numbers to the east in Zimbabwe, some Kalanga have resisted full incorporation.
The Tawana state of northwestern Botswana can be seen as the least successful in incorporating other ethnic groups. Most of its population is Yei and Mbukushu by origin, related to riverine peoples in the Caprivi Strip, Angola, and Zambia to the north. Smaller numbers of Mbanderu and Herero have greater numbers of close relatives across the border in Namibia. The Subiya along the Chobe, closely related to people in the Caprivi Strip and Zambia, were excluded from the Tawana “tribal” reserve by the British.
Small scattered groups of Khoisan people inhabit the southwestern districts of Botswana, as well as being incorporated with other ethnic groups. The Khoisan speak languages characterized as Khoe, or Khwe, and San. They include communities with their own headmen and livestock, as well as poorer groups employed by Tswana and white cattle farmers.
White settlement in Botswana, consisting of some Afrikaners and fewer English settled in border farms, totaled fewer than 3,000 people in the colonial period.
Religious groups
Christianity, brought by missionaries from the south such as David Livingstone, was established as the official religion of the eight Tswana states by the end of the 19th century. Indigenous religious and medical practices, notably respect for patriarchal ancestors, either declined or were assimilated within popular Christian beliefs. Allegiance to the old state churches, notably those of the Congregationalists (London Missionary Society), has declined since the 1950s. The two most active and popular churches are the Zion Christian church (based in South Africa) among the working class and the Roman Catholic church among the middle class. There are also numerous other small Zionist and Apostolic churches in rural villages, as well as United Reformed (Congregational and Methodist), Dutch Reformed, and Anglican churches, and predominantly expatriate Muslim, Quaker, Hindu, and Bahāʿī congregations.
Demographic trends
After six previous censuses of variable quality, Botswana had its first systematic national census in 1964. Total population was estimated at 550,000, with 35,000 absentees—mostly adult male workers in South Africa. Since 1964, the population has grown at about 3.4 percent a year, thus exceeding 1,000,000 in the early 1980s and doubling every 20 years. Meanwhile, the rate of labour migration abroad has been reduced by a combination of restrictions by South Africa and increased employment opportunities at home. Between the 1950s and the 1970s Botswana also provided a home and eventual citizenship for significant numbers of refugees from South Africa, Angola, and Zimbabwe.
The age and gender composition of the country is weighted by an increasingly youthful population: approximately one-fifth are under age 5, and nearly half are younger than age 15. Females exceed males in age groups over 15; below that age the gender ratio is more or less equal because of recently reduced male infant mortality. The 1991 census showed improved life expectancy of 63.1 years at birth for females and 57 years for males, over the 1981 figures of 61.2 and 54.7 years, respectively. Botswana is also the first African country to experience a falling birth rate in response to improved life expectancy.
The economy
Botswana has a free market economy with a strong tradition of central government planning to provide infrastructure for private investment. The economy has grown rapidly since the mid-1960s, with the gross domestic product per capita increasing from less than $50 to more than $1,000 by the mid-1980s.
Less than a quarter of the adult workforce is in formal paid employment. Relatively few rural households benefit from cattle sales: almost half of them have no cattle, and less than 10 percent own about half of the country's cattle (averaging 100 head each). Few households produce enough crops to cover even their own subsistence, let alone to sell on the market. Four out of five rural households survive on the income of a family member in town or abroad. That still leaves a significant number of rural households, usually female-headed, with no source of income known to statisticians.
State revenues reaped from mining development have been spent on basic rural infrastructure and welfare services and on schemes to subsidize the development of cattle and crop production, which have in general benefited the richer rural households. Trade unionism, restricted by legislation, is as yet underdeveloped in Botswana.
Resources
Diamonds (diamond), the major economic resource of the country, have been exploited on a large scale since 1970. They are mined from some of the world's largest diamond pipes at Orapa and Letlhakane, south of the Makgadikgadi pans, and at Jwaneng in the southeastern sandveld. Nickel and copper have been mined at Selebi-Phikwe near the Motloutse River since 1974. Coal is mined for power generation at Morupule near Palapye. Botswana's other major proven mineral resources are salt and soda ash, which was fully exploited at Sua on the eastern Makgadikgadi pans from 1991.
Surface water resources are limited to the wetlands and perennial rivers in the north and three major dam lakes at Gaborone, Shashe, and Mopipi (serving Orapa). Plans are under active consideration to canalize water through the Okavango wetlands toward Mopipi via a holding dam at Maun. Underground water is tapped in large quantities near Palapye and south of Gaborone.
Agriculture
Most of the population is partially engaged in agricultural production, but there is little land suitable for productive cultivation. Agricultural output constitutes less than one-tenth of gross national product, and most of that is in the form of livestock production for urban and export markets. Grain production (mostly sorghum and corn) fell short of national consumption for most of the 20th century, and foodstuffs from South Africa and Zimbabwe are Botswana's major import commodities. Fishing and forestry production are limited and largely confined to the extreme north.
Botswana, with terrain comparable to Texas or Australia, is traditionally seen as cattle country. Given sufficient water and pasture and controls on the spread of hoof-and-mouth disease from wetland buffalo, it is a healthy environment for raising high-bulk, high-quality indigenous beef cattle. The government has invested heavily in disease prevention, modern abattoirs, and support services to cattle producers. Because of drought, the national herd has fluctuated between one million and three million head since the 1960s, with an export offtake of up to a quarter of a million per annum and a growing internal market. Various schemes—so far unsuccessful—have been attempted to improve range management. Meanwhile, the main export market for beef, the European Community, has become increasingly unreliable.
Industry
Industrial development in Botswana has been limited by the high costs of power and water, the lack of appropriate management and labour skills, and the small domestic market. Manufacturing activity up to the 1980s largely consisted of meat processing at Lobatse in the south. In the early 1980s capital and textile production were transferred from Zimbabwe to nearby Francistown in Botswana, and diamond sorting and service industries grew in the booming capital city, Gaborone.
The national electric power grid, serving mines and eastern towns, is based on a large coal-powered generating station at Morupule near Palapye, supplemented by connections to the Zimbabwean and South African national grids.
Tourists are attracted to Botswana by relatively unpopulated and “remote” wetland and thirstland environments. Government policy is to limit the density and environmental impact of tourism through licensing of a limited number of high-cost safari companies.
Finance
The Botswana economy is regulated by a central bank, the Bank of Botswana, and a strong ministry of finance and development planning. There are two major multinational commercial banks, with branch operations that extend to village level. Botswana has had the unusual problems, for a developing country, of a government budget surplus running into billions of dollars and excess capital lying unutilized in private banks. The budget surplus and bank liquidity were partially depleted by diversion into a construction boom in the late 1980s and early '90s, including infrastructure for new mining operations and military airports. A small stock exchange has been set up. The economy, from diamonds to nickel-copper to soda ash and construction, remains dominated by South Africa's De Beers–Anglo American Corporation conglomerate.
Trade
Botswana sends the great bulk of its exports to the world market beyond Africa, mainly to Europe and North America. It takes nearly three-fourths of its imports from South Africa, its neighbour with a gross national product vastly larger than that of Botswana. Imports consist of machinery and transport equipment, food products, and consumer goods, often manufactured or serviced by multinational companies based in South Africa. From Zimbabwe, Botswana imports mainly food products. Other imports from the rest of the world consist largely of high-technology equipment.
Botswana is joined in a customs union with South Africa, Lesotho, Swaziland, and Namibia (the Southern African Customs Union) and, along with the other countries of southern Africa, is a member of the Southern African Development Community (SADC). Domestic trade patterns within Botswana are dominated by large, mostly foreign-owned wholesale operations and large foreign retailers in urban areas, though there is also an increasing proliferation of small stores owned by citizens.
Transport
The 400-mile railway along the eastern side of the country was completed in 1897, linking South Africa and Zimbabwe, but had limited impact on the Botswana economy until the 1970s, when the first branch lines were opened to serve mining areas. At independence in 1966, there were only a few miles of paved roads—all inside town boundaries. Since then the major towns have been linked by paved main highways. Most of the sandveld, however, is accessible only to four-wheel-drive vehicles.
International air traffic in Botswana, though dating to 1919, was limited until the opening up of the Sir Seretse Khama Airport at Gaborone in 1984. Gaborone is now served by British and French airlines as well as by regional airlines and the national parastatal airline, Air Botswana.
Administration and social conditions
Government
Botswana is a unitary state with a multiparty parliamentary system and an executive presidency. Since independence Botswana has held free elections every five years, a relatively uncorrupt bureaucracy, and judicial respect for human rights and the rule of law. The government has also distributed increasing resources widely if not always equally among the people.
Parliament consists of a National Assembly of elected members (elected by universal adult suffrage in single-member constituencies) and a handful of ex officio members nominated by the ruling political party. There is also a House of Chiefs, with an advisory role on matters of legislation pertaining to tribal law and custom.
The ruling party, first elected in 1965 and reelected at five-year intervals since then, is the Botswana Democratic Party. Its overwhelming majorities in elections have been based on rural support; opposition parties have drawn their strength generally from urban areas. The Botswana People's Party was the main opposition in the 1960s, when urban areas were small. Since then the Botswana National Front has grown in strength, holding the majority of the city council of Gaborone and both of Gaborone's parliamentary seats.
Local councils, rural and urban, have been elected since 1969 simultaneously with national parliamentary elections. The power of local councils is limited by the right of the central government to nominate ex officio voting members and by central government appointment of supervisory district commissioners and planning staff.
The evolving political and economic alignments of Botswana's foreign policy are indicated by the countries to which it has sent resident ambassadors—originally the United States, the United Kingdom, and Zambia in the 1960s, followed by Belgium, Zimbabwe, and Sweden in the 1980s and by Namibia, Russia, and China in the early 1990s. Full diplomatic relations were established with South Africa in 1994.
Education
Since independence, enrollment at all levels of education has increased steadily. Enrollments in primary education are still lower in the remote western and northwestern districts than in other areas of the country, however, as poorer non-Tswana children often miss out on school.
International interest has been aroused by an alternative system of education, integrating vocational skills into the secondary curriculum, developed by the educationist Patrick van Rensburg at Swaneng Hill near Serowe. But “education with development” has had little impact on the general curriculum within Botswana's schools.
A university campus in Gaborone, founded in 1976, became the University of Botswana in 1982. Officially, more than three-fourths of the population is considered literate, although this is probably an overestimate. Rural literacy rates are higher in the east and northeast and lower in the west and northwest. More women than men are literate, as many boys traditionally are employed in cattle herding rather than being sent to school.
Health and welfare
Botswana has a dry and warm climate generally conducive to good health. The incidence of tropical diseases—notably malaria, bilharzia ( schistosomiasis), and sleeping sickness—is limited by the environment and lack of surface water. The most common fatal diseases are intestinal (diarrheal and digestive diseases) and respiratory (pneumonia and tuberculosis).
The main threats to health are diseases associated with changing lifestyle, particularly diet. There has been an increased incidence of high blood pressure, strokes, and heart disease, as well as dental caries in older children. The spread of AIDS has had a devastating effect in Botswana, where the rate of infection has been one of the highest in the world; by 2000 more than one-third of the adult population was infected with HIV, and the growing number of AIDS orphans loomed as a serious social problem.
Since 1973, government health policy has been based on the provision of basic health services in the form of health posts in every village with a population of more than 500 and clinics in every area with more than 4,000 in a nine-mile radius. Since the late 1980s there has also been extensive investment in two large national referral hospitals, at Gaborone and Francistown.
The use of government health services is free of charge. There are also a number of Western-certified physicians in private practice and many traditional herbalists, healers, and diviners.
Cultural life
The cultural life of Botswana reflects the dual heritage and intermingling of Tswana and English cultural domination. The two languages and cultures are subtly mixed and alternated in urban and official situations.
Western dress has been general among people in Botswana, except at the poorest level, since the late 19th century. Common diet and cuisine consist of sorghum and corn porridge, beans and pulses and traditional spinach, supplemented by tomato, potato, onion, and cabbage usually purchased from stores. Meat consumption has become more common with the opening of small butcheries selling beef. Traditional foods include dried phane caterpillars from mopane woodland, eaten as relish or snacks, fruits such as the wild morulaplum, and beer made from sorghum or millet.
Families in rural villages live in traditional compounds, usually with two or three small houses of cylindrical clay walls and conical thatch roofs, set around an open fireplace and surrounded by low clay walls. Most recent houses are square with metal roofs, while many houses in the northwest are made of reed.
Rites of burial, marriage, and birth have been adapted to Christianity but remain extremely important in Botswana life.
Traditional music, based on stringed instruments, and dance generally declined during the colonial period. After independence there was a revival of interest, particularly in music on the radio.
The best-known modern art form incorporating traditional craftwork is basketry—most of it from northwestern Botswana—which is widely exported overseas.
The author Bessie Head (Head, Bessie Emery) (1937–86) wrote novels in English that reflect the contemporary realities and history of Serowe. The publishing of fiction in Setswana was revived in the 1980s.
There is a national museum and art gallery in Gaborone and an increasing number of district museums founded by local community initiative. A national learned and scientific society, the Botswana Society, holds regular lectures and publishes an annual journal and books.
Football (soccer) is the national sport, played on fields and in stadiums across the country every Saturday.
The government issues a free daily newspaper, mostly in English, and runs a radio service, mostly in Setswana. There are also several separate private weekly newspapers, with circulation in eastern towns, and private local television stations, mostly relaying broadcasts from neighbouring countries. There is no government censorship. During the 1980s three multinational publishers set up branches to generate published materials for schools.
History
The history of Botswana is in general the history of the Kalahari area, intermediate between the more populated savanna of the north and east and the less populated steppe of the south and west. Although reduced to a peripheral role in southern Africa for most of the 20th century, at other times Botswana has been a central area of historical development.
Early pastoral and farming peoples
Khoisan (Khoisan languages)-speaking hunters and herders
People speaking Khoisan (Khoe and San) languages have lived in Botswana for many thousands of years. Depression Shelter in the Tsodilo Hills has evidence of continuous Khoisan occupation from about 17,000 BC to about AD 1650. During the final centuries of the last millennium before Christ, some of the Khoi (Tshu-khwe) people of northern Botswana converted to pastoralism, herding their cattle and sheep on the rich pastures revealed by the retreating lakes and wetlands.
Bantu-speaking farmers
Meanwhile, the farming of grain crops, and the speaking of Bantu languages, were carried gradually southward from the Equator. By about 20 BC such farmers were making and using iron tools on the upper Zambezi.
The earliest dated Iron Age site in Botswana is an iron-smelting furnace in the Tswapong Hills near Palapye, dated about AD 190 and probably associated with Iron Age farmers from the Limpopo valley. The remains of small beehive-shaped houses made of grass matting, occupied by early Iron Age farmers around Molepolole, have been dated from about AD 420. There is also evidence of early farming settlement west of the Okavango delta, in the Tsodilo Hills alongside Khoisan hunter and pastoralist sites, dated from about AD 550. Archaeologists therefore have difficulty in interpreting the hundreds of rock paintings in the Tsodilo Hills that were once assumed to be painted by “Bushman” ( San) hunters remote from all pastoralist and farmer contact.
Iron Age states and chiefdoms
Eastern states and chiefdoms
From about AD 1095 southeastern Botswana saw the rise of a new culture, characterized by a site on Moritsane hill near Gabane. The Moritsane culture is historically associated with the Khalagari (Kgalagadi) chiefdoms, the westernmost dialect group of Sotho (or Sotho-Tswana) speakers.
The area within 50 or 60 miles of Serowe saw a thriving farming culture, dominated by rulers living on Toutswe hill, between about the 7th and 13th centuries. The prosperity of the state was based on cattle herding, with large corrals in the capital town and in scores of smaller hilltop villages. (Ancient cattle corrals are identified by the peculiar grass growing on them.) The Toutswe people also hunted westward into the Kalahari and traded eastward with the Limpopo.
The Toutswe state appears to have been conquered by its neighbour, the Mapungubwe state, centred on a hill at the Limpopo-Shashi confluence, in the 13th century. But Mapungubwe's triumph was short-lived, as it was superseded by the new state of Great Zimbabwe, north of the Limpopo River. Great Zimbabwe's successor from about 1450, the Butua state based at Khami (Kame) near Bulawayo in western Zimbabwe, controlled trade in salt and hunting dogs from the eastern Makgadikgadi Pans, around which it built stone-walled command posts.
Western chiefdoms
From about AD 850 farmers from the upper Zambezi, ancestors of the Mbukushu and Yei peoples, reached as far south and west as the Tsodilo Hills (Nqoma). The oral traditions of Herero and Mbanderu pastoralists, west of the Okavango, relate how they were split apart from their Mbandu parent stock by 17th-century Tswana cattle-raiding from the south.
Rise of Tswanadom
During the 13th and 14th centuries AD a number of powerful dynasties began to emerge among the Tswana in the western Transvaal region. Rolong chiefdoms spread westward over lands controlled by Khalagari peoples. Khalagari chiefdoms either accepted Rolong rulers or moved westward across the Kalahari.
The main Tswana dynasties of the Hurutshe, Kwena, and Kgatla were derived from the Phofu dynasty, which broke up in its home in the western Transvaal region in the 16th century. The archaeology of the Transvaal region shows that, after about 1700, stone-walled villages and some large towns developed on hills. These states were probably competing for cattle wealth and subject populations, for control of hunting and mineral tribute, and for control of trade with the east coast.
Growth of Tswana states
Kwena and Hurutshe migrants founded the Ngwaketse chiefdom among the Khalagari-Rolong in southeastern Botswana by 1795. After 1750 this chiefdom grew into a powerful military state controlling Kalahari hunting and cattle raiding and copper production west of Kanye. Meanwhile, other Kwena had settled around Molepolole, and a group of those Kwena thenceforth called Ngwato settled farther north at Shoshong. By about 1795 a group of Ngwato, called the Tawana, had even founded a state as far northwest as Lake Ngami.
Times of war
From about 1750, trading and raiding for ivory, cattle, and slaves spread inland from the coasts of Mozambique, the Cape Colony, and Angola. By 1800, raiders from the Cape had begun to attack the Ngwaketse. By 1824 the Ngwaketse were being attacked by the Kololo, a military nation on the move that had been expelled northwestward by raiders from the east. The great Ngwaketse warrior king Makaba II was killed, but the Kololo were pushed farther north by a counterattack in 1826.
The Kololo moved through Shoshong to the Boteti River, expelling the Tawana northward. In about 1835 the Kololo settled on the Chobe River, extending their power to the upper Zambezi, until their final defeat there by their Lozi subjects in 1864. The Kololo were followed by the Ndebele, a military nation led by Mzilikazi, who settled in the Butua area of western Zimbabwe in 1838–40, after the local Rozvi state was conquered.
Prosperous trading states
The Tswana states of the Ngwaketse, Kwena, Ngwato, and Tawana were reconstituted in the 1840s after the wars ended. The states competed with each other to benefit from the increasing trade in ivory and ostrich feathers being carried by wagons down new roads to the Cape Colony in the south. Those roads also brought Christian missionaries to Botswana and Boer trekkers who settled in the Transvaal to the east.
The most remarkable Tswana king of this period was Sechele (ruled 1829–92) of the Kwena around Molepolole. He allied himself with British traders and missionaries and was baptized by David Livingstone. He also fought the Boers, who tried to seize people who fled from the Transvaal to join Sechele's state. But by the later 1870s the Kwena had lost control of trade to the Ngwato under Khama III (ruled 1872–73; 1875–1923), whose power extended to the frontiers of the Tawana in the northwest, the Lozi in the north, and Ndebele in the northeast.
British (British Empire) protectorate
White miners and prospectors flooded Botswana in 1867–69 to start deep gold mining at Tati near Francistown. But the gold rush was short-lived, and the diamond mines at Kimberley south of Botswana became southern Africa's first great industrial area from 1871. Migrant labourers from Botswana and countries farther north streamed to Kimberley and later to the gold mines of the Transvaal.
The “Scramble for Africa” in the 1880s resulted in the German colonization of South West Africa. The new German colony threatened to join across the Kalahari with the independent Boer republic of the Transvaal. The British in the Cape Colony responded by using their missionary and trade connections with the Tswana states to keep the roads through Botswana open for British expansion to Zimbabwe and the Zambezi. In 1885 the British proclaimed a protectorate over their Tswana allies and the Kalahari as far north as the Ngwato; the protectorate was extended to the Tawana and the Chobe River in 1890.
British colonial expansion was privatized in the form of the British South Africa Company, which used the road through the Bechuanaland Protectorate to colonize Zimbabwe (soon to be called Rhodesia) in 1890. But the protectorate itself remained under the British crown, and white settlement remained restricted to a few border areas, after an attempt to hand it over to the company was foiled by a delegation of three Tswana kings to London in 1895. The kings, however, had to concede to the company the right to build a railway to Rhodesia through their lands.
The British government continued to regard the protectorate as a temporary expedient, until it could be handed over to Rhodesia or, after 1910, to the new Union of South Africa. Hence the administrative capital remained at Mafeking (Mafikeng)—actually outside the protectorate's borders in South Africa—from 1895 until 1964. Investment and administrative development within the territory were kept to a minimum. It declined into a mere appendage of South Africa, for which it provided migrant labour and the rail transit route to Rhodesia. Short-lived attempts to reform administration and to initiate mining and agricultural development in the 1930s were hotly disputed by leading Tswana chiefs, on the grounds that they would only enhance colonial control and white settlement. The territory remained divided into eight largely self-administering “tribal” reserves and five white settler farm blocks, with the remainder classified as crown (i.e., state) lands.
The extent of the Bechuanaland Protectorate's subordination to the interests of South Africa was revealed in 1950. In a case that caused political controversy in Britain and the empire, the British government barred Seretse Khama (Khama, Sir Seretse) from the chieftainship of the Ngwato and exiled him from Botswana for six years. This, as secret documents have since confirmed, was in order to satisfy the South African government, which objected to Seretse Khama's marriage to a white Englishwoman at a time when racial segregation was being reinforced in South Africa under apartheid.
Advance to independence
From the late 1950s it became clear that Bechuanaland could no longer be handed over to South Africa and must be developed toward political and economic self-sufficiency. The supporters of Seretse Khama began to organize political movements from 1952, and there was a nationalist spirit even among older “tribal” leaders. Ngwato “tribal” negotiations for the start of copper mining led to an agreement in 1959. A legislative council was eventually set up in 1961 after limited national elections. The Bechuanaland People's Party was founded in 1960, and the Bechuanaland Democratic Party (BDP)—led by Seretse Khama—in 1962.
After long resistance to constitutional advance before economic development could pay for it, the British began to push political change in 1964. A new administrative capital was rapidly built at Gaborone. Bechuanaland became self-governing in 1965, under an elected BDP government with Seretse Khama as prime minister. In 1966 the country became the Republic of Botswana, with Seretse Khama as its first president.
For its first five years of political independence, Botswana remained financially dependent on Britain to cover the full cost of administration and development. The planning and execution of economic development took off in 1967–71 after the discovery of diamonds at Orapa. The essential precondition for this was renegotiation of the customs union with South Africa, so that state revenue would benefit from rising capital imports and mineral exports rather than remain at a fixed percentage of total customs union income. This renegotiation was achieved in 1969.
Botswana since independence
From 1969 Botswana began to play a more significant role in international politics, putting itself forward as a nonracial, liberal democratic alternative to South African apartheid. In 1974 Botswana was—together with Zambia and Tanzania and later Mozambique and Angola—one of the “Frontline States” seeking to bring majority rule to Zimbabwe, Namibia, and South Africa. The organization of the Frontline States led to the formation of the Southern African Development Coordination Conference (Southern African Development Community) (SADCC; since 1992 known as the Southern African Development Community 【SADC】) in 1980. The idea behind the SADCC, largely structured by Khama (Khama, Sir Seretse), was to build a better future for the region by coordinating disparate economies and promoting development in each of the member countries.
Benefiting from a rapidly expanding economy in the 1970s and '80s, Botswana was able to extend basic infrastructure for mining development and basic social services for its population. More diamond mines were opened, on relatively favourable terms of income to the state. The BDP was consistently reelected with a large majority, though the Botswana National Front (BNF; founded 1965) became a significant threat after 1969, when “tribal” conservatives joined the socialists in BNF ranks attacking the “bourgeois” policies of government.
Khama died in 1980 and was succeeded by Quett Masire, who had been his deputy since 1965. Masire was faced with such internal issues as a high rate of unemployment and the increasing gap between urban rich and rural poor, as well as with international concerns; between 1984 and 1990, Botswana suffered from upheavals in South Africa when South African troops raided the Frontline States. Two raids on Gaborone by the South African army in 1985 and 1986 killed 15 civilians. But a new era in southern African relations dawned after Namibia gained independence in 1990, and the internal political changes in South Africa resulted in full diplomatic relations being established with Botswana in 1994.
The economic expansion of previous decades slowed and even reversed in the early 1990s but bounced back within a few years. However, there were still other issues facing the country. Looting and rioting, unusual behaviour in Botswana, killed one person in 1995. Although the apparent cause of the violence was outrage over the release of three people charged in the murder of a young girl, government critics asserted that frustration with social conditions and the high rate of unemployment were the underlying reasons that fueled the unrest. Of greater concern was the AIDS epidemic that had exploded in the country during the 1990s, leaving Botswana with one of the highest rates of infection in the world. The government responded aggressively by increasing HIV/AIDS awareness and by coordinating efforts to curtail the epidemic. In the early 21st century, Botswana became the first African country to provide free HIV antiretroviral medication to all citizens.
Masire retired in 1998 and was succeeded by Festus Mogae, a former cabinet minister and vice president; Mogae was elected to serve a full term in 1999 and reelected in 2004. Also in 1998, more than 2,400 refugees from Namibia's Caprivi Strip began fleeing into Botswana; some were Caprivian secession leaders that Namibia demanded be extradited. Botswana's decision to instead grant them refugee status led to tension between the two countries. Mogae's administration also had to address worldwide criticism over the relocation of the Basarwa ( San), which had been an issue under Masire's administration as well. The reasons for relocating the Basarwa to settlements outside of the Central Kalahari Game Reserve (the Basarwa ancestral land) and the methods used to carry out the relocation continued to be a source of domestic and international consternation. Although the Basarwa were eventually awarded the right to return to their land in a December 2006 ruling from the Botswana High Court, disagreements remained between the Basarwa and the government about such issues as hunting and water rights.
Mogae retired in April 2008 and was succeeded by vice president Ian Khama, the son of Botswana's first president, Seretse Khama.
Additional Reading
Robson M.K. Silitshena and G. McLeod, Botswana: A Physical, Social, and Economic Geography (1989), briefly but authoritatively covers all aspects of Botswana's geography from climate to patterns of human settlement. Botswana Notes and Records (annual), is a scholarly journal covering research in natural and social science and in humanities. Botswana Society, The Botswana Society Social Studies Atlas (1988), contains maps of the country's physical and human geography and history as well as environmental and thematic maps of the southern African region. Studies of the plant and animal life include Ronald Daniel Auerbach, The Amphibians and Reptiles of Botswana (1987); Michael Main, Kalahari: Life's Variety in Dune and Delta (1987), a popular survey of scientific research on the natural and human aspects of the desert from prehistory to future prospects; Kenneth Newman, Newman's Birds of Botswana (1989); Mark Owens and Delia Owens, Cry of the Kalahari (1984); Karen Ross, Okavango: Jewel of the Kalahari (1987), an illustrated description of wetland wildlife and the environment of the delta; and David S.G. Thomas and Paul A. Shaw, The Kalahari Environment (1991), an extensive scholarly study of the Kalahari Basin, detailing present geology, tectonics, climate, and vegetation and discussing the findings of research on prehistoric lakes and rivers from the Cretaceous to the Quaternary as well as presenting debate on land use and water resources. Tore Janson and Joseph Tsonope, Birth of a National Language: The History of Setswana (1991), traces the development of a standardized national dialect beginning in the 19th century to the increasing distinction since the 1960s between Botswana and South African official Setswana. Studies of the people include Laurens Van der Post and Jane Taylor, Testament to the Bushmen (1984); Bessie Head, Serowe, Village of the Rainwind (1981), a novelist's view of local social history based on interviews; and Diana Wylie, A Little God: The Twilight of Patriarchy in a Southern African Chiefdom (1990), a historian's view of disappearing chieftainship. The economy is addressed in Christopher Colclough and Stephen McCarthy, The Political Economy of Botswana: A Study of Growth and Distribution (1980), a scholarly survey of economic development, 1965–77; Charles Harvey and Stephen R. Lewis, Jr., Policy Choice and Development Performance in Botswana (1990), an analysis of the successful government negotiation of terms with mining companies and the management of the resulting financial surplus; John Holm and Patrick Molutsi (eds.), Democracy in Botswana (1989), a collection of symposium proceedings that emphasizes the adaptation of indigenous institutions, the roles of bureaucrats and foreign capital, the group rights of cultural minorities, and the efficacy of regular general elections; and Louis A. Picard, The Politics of Development in Botswana: A Model for Success? (1987).Historical treatments include Thomas Tlou and Alec Campbell, History of Botswana (1984); Fred Morton, Andrew Murray, and Jeff Ramsay, Historical Dictionary of Botswana, new ed. (1989), a reference work with an excellent bibliography; Fred Morton and Jeff Ramsay (eds.), The Birth of Botswana: A History of the Bechuanaland Protectorate from 1910 to 1966 (1987), on the rise and fall of powerful local sovereignties headed by chiefs under colonial rule; Michael Crowder, The Flogging of Phineas McIntosh: A Tale of Colonial Folly and Injustice: Bechuanaland, 1933 (1988); Louis A. Picard (ed.), The Evolution of Modern Botswana (1985), the country's administrative history from the 1930s to postcolonial development; Michael Dutfield, A Marriage of Inconvenience: The Persecution of Ruth and Seretse Khama (1990); Jack Parson (ed.), Succession to High Office in Botswana: Three Case Studies (1990); and Jack Parson, Botswana: Liberal Democracy and the Labor Reserve in Southern Africa (1984).
- Greek alphabet
- Greek Anthology
- Greek calendar
- Greek Catholic church
- Greek Civil War
- Greek-cross plan
- Greek fire
- Greek Independence Day
- Greek Independence, War of
- Greek language
- Greek law
- Greek literature
- Greek mythology
- Greek Orthodox Church
- Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria
- Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East
- Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem
- Greek pottery
- Greek religion
- Greek Revival
- Greeley
- Greeley, Horace
- Greely, Adolphus Washington
- Green, Al
- green algae