Emperors and empresses regnant of Japan
Table
Emperors and empresses regnant of Japan
reign*
Jimmu (660)–585 BC
Suizei (581)–549 BC
Annei 549–511 BC
Itoku (510)–477 BC
K d;sh d; (475)–393 BC
K d;an (392)–291 BC
K d;rei (290)–215 BC
K d;gen (214)–158 BC
Kaika 158–98 BC
Sujin (97)–30 BC
Suinin (29 BC)–AD 70
Keik d; (71)–130
Seimu (131)–190
Ch b;ai (192)–200
Jing b; (Jingū) (regent) 201–269
c;jin (Ōjin) (270)–310
Nintoku (313)–399
Rich b; (400)–405
Hanzei (406)–410
Ingy d; (412)–453
Ank d; 453–456
Y b;ryaku 456–479
Seinei (480)–484
Kenz d; (485)–487
Ninken (488)–498
Buretsu 498–506
Keitai (507)–531
Ankan 531(534)–535
Senka 535–539
Kimmei 539–571
Bidatsu (572)–585
Y d;mei 585–587
Sushun 587–592
Suiko (empress regnant) 593–628
Jomei (629)–641
K d;gyoku (empress regnant) (642)–645
K d;toku 645–654
Saimei (empress regnant: K d;gyoku rethroned) (655)–661
Tenji 661(668)–672
K d;bun 672
Temmu 672(673)–686
Jit d; (empress regnant) 686(690)–697
Mommu 697–707
Gemmei (empress regnant) 707–715
Gensh d; (empress regnant) 715–724
Sh d;mu (Shōmu) 724–749
K d;ken (Kōken) (empress regnant) 749–758
Junnin 758–764
Sh d;toku (Kōken) (empress regnant: K d;ken rethroned) 764(765)–770
K d;nin 770–781
Kammu 781–806
Heizei 806–809
Saga 809–823
Junna 823–833
Nimmy d; 833–850
Montoku 850–858
Seiwa 858–876
Y d;zei 876(877)–884
K d;k d; 884–887
Uda 887–897
Daigo 897–930
Suzaku 930–946
Murakami 946–967
Reizei 967–969
En'y b; 969–984
Kazan 984–986
Ichij d; 986–1011
Sanj d; 1011–16
Go-Ichij d; 1016–36
Go-Suzaku 1036–45
Go-Reizei 1045–68
Go-Sanj d; (Sanjō, Go-) 1068–72
Shirakawa 1072–86
Horikawa 1086–1107
Toba 1107–23
Sutoku 1123–41
Konoe 1141–55
Go-Shirakawa (Shirakawa, Go-) 1155–58
Nij d; 1158–65
Rokuj d; 1165–68
Takakura 1168–80
Antoku 1180–85**
Go-Toba (Toba, Go-) 1183(1184)–98
Tsuchimikado 1198–1210
Juntoku 1210(1211)–21
Ch b;ky d; 1221
Goshirakawa 1221(1222)–32
Shij d; 1232(1233)–42
Go-Saga 1242–46
Go-Fukakusa 1246–59/60
Kameyama 1259/60–74
Gouda 1274–87
Fushimi 1287(1288)–98
Go-Fushimi 1298–1301
Go-Nij d; 1301–08
Hanazono 1308–18
Go-Daigo (Daigo, Go-) 1318–39
Go-Murakami 1339–68
Ch d;kei 1368–83
Go-Kameyama 1383–92
The Northern court
K d;gon 1331(1332)–33
K d;myo 1336(1337/38)–48
Suk d; 1348(1349/50)–51
Go-K d;gon 1351(1353/54)–71
Go-En'y b; 1371(1374/75)–82
Go-Komatsu 1382–92
Go-Komatsu 1392–1412
Sh d;k d; 1412(1414)–28
Go-Hanazono 1428(1429/30)–64
Go-Tsuchimikado 1464(1465/66)–1500
Go-Kashiwabara 1500(1521)–26
Go-Nara 1526(1536)–57
c;gimachi 1557(1560)–86
Go-Y d;zei 1586(1587)–1611
Go-Mizunoo 1611–29
Meish d; (empress regnant) 1629(1630)–43
Go-K d;my d; 1643–54
Go-Sai 1654/55(1656)–63
Reigen 1663–87
Higashiyama 1687–1709
Nakamikado 1709(1710)–35
Sakuramachi 1735–47
Momozono 1747–62
Go-Sakuramachi (empress regnant) 1762(1763)–71
Go-Momozono 1771–79
K d;kaku 1780–1817
Nink d; 1817–46
K d;mei 1846(1847)–66
Meiji, personal name Mutsuhito, era name Meiji 1867(1868)–1912
Taish d; (Taishō), personal name Yoshihito, era name Taish d; 1912(1915)–26
Hirohito, era name Sh d;wa 1926(1928)–1989
Akihito, era name Heisei 1989(1990)–
*Reign dates for the first 28 sovereigns and the regent Jing b; (given in italics) are taken from the Nihon shoki ("Chronicles of Japan"). The first 14 sovereigns are considered legendary; and while the latter 14 are known to have existed, their exact reign dates have not been verified historically. When the year of actual accession and year of formal coronation are different, the latter is placed in parenthesis after the former. If the two events took place in the same year, no special notation is used. If only the coronation year is known, it is placed in parenthesis.
**Antoku's reign overlaps that of Go-Toba. Go-Toba was placed on the throne by the Minamoto clan after the rival Taira clan had fled Ky d;to with Antoku.
See as table: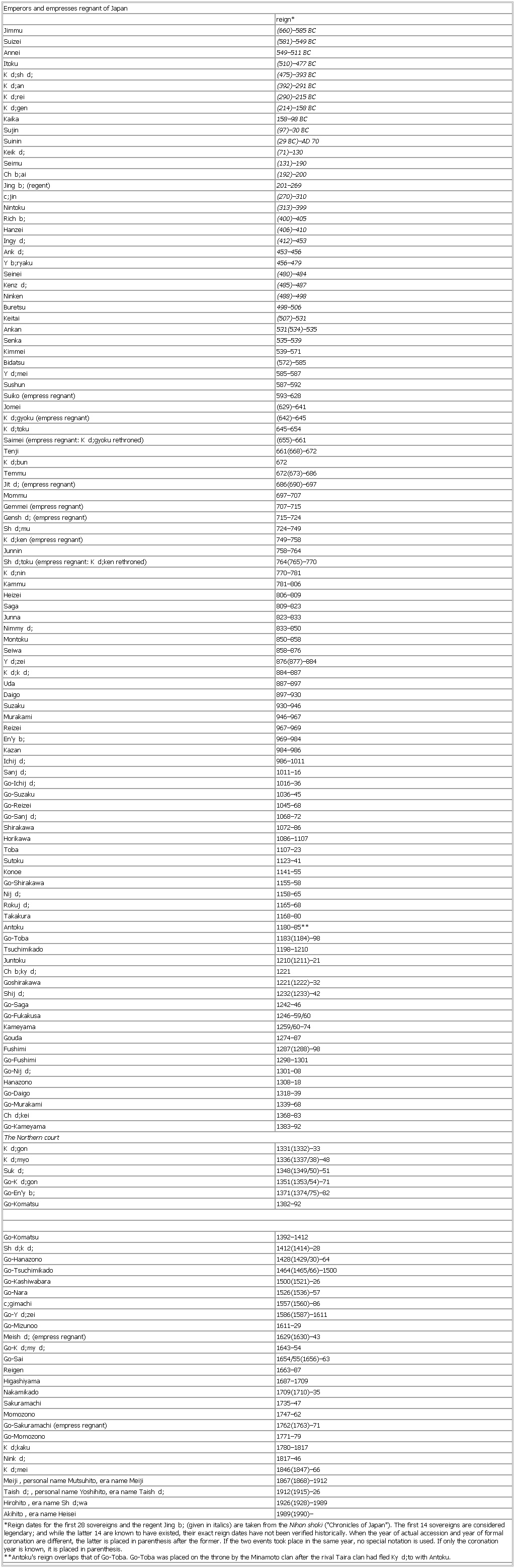

- mean life
- meantone temperament
- mean-value theorem
- Meany, George
- Mears, Helen Farnsworth
- measles
- measure
- Measured susceptibilities for rock types
- Measure for Measure
- measurement
- measurement system
- Measurement systems employed in petroleum refining
- measuring worm
- Meath
- Meath, Hugh de Lacy, 1st Lord of
- meat processing
- Meaux
- Meave G. Leakey
- Mecca
- Mechain, Pierre
- mechanical advantage
- mechanical efficiency
- mechanical energy
- mechanical engineering
- mechanics