piano
musical instrument
also called pianoforte, French piano, or pianoforte, German Klavier,
a keyboard musical instrument (keyboard instrument) having wire strings that sound when struck by felt-covered hammers operated from a keyboard. The standard modern piano contains 88 keys and has a compass of seven full octaves plus a few keys.
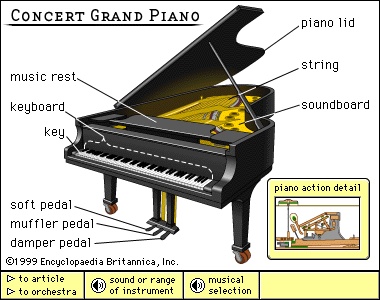 The vibration of the strings is transmitted to a soundboard by means of a bridge over which the strings are stretched; the soundboard amplifies the sound and affects its tone quality. The hammers that strike the strings are affixed to a mechanism resting on the far ends of the keys; hammer and mechanism compose the “action.” The function of the mechanism is to accelerate the motion of the hammer, catch it as it rebounds from the strings, and hold it in position for the next attack. Modern hammers are covered with felt; earlier, leather was used. The modern piano has a cast-iron frame capable of withstanding the tremendous tension of the strings; early pianos had wood frames and thus could only be lightly strung. Modern pianos are therefore much louder than were those of the 18th century, an increase in loudness necessitated in part by the size of 19th-century concert halls. Of the three pedals found on most pianos, the damper pedal on the right lifts all the felt dampers above the strings, allowing them all to vibrate freely; the left pedal shifts the keyboard and action sideways to enable the hammer to strike only one of the two or three unison strings of each tenor and treble key (the bass notes are only single-strung); and the middle pedal (generally available on grand pianos but also found on some upright pianos) usually holds up the dampers only of those keys depressed when the pedal is depressed.
The vibration of the strings is transmitted to a soundboard by means of a bridge over which the strings are stretched; the soundboard amplifies the sound and affects its tone quality. The hammers that strike the strings are affixed to a mechanism resting on the far ends of the keys; hammer and mechanism compose the “action.” The function of the mechanism is to accelerate the motion of the hammer, catch it as it rebounds from the strings, and hold it in position for the next attack. Modern hammers are covered with felt; earlier, leather was used. The modern piano has a cast-iron frame capable of withstanding the tremendous tension of the strings; early pianos had wood frames and thus could only be lightly strung. Modern pianos are therefore much louder than were those of the 18th century, an increase in loudness necessitated in part by the size of 19th-century concert halls. Of the three pedals found on most pianos, the damper pedal on the right lifts all the felt dampers above the strings, allowing them all to vibrate freely; the left pedal shifts the keyboard and action sideways to enable the hammer to strike only one of the two or three unison strings of each tenor and treble key (the bass notes are only single-strung); and the middle pedal (generally available on grand pianos but also found on some upright pianos) usually holds up the dampers only of those keys depressed when the pedal is depressed.Credit for priority of invention has been much disputed, but there is little doubt that it belongs to Bartolomeo Cristofori (Cristofori, Bartolomeo), who devised his gravecembalo col piano e forte (“harpsichord with soft and loud”) in Florence in approximately 1709. This was not the first instrument using keyboard striking action; examples of the piano principle existed as early as about 1440. Cristofori had arrived at all the essentials of the modern piano action by 1726, and it is from Cristofori's piano that the modern piano stems.
The piano, made in a variety of forms, was widely popular in the mid-18th century. Preferring a lighter, less-expensive instrument with a softer touch, German piano makers perfected the square piano. When Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (Mozart, Wolfgang Amadeus) and Muzio Clementi (Clementi, Muzio) began to write for the piano, a distinctively pianistic style of playing and composing developed. From that point on, the piano became the preferred medium for salon music, chamber music, concerti (concerto), and song accompaniments.
By roughly 1860 the upright piano had virtually replaced the square piano for home use. Early upright pianos were made according to the design of upright harpsichords (harpsichord) with the strings rising from keyboard level. They were consequently very tall, and many were made in elegant shapes. But by taking the strings down to floor level, John Isaac Hawkins made the upright shorter and more suitable for small rooms.
A number of developments followed in the 19th and 20th centuries. String tension, determined at 16 tons in 1862, increased to as much as 30 tons in modern instruments. The result is a dynamic range, sostenuto (ability to sustain a tone), and tonal spectrum unknown to Frédéric Chopin (Chopin, Frédéric), Ludwig van Beethoven (Beethoven, Ludwig van), and even Franz Liszt (Liszt, Franz). A significant development in the 20th century (beginning in the 1930s) was the appearance of the electronic, or electric, piano, which relied on electroacoustic or digital methods of tone production and was heard through an amplifier and loudspeaker. See also barrel piano; player piano.
- Talca
- Talcahuano
- Talcott Parsons
- Taldy-Kurgan
- Talence
- talent
- Talented Tenth
- Tale of Genji, The
- Taliban
- Taliesin
- Taliesin and Taliesin West
- talion
- Talish Mountains
- talisman
- talking drum
- Talking Heads
- talk, Table
- Talladega
- Talladega Mountain
- tallage
- Tallahassee
- Tallahatchie River
- Tall al- Farʿah
- Tall al- Fāriʿah
- Tall al- Zaʿtar